
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the two-member frame shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that w1 = 250 N/m , w2 = 420 N/m . Follow the sign convention.
Determine the internal normal force at point E.
Determine the internal shear force at point E.
Determine the internal moment at point E.
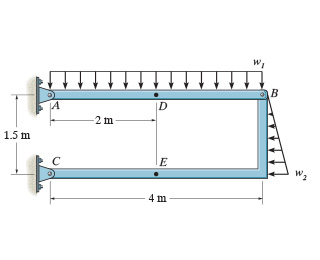
Transcribed Image Text:В
|D
-2 m
1.5 m
E
4 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the above diagram, given that F1 = 450 N, θ = 30 degrees and d = 5 m, calculate the following (neglect the depth of the beam). Note that there is a pin support at A and a roller support at B.arrow_forwardDetermine the normal force, shear force, and moment about point C.arrow_forwardConsider the compound beam shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that P1 = 950 N, P2 = 1500 N, w = 550 N/m, and point E is located just to the left of the 950-N force. Follow the sign convention.determine the Normal, Shear, and moment Forces at point E and Farrow_forward
- A 5.1 m long simply supported wood beam carries a uniformly distributed load of 11.3 kN/m, as shown in Figure A. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam as shown in Figure B are b = 205 mm, d = 460 mm, yH = 77 mm, and yx = 162 mm. Section a-a is located at x = 1.3 m from B. (a) At section a-a, determine the magnitude of the shear stress in the beam at point H. (b) At section a-a, determine the magnitude of the shear stress in the beam at point K. (c) If the allowable shear stress for the wood is 850 kPa, what is the largest distributed load w that can be supported by the beam? х В L Figure Aarrow_forward2. In the figure below, a lug wrench is subjected to loads as shown. The tool body is a hollow cylinder with an outer diameter D = 25 mm, and thickness t. Ignore the changes in diameter (i.e., assume they are all the same), and model it as a cantilever beam. 250N x Z y 500N(+z) 350 mm 500 mm 350 mm 250N B 500N(-z) Cross-section A Z B Useful Cross-section properties for thin walled tubes: I = J = "D³t_A = πDt πD³t 8 a. Sketch elements A and B and show the stress states. Clearly label the coordinate axes on the elements. Make sure you calculate the normal (o) and shear stresses (T). Neglect Tv. b. Find the principal stresses for each element using Mohr's Circle.arrow_forwardFigure Q2 shows the cross section of a beam. The beam is simply supported over a span of 6 m and carries a vertical point load of 40 kN acting at its mid-span. Calculate The position of the horizontal centroidal axis of the cross-section from its bottom. The second moment area of the cross-section about the horizontal centroidal axis The maximum shear load per unit length (metre) at the lower surface of the top flangearrow_forward
- Pravinbhaiarrow_forwardDetermine the axial force, shear force, and bending moment at point J located on member AB of the landing gear of an airplane, as shown in the figure.All distances are in inches.arrow_forwardThe bending moment in a horizontally placed beam at distance x from one of the ends is given by the expression M = 13x - 3x - 12 . The shear force in the beam is zero at, O a. x = 7.12 O b.x = 3 and x = 1.33 O C. X = 2.16 O d. Need more data and a figure to solve the problem.arrow_forward
- In the following figure, there are two equal couples with a magnitude of M = 15 kNm. They act in opposite directions while being applied to the channel beam AB. These couples cause the beam to bend in the horizontal plane. Find: 1) Stress at point C 2) Stress at point D 3) Stress at point Earrow_forwardA cable is enacting a force, F, on a built-in hook at an angle 9 as shown in the figure. Determine the displacement of the point at which the force acts, in the direction of the cable if the shaft of the hook has a length L, radius r and elastic modulus E. Ignore the deformation of the circular hook. If E= 200 GPa, F = 50 kN, 0 = 25°, L = 1 m, r- 100 mm: Answer: 8 = 0.196 mmarrow_forwardConsider the two bars of identical material with their elastic modulus E as shown in Figure below. Both bars have the same circular cross-section with diameter of d. The length of the longer bar is 2L and the length of the shorter bar is L. The angle between the bars is B. The system is subjected to a vertical force acting at point Pas shown in the figure with a magnitude of F. Calculate horizontal and vertical components of the displacement of point P. Use engineering notation (ENG display mode on scientific calculators) with 3 significant figures after the decimal point. E (psi) 1.50E+06 d (in) 1.25 L (in) 12 Beta (degrees) 30 F (Ibf) 110 F P L 2Larrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY