
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Pls help ASAP

Transcribed Image Text:Using the reagents below, list in order (by letter, no period) those necessary to transform benzene into p-chlorobenzenesulfonic acid.
You may assume any undesired regioisomers can be separated.
Note: Not all spaces provided may be needed. Type "na" in any space where you have no reagent.
A.H₂, Pd
B.H2, Pd/CaSO4, quinoline M. SOCI₂
2
C. H₂, Ni₂B(P-2)
N. Br2, FeBr 3
D. Zn(Hg), HCI, reflux
O. Cl2, hv
E. i.O3, H₂O ii. Zn, H₂O
P. Cl2, FeCl3
F. MMPP, CH3CH₂OH
Q. H₂O
G. i. BH3; ii. H₂O2, NaOH
R. CH3CH₂CH₂CI, AICI 3
H.KOC(CH3)3, HOC(CH3)3
S. (CH3)3CCI, AICI3
Papa
L.HCI, peroxide
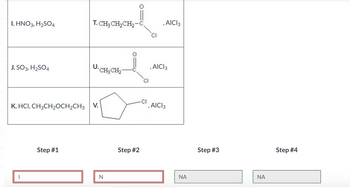
Transcribed Image Text:■ni
Kal
inc
I. HNO3, H₂SO4
J. SO3, H₂SO4
1
K. HCI, CH3CH₂OCH₂CH3 V.
Step #1
T. CH3 CH₂CH₂-C
2016-1
U. CH₂ CH₂
N
Step #2
CI
CI
CI
, AICI 3
, AICI 3
, AICI 3
ΝΑ
Step #3
ΝΑ
Step #4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you please answer the second question? Thank you.arrow_forwardWhich question will your experiment investigate? (select one and delete the others) How does temperature affect how lactase drops work to break down lactose into glucose and galactose? How does pH affect how lactase drops work to break down lactose into glucose and galactose? How does agitation (movement) affect how lactase drops work to break down lactose into glucose and galactose? What variable will you change in this experiment? This is also called the Independent variable. How will you change it? What variable will you measure in this experiment to determine the effect of the variable you changed? This is also called the Dependent variable. How will you measure it? What variables will you keep the same in this experiment? Check off the items in this list that you would use for this experiment. You may add any items you feel you would need. O skim milk (which contains lactose) O Lactase drops O Graduated cylinder Eye dropper Ice cubes O pH paper O Hot plate Mixing spoon O…arrow_forward5. The monomer of a carbohydrate? _________; polymer example of a carbohydrate? ______________ 6. How many rings are in a monosaccharide? _____ disaccharide? _____ polysaccharide? _____What is the most common monosaccharide? _________What is the most common polysaccharide in plants? _________; in animals? _________arrow_forward
- Q3: Use arrows to match the terms (A) column with (B) column. Some may be used more than once and others not at all. 1- Tirglyceride 2- Glycogen 3- Sphingomyelins 4- Membranes 5- Starch 6- Proteins 7- Cholesterol 8- Lactose B a- contain glycerol backbone b- glucose é- amino acids d- esters of fatty acids e- octapeptide f- disaccharide g- polysaccharide K- compound lipids i- steroid-like j- lipids k- polar lipids + glucose storage in animals 9- Waxes 10AngiotensinlIarrow_forwardunsaturation test for oil - add 5 drops of each t oil with 1 drop of alcoholic iodine solution - observe the color of each Coconut oil -- > Cotton-seed oil -- > Linseed oil -- > Olive oil -- >arrow_forwarduestion 6 of 20 Four major contributing resonance structures are possible for the given cation, which is the intermediate o complex of an electrophilic aromatic substitution involving phenol and bromine. Two structures are given but are incomplete. Complete the given structures by adding nonbonding electrons and formal charges. Draw the remaining structures (in any order), including nonbonding electrons and formal charges. Complete structure A. Complete structure B. Erase Rings More Erase Select Draw Rings More Select Draw |//の H Br Br Br Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY