
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
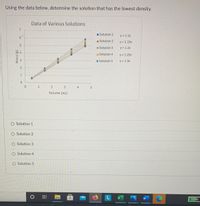
Transcribed Image Text:## Determining Solution with Lowest Density
### Overview
The task is to determine which solution among five has the lowest density using the data provided in the graph.
### Graph Explanation: Data of Various Solutions
- **Axes:**
- The x-axis represents the Volume in milliliters (mL), ranging from 0 to 5.
- The y-axis represents the Mass in grams (g), ranging from 0 to 7.
- **Lines and Data Points:**
The graph displays data points for five different solutions, each represented by a distinct color:
- **Solution 1:** Blue, Line equation: \( y = 1.1x \)
- **Solution 2:** Red, Line equation: \( y = 1.15x \)
- **Solution 3:** Green, Line equation: \( y = 1.2x \)
- **Solution 4:** Orange, Line equation: \( y = 1.25x \)
- **Solution 5:** Light blue, Line equation: \( y = 1.3x \)
### Task
Determine which solution has the lowest density.
### Density and Line Equation
- Density is mass per unit volume, often represented by the slope in a linear relationship like those on the graph.
- The solution with the smallest slope value will have the lowest density.
### Options
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
- Solution 4
- Solution 5
### Conclusion
Observe the slope values provided in each solution's equation. The solution with the smallest coefficient in front of \( x \) has the lowest density.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The solubility of NH3 is 7006g/L H2O at 20°C. Several solutions of NH3 (at 20°C) have been prepared. Categorize each solution as unsaturated, saturated, or supersaturated. Solution 1: 730.9g solute is completely dissolved in 118.6mL water. Solution 2: 9.885g solute is completely dissolved in 1.411 mL water. Solution 3: 5.158g solute is completely dissolved in 0.7221 mL water. Solution 4: 129.7g solute is completely dissolved in 17.46 mL water.arrow_forwardWhat is the concentration in molarity of an aqueous solution which contains 1.15% by mass acetone (MM = 58.08 g/mol)? The density of the solution is 0.971 g/mL.arrow_forwardThe total mass of a solution is 159.0 g. The solvent mass is 125.2 g. What is the mass percent of the solute? Aarrow_forward
- A 106.1 mL of an H2SO4 solution contains 2.49 g of H2SO4. Calculate the normality of the solution. Molar mass of H2SO4 is 98.08 g/molarrow_forwardA solution contains 4.604.60 g of solute in 13.413.4 g of solvent. What is the mass percent of the solute in the solution?arrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a 7.4 % by mass Mg(NO3)2 solution? Assume the density of the solution is 1.0 g/mL.arrow_forward
- What volume of 12.1 M HCl must be diluted to prepare a 0.250 0 M HCl solution with a volume of 2.000 L? O 41.3 mL 96.8 mL O 10.3 mL ○ 24.2 mL O 6.05 mLarrow_forwardWhat is the mass percent of 1.39 M NaCi solution? The density of this solution is 1.05 g/ml.arrow_forwardA 0.699 M Na2SO4 (molar mass=142.04g/mol) solution has a density of 1.139 g/mL. Calculate the mass percent of this solution.arrow_forward
- What is the concentration in molarity of an aqueous solution which contains 1.31% by mass ethylene glycol (MM = 62.07 g/mol)? The density of the solution is 1.04 g/mL.arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows the different parts of a solution. Match each letter to the term it represents in the diagram. solution A B Solubility a b C 0 C 3] Xarrow_forwarda 64.0mL portion of a 1.60M solution is diluted to a total volume of 238mL. A 119mL portion of that solution is diluted by adding 125mL of water. what is the final concentration? assume the volumes are additive.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY