
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079250
Author: Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
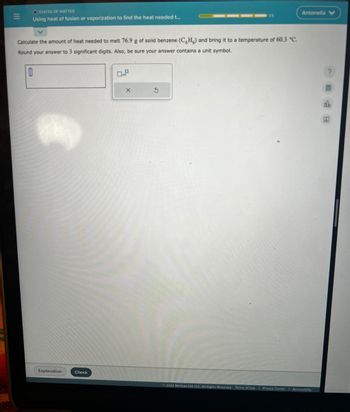
Transcribed Image Text:N
STATES OF MATTER
Using heat of fusion or vaporization to find the heat needed t...
Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 76.9 g of solid benzene (CH) and bring it to a temperature of 60.3 °C.
Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol.
0
Explanation
Check
X
15
3
Antonella V
Ⓒ2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility
?
db
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Weight of solid benzene = 76.9 gm
Final temperature = 60.3°C
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- esc V Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 152. g of solid methanol (CH3OH) and bring it to a temperature of -23.9 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 0 Explanation Check → x10 X с L Ś G Search or type URL % MacBook Pro A C ✰ 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility ‹ 6 ol. Ararrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to melt 116. g of ice (H₂O) and bring it to a temperature of 90.7 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 0 I Don't Know 36°F Light rain/snow Submit G 4 © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accessibility OL F Ararrow_forwardHelp with the following question Round the answer to 3 sig figs and include unit symbolarrow_forward
- 1 2 4 Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 119. g of solid benzene (C.H) and bring it to a temperature of 53.9 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. Submit Assignment Continue O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use |Privacy Center| Accessibility II Finder F10 F11 F12 F7 F8 F9 F4 F5 F3 APP3 F1 APP1 F2 APPZarrow_forwardO Advanced Material Using heat of fusion or vaporization to find the heat needed to melt or bo... esc Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 142. g of solid hexane (C6H14) and bring it to a temperature of 44.8 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 0 ! 1 0² Explanation. F1 @ https://azinsight.adsrvr.org/track/clk?imp=fbec12b0-7f3d-4127-929d-a59782e61fbb&ag=r735012&sfe=1788cd47&sig=PCK7iCABpePPZol9wV E9gKn0P16FOT7R3rMUmfWw.&crid=2zvfx50b&cf=5773664&q=0&t=2&tds-www.chegg.com&rca 2 * Check F2 #3 0.0 80 F3 X $ 4 ds Ś F4 do 5 % f F5 6 F6 & 7 F7 * 8 DII FS ( 9 FO 0 F10 0/5 - C Danasia V F11 园长园 + = 112arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to melt 19.6g of solid octane (C8H18) and bring it to a temperature of 42.0°C . Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol.arrow_forward
- Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 76.0 g of solid ethanol (CH3CH₂OH) and bring it to a temperature of -1.5 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 01 x10 X Ś ? OFF olo Ararrow_forwardPlease don,t provide handwritten solution ..arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to melt 53.7 g of solid benzene (C,H¸) and bring it to a temperature of 12.5 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. x10 ?arrow_forward
- Calculate the amount of heat needed to melt 33.8g of solid acetic acid (HCH3CO2) and bring it to a temperature of 76.0°C. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol and the correct number of significant digits. (Please type answer not write by hend)arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to melt 114. g of solid methanol (CH3OH) and bring it to a temperature of -20.4 °C Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 0 x10 X S ? da Ar ERarrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat needed to melt 111. g of solid hexane (C6H₁4) and bring it to a temperature of -30.7 °C. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. Also, be sure your answer contains a unit symbol. 0 ☐x10 Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning