
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
1. Using the midpoint method, compute the price elasticity between points X and Y.
2. Use the midpoint method and compute the price elasticity between points X and Y.
select from:
Demand between X and Y is elastic.
Demand between X and Y is inelastic.
Demand between X and Y is unit elastic.
3. Using the midpoint method, compute the price elasticity between points Y and Z.
4. Use the midpoint method and compute the price elasticity between points Y and Z.
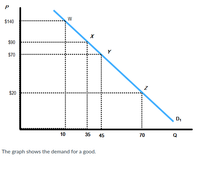
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding the Demand Curve: A Visual Representation**
**Graph Description:**
The graph provided illustrates the demand for a good. This demand curve, labeled \(D_1\), shows the relationship between the price of the good (\(P\)) and the quantity demanded (\(Q\)).
**Axes:**
- The vertical axis (\(P\)) represents the price of the good in dollars, marked at $20, $70, $90, and $140.
- The horizontal axis (\(Q\)) denotes the quantity of the good demanded. Key points are marked at quantities of 10, 35, 45, and 70.
**Points and Demand Curve:**
The demand curve \(D_1\) is a downward-sloping line, indicating the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. The specific points marked on the demand curve (\(W\), \(X\), \(Y\), \(Z\)) correspond to different price-quantity pairs:
- **Point \(W\)**: At a high price of $140, the quantity demanded is low at 10.
- **Point \(X\)**: When the price drops to $90, the quantity demanded increases to 35.
- **Point \(Y\)**: Further price reduction to $70 leads to a rise in quantity demanded to 45.
- **Point \(Z\)**: At a relatively low price of $20, the quantity demanded significantly increases to 70.
**Key Takeaways:**
1. **Inverse Relationship:** The graph clearly demonstrates the law of demand, showing that as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases.
2. **Movement Along the Curve:** This graph represents movements along the demand curve due to changes in price.
3. **Application:** Understanding this demand curve is crucial for setting prices and predicting consumer behavior in response to price changes.
**Conclusion:**
The graph succinctly depicts the basic principles of demand in economic theory, offering insight into how pricing affects consumer purchasing decisions. This foundational concept is essential for further studies in economics, business strategy, and market analysis.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the cross price elasticity?arrow_forward4-6 Suppose that the price of croissants rises from $2 to $3 per unit. Use the mid-point approach to get the elasticity. The quantity of orange juice purchased falls from 10 million bottles to 5 million bottles. What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and orange juice? Are they complements or substitutes? The quantity of jelly purchased increases from 10 million jars to 20 million jars. What is What is the cross-price elasticity of demand between croissants and orange juice? Are they complements or substitutes?arrow_forwardUsing the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand for a good is computed to be approximately 0.55. Which of the following events is consistent with a 20 percent decrease in the quantity of the good demanded? a. An increase of 11.0 percent in the price of the good b. an increase of 36.36 percent in the price of the good c. An increase in the price of the good from $11.00 to $20.00 d. an Increase in the price of the good from $20 to $31.00arrow_forward
- Answer the following questions in your own words. Start a new thread while replying. 1. What are the determinants of price elasticity of demand? Explain the determinants. 2. What is the difference between inelastic demand and elastic demand? Provide an example of each from real life. 3. Refer to the graph below: Price 22 20 + 18 +- 16 + 14 B 12 10 + 4 Demand +++ 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Buaxtity From the graph above calculate: a. Price elasticity of demand from point A to point B (use the mid-point method). Is it an elastic situation or an inelastic situation? b. Price elasticity of demand from point B to point C (use the mid-point method). Is it an elastic situation or an inelastic situation?arrow_forwardThe following table below shows the information on price, quantity of goods and income level. PRICE OF GOOD A QUANTITY GOOD A GOOD B GOOD C 20 150 80 40 30 100 50 70 Based on the information above, a) Calculate the price elasticity of demand for good A when the price increases from RM 20 to RM 30. b) Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand for good A and Good B when price increases from RM 20 to RM 30. State the relationship between good A and Good B and give an example of good that has the same relationship with A and good B. c) Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand for good A and good C when price increases from RM 20 to RM 30. State the relationship between good A and good C and provide an example of good that has the same relationship with A and good C.arrow_forwardSuppose that your demand schedule for DVDs is as follows: Price Quantity Demanded (income - $10,000) $8 40 DVDs 10 32 12 24 14 16 16 B Quantity Demanded I (income-$12,000) 50 DVDs 45 30 20 12 a. Use the midpoint method to calculate your price elasticity of demand as the price of DVDs increases from $12 to $16 if (i) your income is $10,000 and (ii) your income is $12,000. b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $10,000 to $12,000 if (i) the price is $10 and (ii) the price is $14. c. Is the DVDs normal good or inferior good?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education