
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Water is siphoned from the tank as shown in the figure below. the length of the pipe is 12 m and has roughness ratio (E/D=0.001)
a) determine the flow rate and the pressure at point A, stagnation point, neglecting all loses.
b) determine the flow rate and pressure at point A, stagnation point, assuming only the major loses are important
c) determine the flow rate and pressure at point A, stagnation point, assuming all loses (minor and major) are important.
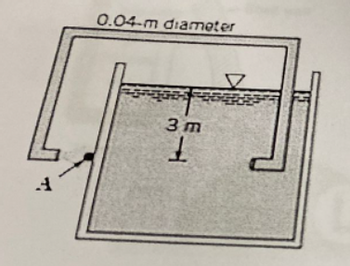
Transcribed Image Text:A
0.04-m diameter
3 m
1.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A straight pipe AB, of length 10 m, tapers from a diameter of 40 cm at A to 20 cm at B. The centre line of the pipe is so located that the end Bis 2 m above the level of A. Liquid of specific gravity 0.9 flows through the pipe at 150 litres/ second. Pressure gauges connected at A and B show the readings of 60 kPa and 40 kPa, respectively, Determine the direction of flow.arrow_forwardA pipe has a uniform diameter of 750 mm. The flow rate entering the pipe is 2.21 m^3/s. The exit velocity has a velocity of 4.75 m/s and the velocity of the leak is 0.7 m/s. Determine the diameter of the leak in mm. 750 mm LEAKarrow_forwardThe three water filled tanks shownin the figure are connected by pipesas indicated. If minor losses areneglected, determine the flow ratein each pipe.arrow_forward
- If the flow into and out of a two-loop pipe system are as shown in Fig. Determine the flow in each pipe using Hardy-Cross method. Value of n is 2.arrow_forwardOil of specific gravity 0.81 flows in the pipe shown in Fig. P4.6.43. If viscous effects are neglected, what isthe flowrate?arrow_forwardAn open cylindrical tank, 2.4 m diameter and 6m tall has 1m of glycerin (Sgglycerin=1.5), 2.5m of water, and 1.5m of oil (Sgoil=0.82). Determine the discharge through the 125mm diameter located at the bottom of the tank. Assume C=0.65arrow_forward
- Problem 6: EGL and HGL (II) Part A Why is the energy gradient (i.e., the slope of the EGL=EL) larger in pipe 2 than in pipes 1 or 3? (<10 words) Part B Why are the EGL and HGL not parallel in this figure? (<10 words) H V² 28 HGL 2 EL Hydraulic grade line, slope = S, Ax - Energy line, slope = Sy Bed ylope Datum h₂ - Az 2 4 Xarrow_forwardIn the branched pipe system shown, 850 L/min of water at 10°C is flowing in a DN 100 Schedule 40 pipe at A. The flow splits into two DN 50 Schedule 40 pipes as shown and then rejoins at B. Calculate (a) the flow rate in each of the branches and (b) the pres- sure difference PA PB. Include the effect of the minor losses in the lower branch of the system. The total length of pipe in the lower branch is 60 m. The elbows are standard.arrow_forwardDesign a rapid mix tank for water at 50° F flowing at Q = 4.0 MGD for a typical process train ina drinking water treatment plant. Use a square tank with a depth 1.25 times the width, a designvelocity gradient G = 900 sec−1, and a hydraulic detention time τ = 30 seconds. Specificallydetermine:a. Rapid mix tank dimensions in feet and inches, to the nearest one inch.b. Input water horsepower (hp).c. Impeller rotational speed if a vane-disc impeller is used having a diameter half of the tankwidth and employing six flat blades and a baffled tank.arrow_forward
- A pipeline 200 meters long delivers water from an impounding reservoir to a service reservoir with the difference in water levels of 20 meters. The pipeline of commercial steel is 400 mm in diameter. It has two 90 degree flanged elbows, a check valve, and an orifice (K_m= 2.5). Determine the flow through the pipe. Use a water temperature of 20 degrees Celcius.arrow_forward4. The pipes shown in the figure below are concrete pipes. The water (T=10° C) flow rate in pipes AB and EF is 9.60 cfs. Find flow in pipe C and D and the total head loss from A to F. Assume f-0.02 3500 ft, 24-in diameter A- E 2000 ft, 15-in diameter 2000 ft, 36 in diameter 3880 ft, 18-in diameterarrow_forwardQ2: A is 4500 m length-gas flow line, and B is 2000 m length-liquid flow line (0.1 m diameter) both are connected with left side of 2500 m in length C-pipeline (0.15 m). If the pressure at A-pipeline inlet = 2400 kPa, pressure at C-pipeline out let = 2000 kPa, liquid flow rate = 0.009 m³/s, Gas Oil Ratio = 40 m³/m², PL 680 kg/m³, p=0.922 kg/m³, gas flowing temperature-300 K, base temperature-288 K, base pressure 101.3 kPa, Z-0.9, gas gravity 9.4x10-3 Pa.s, calculate the 0.6, gas viscosity-0.015x10³ Pa.s, and liquid viscosity diameter of gas pipeline and inlet pressure of liquid pipeline? Assume all pipes are flat and horizontal. =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning