Comparisons of the energy differences between two states with that predicted by theory can test the theoretical model. For the case of the muon g-value, there's a small discrepancy between it and the Standard Model of particle physics. We can see atomic transitions in cesium in atomic clocks. We can measure the frequency by applying pulses at frequencies to observe the resonance (see the provided equation, Rabi's formula).
Consider a spin-1/2 particle that precesses in a magnetic field in the z direction. The probability of the particle being spin up or spin down along z doesn’t vary with time. The states |+z> and |—z> are stationary states of the Hamiltonian H-hat = ω0 S-hatz. If we alter the Hamiltonian by applying in addition an oscillating magnetic field transverse to the z axis, we can induce transitions between these two states by properly adjusting the frequency of this transverse field. The energy difference E+—E_ = h-bar ω0 can then be measured with high accuracy. This magnetic resonance gives us an excellent way of determining ω0. Initially, physicists used magnetic resonance techniques to make accurate determinations of g factors and thus gain fundamental information about the nature of these particles. On the other hand, with known values for g, one can use the technique to make accurate determinations of the magnetic field B0 in which the spin is processing. For electrons or nuclei in atoms or molecules, this magnetic field is a combination of the known externally applied field and the local magnetic field at the site of the electron or nucleus.
Question:
- If you start this spin-1/2 system in the spin-up and drive on-resonance, where ω = ω0, for a time Tπ, you'll end up spin-down. We call a drive of this length a pi-pulse. What is Tπ in terms of ω1 and/or ω0?
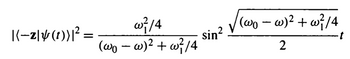
to generate a solution
a solution
- An antimuon with 1000 MeV total energy crosses a 10 cm long silicon target. Calculate the energy loss.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardThe un-normalized wave function for a negatively charged poin that is bound to a proton in an energy eigenstate is given by the equation in the provided image. b0 is a constant for this "pionic" atom that has the dimensions of length. What is the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum of the pion?arrow_forward
- List as many nuclear reactions as you can that use deuterons and alpha particles for projectiles with stable targets that will populate 22Ne as the fi nal state in direct reactions.arrow_forwardDraw the Multi Cavity Klystron Functi onal Diagram and explain its operation, advantages and disadvantages. ) A one cavity Klystron is operated at 45 GHz with a D.C beam voltage of 650V for 4.75 mode, repeller space length of 0.8cm, and a D.C beam current of 50mA. The beeam coupling coefficient is assumed to be 1. a) calculate the repeller voltage b) electronic efficiency and output power.arrow_forwardJust solve Earrow_forward
- If the energy levels of an oscillator are given by r, - ¿nhv, where n - 0, I and 2. Assuming that B-Lhv, the probubility of the oscillator to occupy the thind energy level is: A 13% B. 19% C. 31% D. 51% E 91% Aarrow_forwardConsider the ground state of 69As. How many protons there are in the 1d5/2 energy level?arrow_forwardHow would you write an N-electron Slater determinant using N atomic spinorbitals χi (x1).arrow_forward
- Consider a proton confined within typical nuclear dimensions of 5×10^(−15) m. Estimate the minimum kinetic energy of the proton. Repeat this calculation for an electron confined within typical nuclear dimensions. Comment briefly on the physical significance of your results, given that the nuclear binding energy for a proton is typically in the range 1−10 MeVarrow_forwardIf a hydrogen atom in the 2p excited state decays to the 1s ground state, explain how the following properties are conserved: energy, linear momentum, and angular momentum.arrow_forwardA spin half particle is prepared in the spin state |S) = 2|+) + (1 + V3i)l-). where |S) = |S - n = th). What is the component în of spin of the particle which is known to be th?arrow_forward