
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
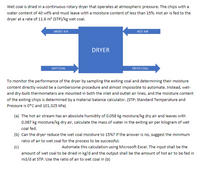
Transcribed Image Text:Wet coal is dried in a continuous rotary dryer that operates at atmospheric pressure. The chips with a
water content of 40 wt% and must leave with a moisture content of less than 15%. Hot air is fed to the
dryer at a rate of 11.6 m (STP)/kg wet coal.
HOT AIR
MOIST AIR
DRYER
WET COAL
DRIED COAL
To monitor the performance of the dryer by sampling the exiting coal and determining their moisture
content directly would be a cumbersome procedure and almost impossible to automate. Instead, wet-
and dry-bulb thermometers are mounted in both the inlet and outlet air lines, and the moisture content
of the exiting chips is determined by a material balance calculator. (STP: Standard Temperature and
Pressure is 0*C and 101.325 kPa)
(a) The hot air stream has an absolute humidity of 0.058 kg moisture/kg dry air and leaves with
0.087 kg moisture/kg dry air, calculate the mass of water in the exiting air per kilogram of wet
coal fed.
(b) Can the dryer reduce the wet coal moisture to 15%? If the answer is no, suggest the minimum
ratio of air to wet coal for the process to be successful.
(c)
amount of wet coal to be dried in kg/d and the output shall be the amount of hot air to be fed in
m3/d at STP. Use the ratio of air to wet coal in (b)
Automate this calculation using Microsoft Excel. The input shall be the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. A natural water with a flow of 4.0 MGD is to be treated with a commercial-grade alum dosage of 80 mg/l. Determine the amount of alum required (expressed in lbs/day), the amount of natural alkalinity required to complete the reaction (expressed in mg/l as CaCO3 and kg/day), and the amount of Al(OH)3(s) sludge produced (expressed in lbs/day and gal/day) if the sludge contains 2.2% solids by weight and the S.G. of the dry solids is 2.0.arrow_forward12.60 The aeration tank for a completely mixed aeration process is being sized for a design waste- water flow of 7500 m³/d. The influent BOD is 130 mg/l with a soluble BOD of 90 mg/l. The design effluent BOD is 20 mg/l with a soluble BOD of 7.0 mg/l. Recommended design para- meters are a sludge age of 10 d and volatile MLSS of 1400 mg/l. Selection of these values takes stants from a bench-scale treatability study are Y into account the anticipated variations in wastewater flows and strengths. The kinetic con- 0.60 mg VSS/mg soluble BOD and k₁ = 0.06 per day. Calculate the volume of the aeration tank, aeration period, food ganism ratio, and excess biomass tharrow_forward4. Problem 5-16 (modified), Davis and Cornwell, Introduction to Environmental Engineering, 5th Ed.: Determine the concentration (mol/L) of hydroxide that must be added to an aqueous solution to produce a concentration of 0.50 mg/L copper if the starting concentration is 3.5 mg/L copper. The solubility product for copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) is 2.2 x 10-20 mol/L. What is the resulting solution pH?arrow_forward
- Problem 8 Given L0,mix=12 mg/L, DO mix=DOsat=11.33 mg/L, kd=0.3 d-1, and kr =0.4 d-1, find the following: (a) Initial oxygen deficit (Do) (b) Critical time on the oxygen sag curve (tc) (c) Critical deficit (Dc)arrow_forwardA 2-tank Step Aeration Activated Sludge (SAAS) system has the following characteristics: V1 V2 Q Waste Recycle Oxygen demand (L) (L) (L/min) Ratio Ratio of Cells 500,000 450,000 100 0.45 0.5 1.2 Xv1 Xv2 Xd1 Xd2 SO S1 S2 Xrv Xrd (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) (mg/L) 1500 ☐ 14 1400 200 150 150 10 2 2000 1000 1. What is the mean cell residence time and hydraulic residence time in days? 2. Write the mass balance equation for required oxygen in tank #1. 3. What is the oxygen requirement for tank #1 in kg/day? (equation will be in units of mg/min)arrow_forwardPlease include Equations. This is for a water and wastewater review, it is not for a grade. I just need to understand the problem.arrow_forward
- Determined and fil-up the unknown data of the given table. Physical Properties Mix Design Specific Dry-rodded Materials Fineness Estimated Absolute gravity weight ft3 Absorption modulus Ib/yd3 Ib/yd3 (SSD) Ib/ft3 Cement 3.15 ? ? Sand 2.64 0.7 2.72 11/2 62.4 Ib/ft Gravel 2.67 0.5 100.5 Water ? Vol. of entrapped air w/C = ? GIVEN: Specification Requirements compressive strength, psi 4000 Slump, in. 3 4arrow_forwardCalculate the R-value of the conventional 12x8x16-in CMU unit (Kerf type) insulated with 4-cm thick layer of the XPS foamarrow_forwardQ- ASP is used to treat a waste water flow of 2MLD having BOD5 of 250 mg/lit. The biomass concentration in the aeration tank is 2500 mg/lit and the concentration of biomass leaving the system is 80 mg/lit, the aeration tank has a volume of 200m³. Find the hydraulic retention time HRT.arrow_forward
- True/False questions. 1 For filtration process: when the water level rises to the point that the filter bed must be cleaned. This point is called terminal head loss ( 2 As the temperature decreases the detention time in 7 slow-mix tank decreases. ( 6 8 When CO₂ is bubbled in water with carbonate buffer system, the pH will decrease slightly and the reaction will shift to the left. ( ) 9 The lower the water turbidity, the higher the allowable ) scour velocity in sedimentation tank.( For mixed-media filter the layer of garnet is used to catch the very fine particles ( 3 The addition of polymers in coagulation process is called inter-particle bridging. ( ) ) 4 Slow-mixing can be accomplished by hydraulic As the weir lengths become shorter the scouring velocity becomes higher ( jump ( ) ) 5 Water with high turbidity requires more coagulant 10 Aluminum sulfate has a wider pH range for effective to be treated. ( coagulation than fèrric salts ( )arrow_forwardA complete-mix flow reactor is designed to treat an influent waste stream containing 130mg/L of casein at a flow rate of 80 liters per minute (lpm). Assume that casein removal follows first-order removal kinetics with a rate constant, k, of 0.5h-1 and that the effluent should contain 13 mg/L of casein at steady state. Determine: a. the detention time in hours b. the volume of the reactor in cubic metersarrow_forwardAn organic matter is degrading in a steady state complete mix type reactor following the firstorder kinetics. The upstream concentration of organic matter is 20 mg/1 and downstream concentration is 4 mg/1. The treatment of water is at the rate of 58 m3/min. and volume of the tank is 580 m³. Which of the following statements is/are correct for the given reactor? Detention time of tank is 10 minutes. B Rate constant is 0.4 min¹ C Average rate of decay is 1.6 mg/1/s. D Correct Option Correct Option Detention time required to achieve 90% efficiency is 20 min.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning