
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
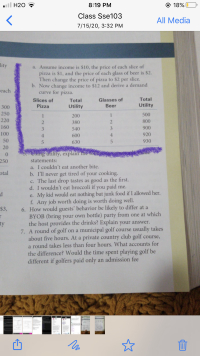
Using the following utility schedule, derive a
curve for pizza.
- Assume income is $10, the
price of each slice of
pizza is $1, and the price of each glass of beer is $2.
Then change the price of pizza to $2 per slice.
- Now change income to $12 and derive a demand
curve for pizza.

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A consumer has a budget set aside for entertainment during the year, and they spend the budget on concerts and plays. The consumer has a strong preference for attending concerts over plays: the two activities are substitutes, but not very strong substitutes. Sketch the indifference curves for this consumer on a graph, with concert tickets on the vertical axis and play tickets on the horizontal axis. Briefly explain why the consumer might ultimately choose to purchase a large number of play tickets, even though they have a strong preference for concerts. Include a budget line on your graph to illustrate this case.arrow_forwardBob consumes food and housing. Suppose his marginal utility from an additional unit of food is 20 and his marginal utility from an additional unit of housing is 180. Furthermore, suppose the price of a unit of food is $1.00 and the price of a unit of housing is $2.00. Can Bob increase his utility without changing his total expenditures on food and housing? Holding expenditures constant, A. Bob can increase utility by spending more on food and less on housing. B. Bob can increase utility by spending more on food and the same amount on housing. C. Bob can increase utility by spending less on food and more on housing. D. Bob cannot increase his utility. E. Bob can increase utility by spending more on food and more on housing.arrow_forwardRick consumes 2 goods, Chicken McNuggets (M) with Szechuan sauce (S). His utility function is U(M, S) = M2/3S1/3 and his income is m. The price of Chicken McNuggets is p, and the price of Szechuan sauce is 1. d. Use the equation from part (c) and the budget constraint from part (a) to find Rick’s demand for each of the two goods. e. Suppose m=100 and p=1. How much of each good does Rick consume? Draw a graph showing Rick’s budget constraint and indifference curve passing through his chosen consumption bundle. f. Suppose m=100 and p=2. How much of each good does Rick consume? On the same graph from part (e), show Rick’s budget constraint and indifference curve passing through his new chosen consumption bundle.arrow_forward
- Suppose that, by law, a person is required to consume a fixed amount of good X, say X0. Assuming X is a normal good, explain how this law reduces utility for both high and low income people.arrow_forwardThe marginal utility for shoes and coffee is given below for five individuals. A pair of shoes costs $2, and a cup of coffee costs $1. Which of these consumers are optimizing over their choices? Explain For those who are not, how should they adjust their spending? Explain “Pasta is Miguel’s favorite meal therefore the law of diminishing marginal utility does not apply”. Do you agree with this statement? It is known that the indifference curve is convex. What does this tell you about the relationship between the goods? The income effect and the substitution effect work in the same direction for a normal good. Explain how this differs for an inferior good.arrow_forwardSuppose the marginal utility of a Coke is 15 utils, and its price is $1.50. The marginal utility of a pizza is 20 utils, and its price is $5. To achieve consumer equilibrium, you need to spendarrow_forward
- A consumer is choosing between magazines and books. His set of čonsumer optimums are shown on the graph to the right. 50 Consumer income allocated for these two goods is equal to $150. The price of magazines (P,) is equal to $5.00. 45- 40 How do these changes in the price of books affect the demand for magazines? 35 demand remains constant 30- We can consider books and magazines to be goods. 25- 20- 15- PCC substitute 10- 5- complementary 0- O 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 unrelated Books O étv 21 MacBook Air DII 80 F10 F11 F7 FB F9 F6 F4 F5 F3 F1 F2 * @ # $ 7 8 9 1 2 4 P T Y Q W J K S F く Z C V command oF option command O 回 .. - つ エ B ** A.arrow_forwardIn Philip's world, only two goods give him utility: economics books (B) and computer games (G). His monthly budget is $100, while a book costs $5 and a game costs $10.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education