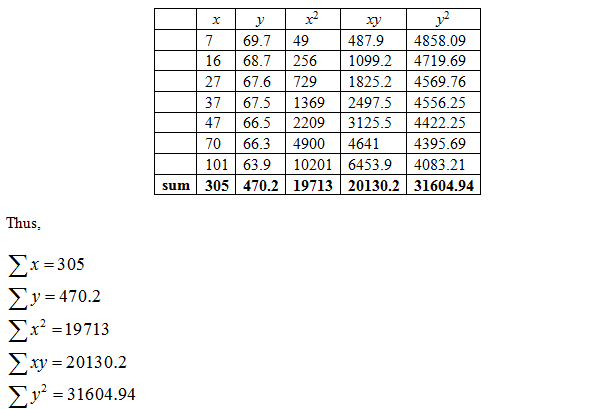
values "alues for Correlation Coefficient n 3 0.997 4 0.950 5 0.878 6 0.811 7 0.754 8 0.707 9 0.666 10 0.632 11 0.602 12 0.576 13 0.553 14 0.532 15 0.514 16 0.497 17 0.482 18 0.468 19 0.456 20 0.444 21 0.433 22 0.423 23 0.413 24 0.404 25 0.396 The data in the table to the right are based on the results of a survey comparing the commute time of adults to their score on a well-being test. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the table of critical values of the correlation coefficient. Commute Time (in minutes) 7 16 27 37 47 70 101 Well-Being Score 69.7 68.7 67.6 67.5 66.5 66.3 63.9 r=0.948 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (d) Does a linear relation exist between the commute time and well-being index score? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) OA. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are positively associated because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OB. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are positively associated because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OC. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are negatively associated because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value O D. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are negatively associated because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OE. No, the variables commute time and well-being score are not linearly related because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is less than the critical value. OF. No, the variables commute time and well-being score are not linearly related because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is less than the critical value.
values "alues for Correlation Coefficient n 3 0.997 4 0.950 5 0.878 6 0.811 7 0.754 8 0.707 9 0.666 10 0.632 11 0.602 12 0.576 13 0.553 14 0.532 15 0.514 16 0.497 17 0.482 18 0.468 19 0.456 20 0.444 21 0.433 22 0.423 23 0.413 24 0.404 25 0.396 The data in the table to the right are based on the results of a survey comparing the commute time of adults to their score on a well-being test. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the table of critical values of the correlation coefficient. Commute Time (in minutes) 7 16 27 37 47 70 101 Well-Being Score 69.7 68.7 67.6 67.5 66.5 66.3 63.9 r=0.948 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (d) Does a linear relation exist between the commute time and well-being index score? Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) OA. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are positively associated because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OB. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are positively associated because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OC. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are negatively associated because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value O D. Yes, the variables commute time and well-being score are negatively associated because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value OE. No, the variables commute time and well-being score are not linearly related because r is negative and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is less than the critical value. OF. No, the variables commute time and well-being score are not linearly related because r is positive and the absolute value of the correlation coefficient is less than the critical value.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
5

Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content on Correlation Coefficient Analysis**
**Understanding Correlation: Commute Time vs. Well-Being Score**
The displayed data come from a survey analyzing the relationship between adults' commute time and their well-being scores. Below are the details of the computation and interpretation of the results.
### Data Overview:
- **Commute Time (in minutes) vs. Well-Being Score:**
- 7 minutes: 69.7
- 16 minutes: 68.7
- 27 minutes: 67.6
- 37 minutes: 67.5
- 47 minutes: 66.5
- 70 minutes: 66.3
- 101 minutes: 63.9
### Correlation Coefficient (r):
- **Calculated r value:** 0.948 (rounded to three decimal places)
### Interpretation of Results:
**Question: Does a linear relationship exist between the commute time and well-being index score?**
- To determine this, select the appropriate interpretation based on the calculated r value and compare it to the critical value provided in a separate table.
- **Options for Analysis:**
- **(A)** Positive association since r is positive and |r| > critical value
- **(B)** Positive association since r is negative and |r| > critical value
- **(C)** Negative association since r is negative and |r| > critical value
- **(D)** Negative association since r is positive and |r| > critical value
- **(E)** No linear relation as r is negative and |r| < critical value
- **(F)** No linear relation as r is positive and |r| < critical value
Understanding which option to select depends on the critical values for the correlation coefficient corresponding to different sample sizes (n), provided on the left side of the table.
### Diagram Explanation:
- **Table of Critical Values for Correlation Coefficient:** Lists critical values based on varying sample sizes (n), ranging from n=3 (0.997) to n=25 (0.396).
### Critical Thinking:
To analyze relationships in datasets effectively, compare correlation coefficients with critical values. A strong positive or negative r, higher than the critical value, indicates a significant linear correlation, helping inform decisions and perspectives on commuting impacts on well-being.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Obtain the value of correlation
The value of correlation is obtained below as follows:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman