
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:VP5.22.2 A competition cyclist rides at a constant 12.5 m/s around a
curve that is banked at 40.0°. The cyclist and her bicycle have a com-
bined mass of 64.0 kg. (a) What must be the radius of her turn if there is
to be no friction force pushing her either up or down the banked curve?
(b) What is the magnitude of her acceleration? (c) What is the magni-
tude of the normal force that the surface of the banked curve exerts on
the bicycle?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given Data:
The uniform velocity of the cycle,
The total mass of bicycle and cyclist,
The angle of banking,
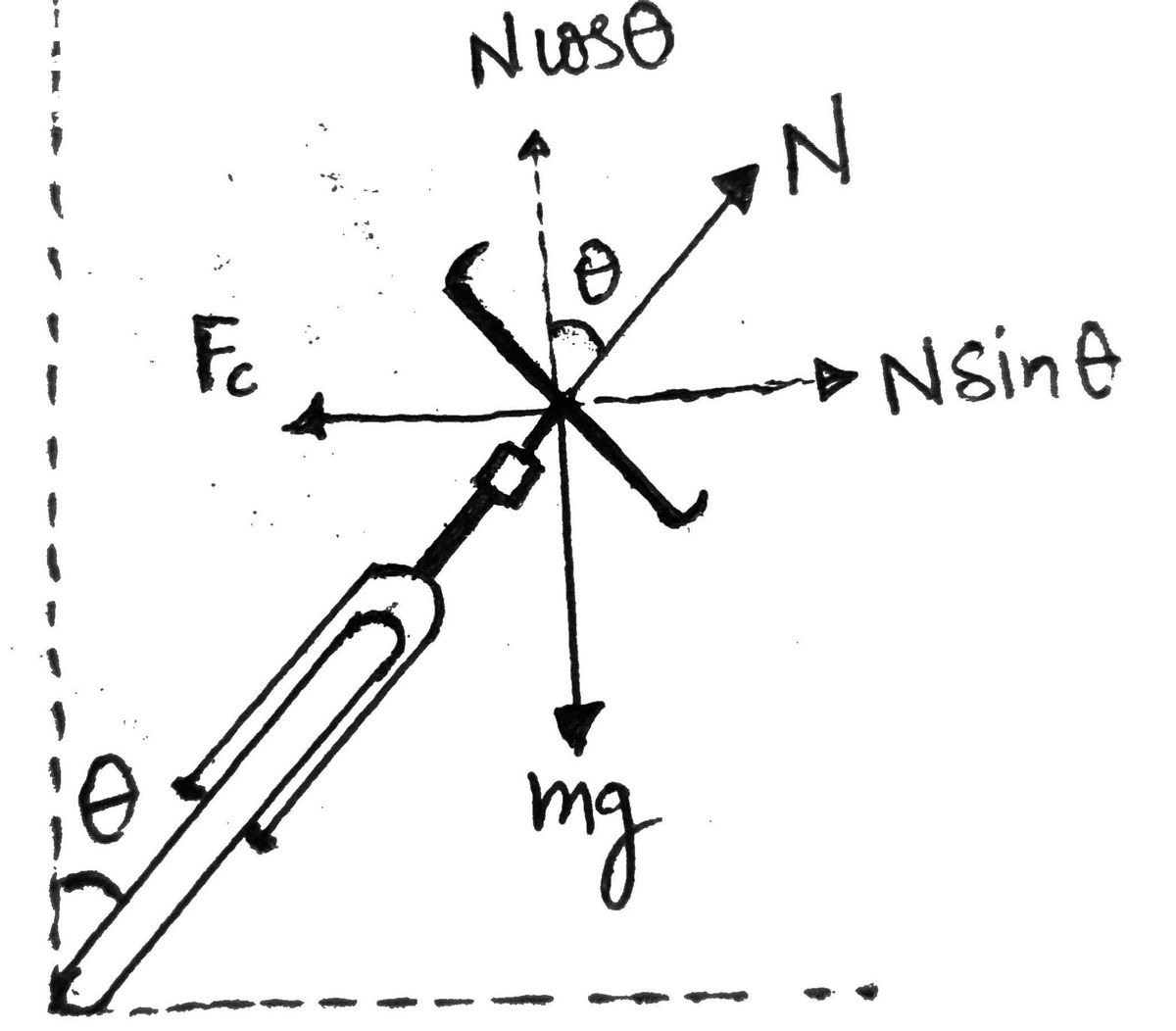
The figure below represents the free body diagram of the bicycle.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In 1589, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei is said to have dropped two spheres of different masses from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass. His experiment is faulty because he neglected: (i) The body force due to gravity. The surface force due to pressure. The surface force due to friction. (ii) (iii) (A) (B) (C) (D) (i) and (ii) (i) and (iii) (ii) and (iii) All of the abovearrow_forward(b) An electric motor lifts a mass of 500 kg from the ground to a height of 30 m in 1.5 minutes. Calculate the motor's output power during operation. The gravitational acceleration, g, is 9.81 m. s-².arrow_forwardEx.5.4 A particle moves such that its velocity varies according to the relation v =v,- kx where k is a constant and v, is the velocity in the position P where x = 0 and t = 0. Derive the expressions for the position coordinate x, velocity v and acceleration a in terms of the time t.arrow_forward
- 4) This Atwood's machine includes two blocks connected by a cable, going over a pulley without slipping. Block 1 (30.0 kg) is connected to a spring (70.0 N/m), and slides on a horizontal surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.0100. Block 2 is 50.0 kg, and hangs vertically from the cable. The pulley is a disk with a radius of 0.500 m, and its moment of inertia about the center of mass is 10. 0 kg-m“. a) Draw the three free body diagrams, and write out Newton's 2nd Law for each. b) Derive the equation of motion (inhomogeneous 2nd order ODE) for this system. c) Use u-substitution to rewrite this as a homogeneous 2nd order ODE. d) Assume the position x as a function of time t is of the form x(t) = A cos (wt + p) I disk for undamped natural frequency w, phase angle P, and amplitude A. The initial conditions are: x(0) v(0) = -3. 00 m/s. Solve for the position of the mass as a function of time (you need to solve for w, 4, and A). = 2. 00 m and Mzarrow_forward5.30arrow_forwardProblem 1 (Lecture 03) Three forces act on the bracket shown to the right. Note that for this problem, the direction (0) of F1 is measured from the positive x' axis, positive clockwise. Complete the following: a) Determine the direction (0) and magnitude of F₁ so that the overall resultant force is directed along the positive x' axis and has a magnitude of 1 kN. b) Determine the unit vector u₂ (in Cartesian notation) for the direction of F2. y Ꮎ F₁ F₂ 45° 30° = 450 N F3 = 200 N Xarrow_forward
- A boxer delivers a hard blow to the chin of his opponent. The inertia of the boxer's hand (with glove) and forearm is 3.0 kg, and the inertia of the opponent's head is 6.5 kg. You learned in neurobiology class about 10 J of extra internal energy will render an opponent wobbly - kneed, and you guess that about half of the converted energy will end up in the opponent's head. Assuming a coefficient of restitution e = 0.20, with what speed does the boxer's fist have to contact the opponent's head in order to deliver the punch?arrow_forwardplease answer this question with explination. many thanks !arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY