
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:I Inbox (29)- kriver1...
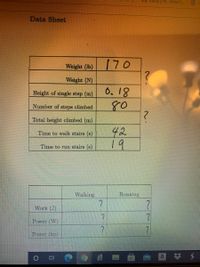
Data Sheet
Weight (lb)
170
Weight (N)
0.18
80
Height of single step (m)
Number of steps climbed
Total height climbed (m)
42
19
Time to walk stairs (s)
Time to run stairs (s)
Walking
Running
Work (J)
Power (W)
Power (hp)
a
近

Transcribed Image Text:66/View
M Recibidos (1,308) -.
M Inbox (29) - kriver1...
OCengageBrain - Log...
Webex Mat 272
Citri
Objective
W
(2)
In this experiment you will calculate the power you
develop when climbing a flight of stairs.
The SI unit of power is a watt (W), which is equivalent
to a J/s.
Apparatus
When James Watt invented his steam engine, he was
asked how many horses the engine could replace. To
find out, he built a rope-and-pulley device with which
he could measure the time it took a horse to lift var-
ious weights.
Stairs, Stopwatch, Meter stick.
Theory
Consider the (rather crude) person climbing a flight Watt defined horsepower as the power a horse can
produce steadily for a sustained period of time. The
SI equivalent of one horsepower is 746W.
of stairs as shown below.
Procedure
1. Record your weight in lb on the Data Sheet; ap-
proximate if you do not know. Convert this to
N.
2. Take a stopwatch and meter stick and locate
Some stairs that can be used for the experiment.
You want to climb at least 2m vertically, so this
Tmight be more than one section of stairs if the
staircase turTIs as it. rises.
Work W is defined as the product of a force F and
distance d; specifically the component of the force in
the direction of the movement.
3. Mcasure the height of one step and count the
total number of steps you will be climbing.
Record these values and calculate the total
tical height.
W = Fd
For the person climbing the stairs the force they are
moving is their own weight w. This force acts straight
down, so in climbing a vertical height y the work done
4. Tine how long it takes vou to walk up the stairs,
repeat for running (safely) up the stairs.
is
5. Calculate the work done both in walking and run-
ning the stains with Equation 1. Calculate the
power in cach case with Equialion 2. Convert the
power in W Lo hp.
(1)
hm = M
The SI unit of work is a joule (J), which is equivalent
to a Nm.
Power is the rate at which work is done If it takes
the person time t to climb then the power P is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 10) Sasha pushes a 15 kg cart full of donated books through a 5.0 m Tong starting area. The cart is then released and must reach the top of the hill 2.5 m in neight, as shown in the diagram below. He must apply enough force on the cart so that the cart is able to travel along the 8.0 m path and reach the top of the hill. The force of friction between the 8.0 m path and the cart is 11.0 N. What minimum force on the cart in the starting area is required to get it to the top of the hill?arrow_forwardA child pulls a sleigh up the incline as shown below. The work done by gravity on the sleigh during this motion is mgL cos? mgL sin? -mgL cos? -mgL sin? none of abovearrow_forwardWhat is the power developed by the student running the stairs? 1N = 0.225 lb 1 hp = 746 watts a) 0.07 hp b) 1.53 hp c) 0.32 hp d) 0.77 hparrow_forward
- 7. A force of 50 lb is required to hold a spring that has been stretched from its natural length of 2 ft to a length of 5 ft. How much work is done in stretching the spring from 5 ft to 8 ft?arrow_forwardDetermine potential energyarrow_forwardHow much work does it take to lift a 30.0 N bag 10.0 m high in 5.00 s?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON