
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
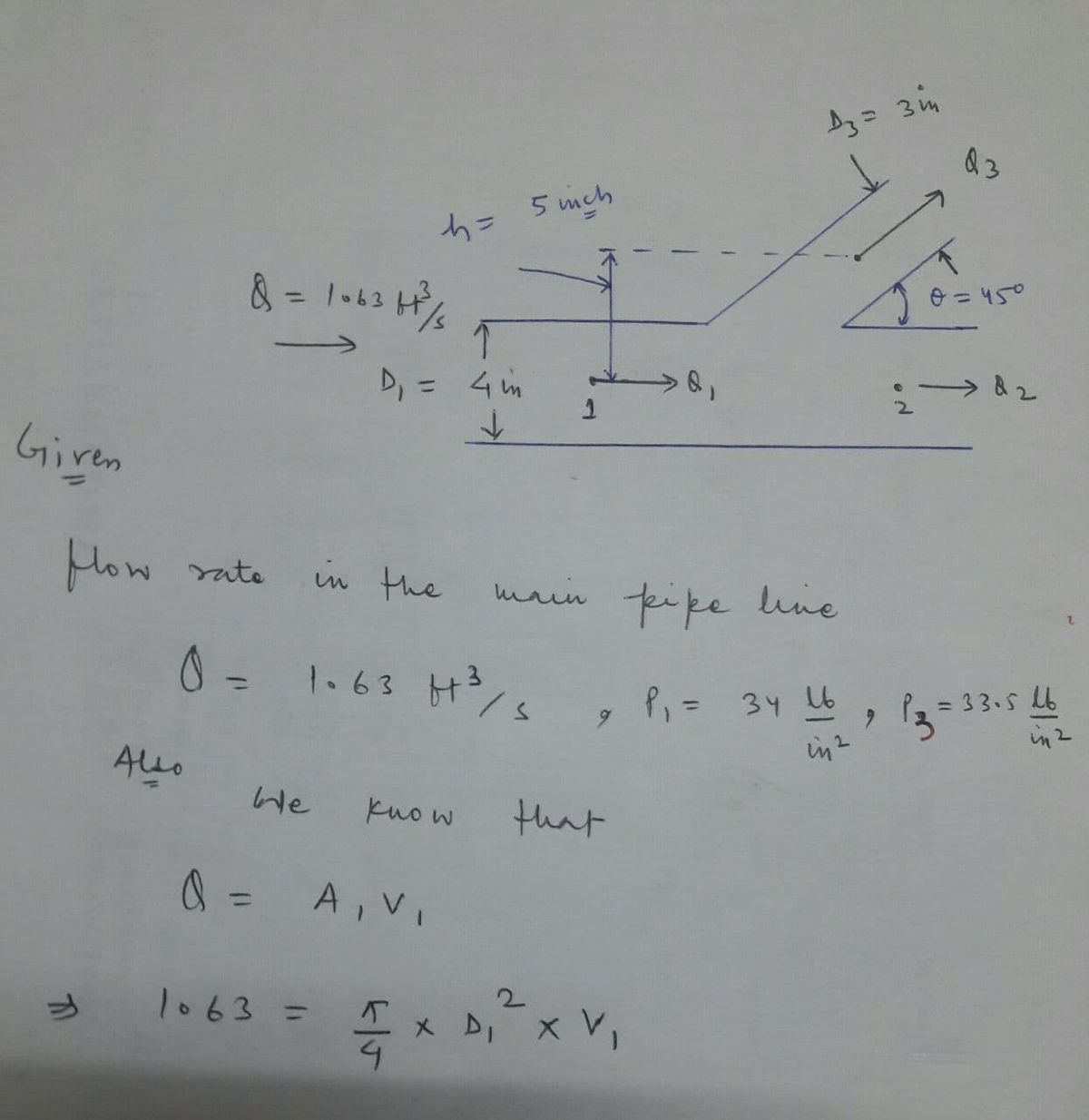
Water flows from a main line to a lateral as shown. The flow in the mainline is 1.63 ft3/s. Measurements show that the pressure at point 1 is 34 psi and at point 3 is 33.5 psi. Determine the velocities at 2 and 3. Assume the distance between the centerline of the main line and point 3 is 5 inches.
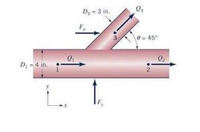
Transcribed Image Text:D3 3 in.
6= 45°
Q2
D: - 4 in.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Plz solve correctlyarrow_forwardWater flows at a rate of 3 m3/s through a 300 mm diameter pipe in which there is a 60o bend. if the pressure at the entrance to the bend is 450 kN/m2 (absolute), determine the total force necessary to anchor (kN) the bend. Friction losses can be neglected.arrow_forwardWater flows through the elbow with a velocity of 12 ft/s. Find the horizontal and vertical components of force the support at C exerts on the elbow. The pressure within the pipe is 28 psi. The flow occurs in the horizontal plane. Assume there is no support at A and B. 12 ft/s 4 in. 4 in. 60° 300arrow_forward
- Water flows steadily with negligible viscous effects through the pipe shown in the figure below. Determine the diameter, D, of the pipe at the outlet (a free jet) if the velocity there is 28 ft/s. Open V=28 ft/s D TUL 15 ft 10 ft 11.5 in. diameterarrow_forwardA Borda's mouthpiece 150 mm in diameter discharges water under a head of 3 m. Determine the discharge in L/s if under ideal conditions, the coefficients of a Borda's mouthpiece are Cc = 0.5 and Cv = 1.0.arrow_forwardWater flows through a Y-shaped horizontal pipe system consisting of two branches and stem, as shown below. The velocity in the stem V is 3m/s and the diameter D1 is 0.3m. Each branch D2 is 0.13m diameter and makes a 30° angle with the axis of the stem. The pressure in the stem P is 196.2kN/m² and the flow is divided equally between the two branches. Water unit weight is 9.81 kN/m³. V m/s D1 D2 Determine the flow velocity in the branches, V2= ?.arrow_forward
- A sharpedged orifice has a diameter of 1′′ and coefficients of velocity and contraction of 0.98 and 0.62, respectively. If the jet drops 3.08 ft in a horizontal distance of 8.19 ft, determine the flow in cfs and the head on the orifice.arrow_forwardWater flows out of the reducing elbow at 1.0 ft3/s(Figure 1). The pipe and elbow and the water within have a total weight of 250 lb. The water is discharged to the atmosphere at B. 0.25 ft 60° 3 ft 0.5 ft a) Determine the horizontal component of force that are necessary to hold the elbow in place at A. b) Determine the vertical component of force that are necessary to hold the elbow in place at A.arrow_forwardWater flows with a velocity of 6 m/s through the pipe at A. (Figure 1). Figure 6 m/s 300 mm F = 5.655 N C www. If the pressure at A is 45 kPa, determine the resultant horizontal shear force developed along the seam at C that holds the cap to the larger pipe. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. < 1 of 1 ? 200 mm Barrow_forward
- Water flows through a uniform diameter pipe of 200 mm diameter. Point A and B are of elevations of 6 m and 8 m respectively along the inclined pipe. Pressure at A and B are 50 kPa and 20 kPa respectively. If rate of flow is 60 litre/seconds. determine : (1) Direction of flow and (ii) Head loss between these points. A ZB = 8m ZA = 6m %3Darrow_forwardWater flows through the elbow with a velocity of 4 m/s, as shown in . The pressure within the pipe at A and B is 220 kPa The flow occurs in the horizontal planc. Assume thero is no support at A and B. m/s 75 mm 75 mm 60 45 Part A Determine the a component of force the support at C exerts on the elbow. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forward4. Water (at 10°C) flows through this nozzle at a rate of Q = +0.3) m³/s and discharges into the atmosphere. D₁ = 65 cm, and D₂= 22.5 cm. Determine the force required at the flange to hold the nozzle in place. Assume irrotational now. Neglect gravitational forces. →D₁ ([LSSID] 106 D₂ LSSJD=27582arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY