
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter: A simple model of
Q) Using the
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
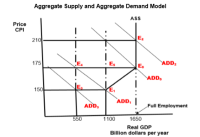
- Question 1 Given the following data on simple closed economy: C= 10 + 0.75 Y I= 20 G= 40 where C is aggregate consumption, Y is national income, G is government expenditure on goods and services, and I is investment expenditure. Note: There is no taxes assumed in parts (i) to (iii). ) What is the equilibrium level of national income? Show all your workings. (ii) What is the value of aggregate consumption and the value of aggregate savings at the equilibrium level of the national income? Show all your workings. ( (iii)What would be the new level of national income if government expenditure increased by 10? Show all your workings.arrow_forwardThe Australia Federal Government established a AUD 2 billion grant to help sectors affected by the bushfires to get the support they needed to recover. Use the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Model below to answer the questions that follow. 1. Using the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Model did the 2019/20 cause economic expansion or economic contraction in Australia. Name at least three sectors that were affected by the bushfires and examine the impact of the bush fires to the economy of Australia. 2.Employ the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Model to explain the benefits of the Australia government AUD2 billion grant to the economy.arrow_forwardQuestion: The attached picture shows the aggregate demand/aggregate supply situation in the U.S. What is the value of actual GDP? What is the value of the GDP deflator? Assume that people and businesses become pessimistic about the future of the economy; how will this affect the graph above in the short run? (i.e., which curve(s) will shift, and in which direction?) After the short-run event in part b, what will happen to actual GDP? What will happen to the price level? After the short-run event in part b, describe how the economy is doing in terms of the business cycle (i.e., recession, full employment, expansion). What long-run adjustments will be made in this economy as a result of the short-run changes in part c? How will the curve(s) shift in response to these long-run adjustments? After the long-run adjustments in part e, describe how the economy is doing in terms of the business cycle (i.e., recession, full employment, expansion).arrow_forward
- a. The key idea of the aggregate expenditure model is that in any particular year, the level of GDP is determined mainly by A) investment spending. B) export spending. C) government spending. D) the level of aggregate expenditure. b. U.S. net export rises when A) the price level in the United States rises relative to the price level in other countries. B) the growth rate of U.S. GDP is slower than the growth rate of GDP in other countries. C) the value of the U.S. dollar increases relative to other currencies. D) the inflation rate is higher in the United States relative to other countries.arrow_forwardIn the graph of Figure I, the annual growth rate of the GDP of the United States economy is presented since the first quarter of 2004, while, in the graphs of Figure II, three different scenarios of the relationship are represented between demand and aggregate supply that reflect different situations of economic growth.2. Explain in detail what is happening in Graph A of Figure II and, after examining the data in the graph of Figure I, identify in what period of time this situation is occurring. Figure I = Real data of the United States economyFigure 2 = Representation of the aggregate demand and supply modelDA = AGGREGATE DEMANDGDP = GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCTNGP = GENERAL PRICE LEVELOAL = LONG TERM AGGREGATE OFFEROAC = SHORT-TERM AGGREGATE OFFER Figure 1arrow_forward10arrow_forward
- In the graph of Figure I, the annual growth rate of the GDP of the United States economy is presented since the first quarter of 2004, while, in the graphs of Figure II, three different scenarios of the relationship are represented between demand and aggregate supply that reflect different situations of economic growth.1. Using the shifts in the aggregate demand curve in each of the three graphs in Figure II, explain the aggregate consumption and investment function. The graphs presented are from Figure 2, which is a representation of the aggregate supply and demand model.DA = aggregate demandGDP = Gross domestic productNGP = general price levelOAL = Long-term aggregate supplyOAC = Short-term aggregate supplyarrow_forwardDo you believe democracy hinders or promotes economic growthSix Debates Over (Professor)Please discuss the six classic questions over macroeconomic policy as delineated in Chapter 23 of the course textbook. Choose two of the questions and take either a pro or con side for each question. Support your responses with a source or sources, including the course textbook (Mankiw).#2 Six Debates Over Macroeconomic Policy (Reading)Consider what causes the lags in the effect of monetary and fiscal policy on aggregate demand. What are the implications of these lags for the debate over active versus passive policy?Consider what might motivate a central banker to cause a political business cycle. What does the political business cycle imply for the debate over policy rules?Be prepared to explain how credibility might affect the cost of reducing inflation.Be prepared to explain why some economists are against a target of zero inflation?Consider what adverse effects might be caused by tax…arrow_forwardEconomicsarrow_forward
- In the graph of Figure I, the annual growth rate of the GDP of the United States economy is presented since the first quarter of 2004, while, in the graphs of Figure II, three different scenarios of the relationship are represented between demand and aggregate supply that reflect different situations of economic growth.2. Explain in detail what is happening in Graph A of Figure II (economic growth, expansion, inflation or reccesion) according to the long and short term aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand and general price level and, examining the data in the graph of Figure I Table 1.1.1., and identify in what period of time this situation (identified in the Graph A) is ocurring. Figure I = Real data of the United States economyFigure 2 = Representation of the aggregate demand and supply modelDA = AGGREGATE DEMANDGDP = GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCTNGP = GENERAL PRICE LEVELOAL = LONG TERM AGGREGATE OFFEROAC = SHORT-TERM AGGREGATE OFFERarrow_forward4. Consider the macroeconomic balance sheets of the following economies. As a policy analyst what would be your monetary and fiscal policy advice in both cases? Explain your answer. Country A Country B GDP Growth Rate: 7% GDP Growth Rate: 0.5% Inflation: 9% Inflation: 2.1% VIX Index (Equity Market Volatility Index): 99 VIX Index (Equity Market Volatility Index): 63 Unemployment: 5% Unemployment: 7% Exchange Rate Volatility: High Exchange Rate Volatility: Low Budget Deficit and Government Borrowing as a share of GDP: High Budget Deficit and Government Borrowing as a share of GDP: High Oil Exporter: Yes Oil Exporter: Noarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education