
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
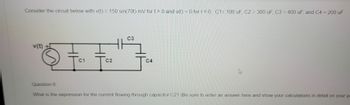
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the circuit below with v(t) = 150 sin(70t) mV for t> 0 and v(t) = 0 for t<0. C1= 100 uF, C2 = 300 uF, C3 = 400 uF, and C4 = 200 uF
v(t)
Fa
C1
C2
C3
C4
Question 6:
What is the expression for the current flowing through capacitor C2? (Be sure to enter an answer here and show your calculations in detail on your pa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- From the circuit shown below calculate the following + Vc - C=0.05pf 10V R1=100k R2=100k a) Find the mathematical expression for the voltage across the capacitor from the previous figure, if the switch is set to position 1 at t=0s. Calculate the voltage vc in t=10ms. Repeat the previous for ic and VR,- b) Find the mathematical expression for the voltages vc and VR, and the current iç if the switch is set to position 2 at t=30ms (Assume that the leakage resistance across capacitor =c0ohms) c) Find the mathematical expression for the voltages ve and (VR, + VR2) and for the current ic, if the switch is set to position 3 at t=48 ms. Find the voltages vc and VR + VR2 and the current iC at t = 100ms. d) Plot the waveforms obtained in the previous on the same time axis for each voltage and for current.arrow_forwardIn the diagram below, the switch S has been closed for a long time. A) What is the output voltage Vout? What is the charge on the capacitor? b) The switch is opened, so the output voltage increases. What is the time constant that describes the charging of the capacitor in terms of R and C? c) When Vout reaches 10 V, the switch closes and the capacitor begins to discharge. What is the time constant that describes the discharging in terms of R and C? Hint: Apply Kirchhoff's Rules to both loops and the sum of the currents at the junction above the capacitor in the diagram, and use I=dq/dt. If the switch opens when Vout reaches a lower value, say 5V, the capacitor will charge again, and thus one can cycle the voltage with a time constant determined by the circuit: this demonstrates the principle of operation of an electronic timer. 4R S 15 V Vout Rarrow_forward2. A devise that stores charge is called An inductor O A potential device A Coulomb O A capacitorarrow_forward
- Please solve and show your detailed solution Number 25arrow_forwardIn the circuit at right, a 100 mH inductor and a 5 N resistor are connected by a switch to a 6 V battery. hlllo a. After the switch is thrown to position a (connecting the battery), what time interval elapses before the current through the inductor is 200 mA? b. What is the current through the inductor 10 seconds later? c. Now the switch is quickly thrown from position a to position b, such that the inductor and resistor form a complete circuit separate from the battery. How much time elapses before the current falls to 200 mA? R L bọarrow_forwardIn the figure ɛ = inductor is ideal. If the switch is closed for a long time, what is the current through the inductor. Give your answer in A. 10.0 V, R, = 4.00 N, and R2 = 1.00 N. The %3D %3Darrow_forward
- A battery is used to charge a capacitor through a resistor as shown in the following figure. After the switch is closed the energy supplied by the batteryis E. Find the Joule heat produced in the resistor and the energy which is stored in the capacitor.arrow_forwardThree capacitors, with capacitances of C1 = 2.0 μF, C2 = 3.0 μF , and C3 = 6.0 μF, respectively, are connected in parallel. A 500-V potential difference is applied across the combination. Determine the voltage across each capacitor and the charge on each capacitor.arrow_forwarda) With switch J2 open, close switch J1. Estimate the time it takes to do it. Obtain the equations for the voltage and current of the capacitor. Determine the energy stored by the capacitor. b) Open switch J1, close switch J2. Estimate the time it takes to do it. Obtain the equations for the voltage and current of the capacitor.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,