
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Instrumental
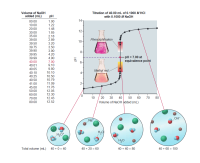
Transcribed Image Text:Volume of NaOH
added (mL)
Titration of 40.00 mL of 0.1000 M HCI
pH
with 0.1000 M NaOH
147
00.00
10.00
20.00
1.00
1.22
1.48
1.85
2.18
2.89
12-
30.00
35.00
39.00
Phenolphthalein
10-
39.50
3.20
39.75
39.90
39.95
39.99
3.50
3.90
4.20
8-
4.90
pH = 7.00 at
equivalence point
40.00
40.01
7.00
9.10
9.80
10.10
10.50
10.79
6-
40.05
Methyl red.
4-
40.10
40.25
40.50
2-
11.09
11.76
12.05
12.30
12.43
41.00
45.00
50.00
60.00
70.00
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
80.00
12.52
Volume of NaOH added (mL)
OH-
Na
CI
H20
Total volume (mL)
40 + 0 = 40
40 + 20 = 60
40 + 40 = 80
40 + 60 = 100
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Calculating the pH at equivalence of a titration A chemist titrates 250.0 mL of a 0.5755 M nitrous acid (HNO,) solution with 0.0749 M NaOH solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of nitrous acid is 3.35. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of NaOH solution added. pH = ||arrow_forwardDetermine the pH during the titration of 60.6 mL of 0.420 M hydrocyanic acid (Ka = 4.0×10-10) by 0.420 M NaOH at the following points.(a) Before the addition of any NaOH(b) After the addition of 14.0 mL of NaOH(c) At the half-equivalence point (the titration midpoint) (d) At the equivalence point (e) After the addition of 90.9 mL of NaOHarrow_forwardUse ICE table and also dont use mmol as your units for stuffarrow_forward
- The beaker contains 0.1 M acetic acid solution with methyl orange as an indicator. Another beaker on the left contains a mixture of 0.1 M acetic acid and 0.1 M sodium acetate with methyl orange, which solution has a higher pH?arrow_forwardIf the concentration of the weak base ammonia is 0.10 M and it is titrated with 0.1 M HCl, and the Kb of ammonia is 1.8 x 10^-5, calculate the pre-titration pHarrow_forward1) Listen A 45.60-mL sample of a 0.476 M solution of acetic acid (HC2H3O2) which is a weak acid with an acid ionization constant of 1.70 X10-5 at 25°C is being titrated by a 0.652 M solution of NaOH which is a strong base. Calculate the pH when 60.00 mL of 0.652 M NaOH has been added. HC2H3O2(aq) + H2O(L) = C2H3O2 (aq) + H3O* (aq) 13.45 12.08 13.06 11.67 13.68 201591....docx LAB EXP. #3 -.docx Show Allarrow_forward
- 16 OF 18 QUESTIONS Question 13 In conductometric titration of strong acid with strong base, which portion or point describes the concentration of H+ and OH- ions as [H+] << [OH-1 Conductanee/ms VaUme of base/m АВ BCarrow_forwardFor 550.0 mLmL of a buffer solution that is 0.135 MM in HC2H3O2 and 0.115 MM in NaC2H3O2, calculate the initial pH and the final pH after adding 0.020 molmol of HCl.arrow_forwardThe pH of a 500.00 mL buffer solution containing sodium mandelate and mandelic acid (ka= 3.89x10-4) ((a,=0.90 Please fill in the space with a numerical value with two digits or decimal places without unitsarrow_forward
- A chemist titrates 150.0 mL of a 0.0676M dimethylamine ((CH,) NH) solution with 0.4402M HBr solution at 25 °C. Calculate the pH at equivalence. The pK, of dimethylamine is 3.27. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Note for advanced students: you may assume the total volume of the solution equals the initial volume plus the volume of HBr solution added. pH = Explanation Check 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Accessibity MacBook Airarrow_forwardCalculate the pH for the complete titration of 100.0 mL of 0.122 M hydrazine, H2NNH2, with 0.200 M nitric acid. The Kb for hydrazine is 3.00x10-6. H2NNH2(aq) +HNO3(aq) ⟶ [H2NNH3]+1(aq) + NO3-1(aq) 1. 4.80 2. 9.60 3. 4.70 4. 9.39 5. 3.22 6. 3.32arrow_forwardSolution X is a 400 mL benzoate/benzoic acid buffer solution with a pH of 3.49. If the concentration of benzoic acid present in solution X is 0.3 mol L–1, calculate the concentration of sodium benzoate (in mol L–1) present in solution X at 25 °C. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5E-5.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY