
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
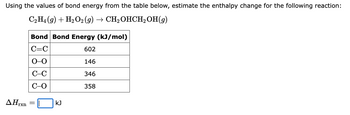
Transcribed Image Text:Using the values of bond energy from the table below, estimate the enthalpy change for the following reaction:
C2H4 (9) + H₂O2 (g) → CH₂OHCH₂OH(9)
ΔΗ,
rxn
Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol)
C=C
602
0-0
146
C-C
346
C-O
358
=
kJ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw Lewis structures for the reactants and products. Use bond enthalpies to calculate ΔH°rxn.HCN(g) + 2 H2(g) → CH3NH2(g)arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution .....arrow_forwardBased on the bond energies for the reaction below, what is the enthalpy of the reaction, in kJ? H₂(g) + N₂(g) + 2 C(g) → 2 HCN(g)arrow_forward
- Suppose there is an element X which occurs naturally as X2(g).X2(g) + 2O2(g) → X2O4(g)X2O4 has a structure ΔHof of O(g) is 249 kJ/molΔHof of X(g) is 470.5 kJ/molΔHof of X2O4(g) is 11 kJ/molThe X-X single bond energy is 148 kJ/molUse the above data to estimate the average bond energy in X2O4. Give your answer to the nearest 1 kJ/mol.arrow_forwardUse the average bond enthalpies from Table 8.3 in your textbook to estimate ΔHΔH for the formation of CO2(g) by the following reaction: CH4(g) + 2O2(g) --> CO2(g) +2H2O(g)arrow_forwardRank the following ionic compounds in order of lattice energy, from the least exothermic (least negative lattice enthalpy) to the most exothermic (most negative lattice enthalpy): KCI, SrO, RbBr, CaOarrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardThe enthalpy change for the following reaction is 66.4 kJ. Using bond energies, estimate the N=O bond energy in NO2(g).N2(g) + 2O2(g)2NO2(g) ____kJ/molarrow_forwardPredict the enthalpy of reaction from the average bond enthalpies for the following reaction: 2C2H6(g) + 7O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 6H2O(g) Bond Enthalpy (kJ/mol) H―H 436.4 H―O 460 C―H 414 C―C 347 C═C 620 C―O 351 O―O 142 O═O 498.7 C═O 745 C═O(in carbondioxide) 799 ______ kJarrow_forward
- The heat of reaction for a chemical reaction can be calculated by finding the sum of the bond energies of the products and subtracting that from the sum of the bond energies of the reactants: Heat of reaction==Sum of the energy for the bonds broken − Sum of the energy for the bonds formedSum of reactant bond energies − Sum of product bond energiesHeat of reaction=Sum of the energy for the bonds broken − Sum of the energy for the bonds formed=Sum of reactant bond energies − Sum of product bond energies When calculating the sum of the bond energies, each bond in the reaction must be accounted for. For example, CH4CH4 is a reagent with a coefficient of 1 in the reaction. There are four C−HC−H bonds in methane and one methane molecule per reaction, for a total of four C−HC−H bonds on the reactant side. All four bonds must be accounted for when finding the sum of the bond energies for the reactants. Calculate the heat of reaction using the average bond dissociation energies given in the…arrow_forwardCH, Use bond dissociation enthalpies to estimate the enthalpy change in this reaction. AH (kJ/mol) Bond H-O C-C H-C 010 C- 010 + H₂O(g) → CH₂CH(OH)CH₂(g) Enthalpy change 44 Submit Substance 463 610 413 346 358 bCalculate the enthalpy change for this reaction from enthalpies of formation. AƒH (kJ/mol) la 272.8arrow_forwardUsing the bond energies as shown, determine the approximate enthalpy change for each of the following reactions:(a) Cl2(g) + 3F2(g) ⟶ 2ClF3(g)(b) H2 C = CH2(g) + H2(g) ⟶ H3 CCH3(g)(c) 2C2 H6(g) + 7O2(g) ⟶ 4CO2(g) + 6H2 O(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY