
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
cyclobutadiene is very unsatble, why metal complex are stable?
(use mo structure to explain)
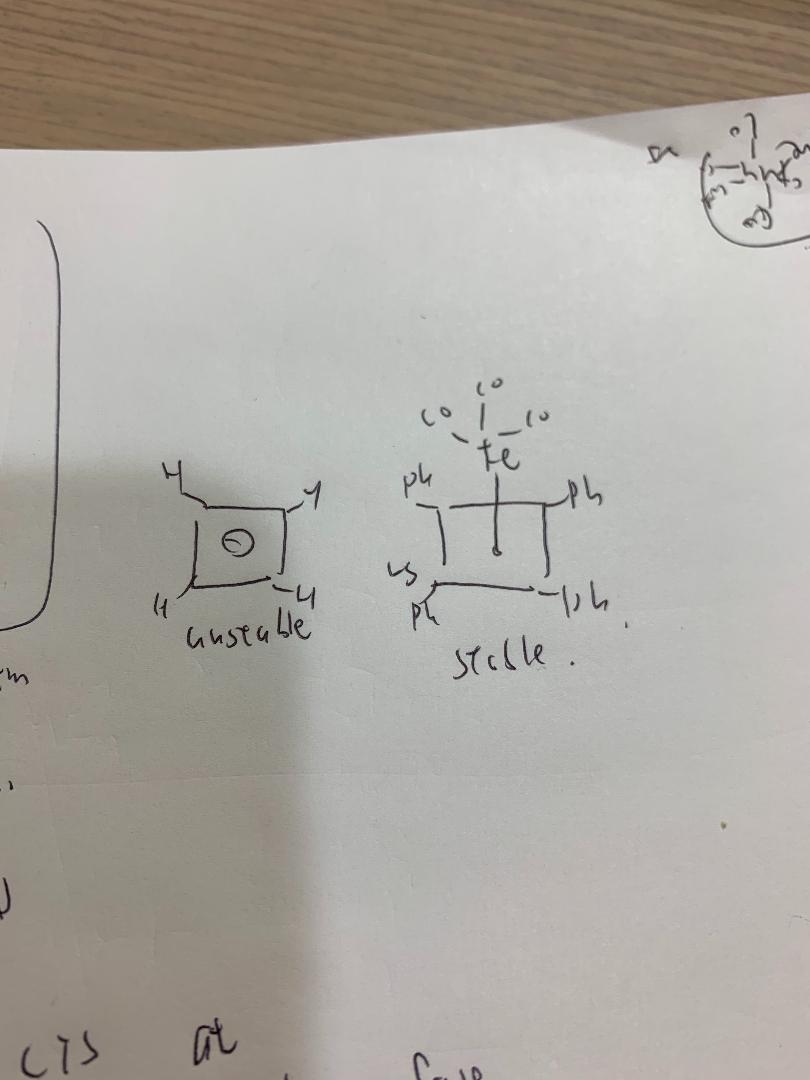
Transcribed Image Text:uusta be'
Stclle.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3) The molecule [CUFJK, has a unique structure (due to jahn-teller distortion) where it has an elongated z-axis in the octahedral structure which changes its point group from On to Dah. Answer the following questions related to elongated structure of [CuFg]K4. a. The oxidation state of Cu: and F: b. Calculate the total number of electrons for (CuFo)*:_ c. Draw the MO diagram for sigma bonding only of (CuF6]K4 including the following i. Correct energy positions for each orbital ii. Symmetry labels including the type of bonding (i.e. t25 (non-bonding) for an octahedral structure) iii. Fill orbitals with the correct number of electronsarrow_forwardPlease ansarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect?arrow_forward
- The ppy ligand bears with inert complex. substituent is expected to form the most CO2ME BF2 OHarrow_forward[Sn(acac)3]NO3arrow_forwardwhat about this answer ? Is this also correct? Isn't it contradict? " However, the back-donation from the metal center to CO's empty 2π* orbital is less extensive than with NO. This is because CO's 2π* orbital is higher in energy compared to NO's 2π* orbital. In summary, both NO and CO are pi-acceptor ligands due to their empty 2π* orbitals. However, NO is expected to be a stronger pi-acceptor ligand than CO because of the presence of the unpaired electron in its 2π* orbital and the lower energy of this orbital. The stronger pi-acceptor ability of NO can lead to a more stable metal-ligand bond, as well as greater electron density redistribution between the metal center and the ligand." I'm so confused NO is weaker or stronger pi-acceptor ligandsarrow_forward
- D. Consider the reaction of RuCl, with terpyridine ligand. I. a. Draw the complex ion structure when 2 terpy ligands attach to the Ru-center.. b. Can it have more than one isomer? If so, neatly draw them. c. Identify the point group of all the isomers you have drawn.arrow_forward15. A complex compound that has an isoelectronic central ion, the greater the charge, the more... A. labileB. stableC. unstableD. inertarrow_forwardThe molecule (CUFJK, has a unique structure (due to jahn-teller distortion) where it has an elongated z-axis in the octahedral structure which changes its point group from O, to Dah. Answer the following questions related to elongated structure of (CuFeJK. a. The oxidation state of Cu: and F: b. Calculate the total number of electrons for [CuFd]: C. Draw the MO diagram for sigma bonding only of (CuFa]Ka including the following i. Correct energy positions for each orbital ii. Symmetry labels including the type of bonding (i.e. the (non-bonding) for an octahedral structure) iii. Fill orbitals with the correct number of electronsarrow_forward
- Consider the pictured structure of a metal complex. Y M. X, Y Determine which letter in the structure represent the different components and geometries of a transitional metal complex. Each letter should only be used once. The only letter that does not represent a ligand Choose... ▼ A pair of trans ligands Choose... A bidentate ligand Choose... - A pair of cis ligands Choose...arrow_forward(Please give detailed answer) is Mo2+ or molybdenum always a predictable ion, why or why not?arrow_forwardInorganic chemistryarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY