
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
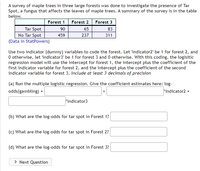
Transcribed Image Text:A survey of maple trees in three large forests was done to investigate the presence of Tar
Spot, a fungus that affects the leaves of maple trees. A summary of the survey is in the table
below.
Forest 1
Forest 2
Forest 3
Tar Spot
No Tar Spot
(Data in StatPowers)
90
65
83
459
237
311
Use two indicator (dummy) variables to code the forest. Let 'indicator2' be 1 for forest 2, and
O otherwise, let 'indicator3' be 1 for forest 3 and 0 otherwise. With this coding, the logisitic
regression model will use the intercept for forest 1, the intercept plus the coefficient of the
first indicator variable for forest 2, and the intercept plus the coefficient of the second
indicator variable for forest 3. Include at least 3 decimals of precision
(a) Run the multiple logistic regression. Give the coefficient estimates here: log-
odds(gambling) =
*indicator2 +
*indicator3
(b) What are the log-odds for tar spot in Forest 1?
(c) What are the log-odds for tar spot in Forest 2?
(d) What are the log-odds for tar spot in Forest 3?
> Next Question
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given that the systolic blood pressure in the right arm is 90 mm Hg, the best systolic blood pressure in the left arm is how many mm Hg?arrow_forwardPlease all the 3 of these sub-questions. Make sure answer is rounded up to 4 decimalsarrow_forwardDevelop a scatterplot and explore the correlation between customer age and net sales by each type of customer (regular/promotion). Use the horizontal axis for the customer age to graph. Find the linear regression line that models the data by each type of customer. Round the rate of changes (slopes) to two decimal places and interpret them in terms of the relation between the change in age and the change in net sales. What can you conclude? Hint: Rate of Change = Vertical Change / Horizontal Change = Change in y / Change in xarrow_forward
- This was not the correct quadratic model for the dataarrow_forwardA particular article proposed a quadratic regression model to describe the relationship between x = degree of delignification during the processing of wood pulp for paper and y = total chlorine content. Suppose that the actual model is the following. y=245+ 75x-4x² + e (a) Mean chlorine content for x = 6 is ---Select--- mean chlorine content for x = 8. (b) What is the change in mean chlorine content when the degree of delignification increases from 8 to 9? What is the change in mean chlorine content when the degree of delignification increases from 12 to 13?arrow_forwardA study tests the effect of earning a Master's degree on the salaries of professionals. Suppose that the salaries of the professionals (S,) are not dependent on any other variables. Let D, be a variable which takes the value 0 if an individual has not earned a Master's degree, and a value 1 if they have earned a Master's degree. What would be the regression model that the researcher wants to test? A. S,= Po + B,D,+u, i=1, .. , n. O B. S,= Po + B, + u, i= 1, .. , n. OC. 1=6o +B1,S, + u, i= 1, .. , n. O D. 0=Bo +B, S, + u,, i= 1, .. , n. Suppose that a random sample of 160 individuals suggests that professionals without a Master's degree earn an average salary of $59,000 per annum, while those with a Master's degree earn an average salary of $80,000 per annum. The OLS estimate of the coefficient B, will be $ and that of B, will be $ Click to select your answer(s). DELLarrow_forward
- Range of ankle motion is a contributing factor to falls among the elderly. Suppose a team of researchers is studying how compression hosiery, typical shoes, and medical shoes affect range of ankle motion. In particular, note the variables Barefoot and Footwear2. Barefoot represents a subject's range of ankle motion (in degrees) while barefoot, and Footwear2 represents their range of ankle motion (in degrees) while wearing medical shoes. Use this data and your preferred software to calculate the equation of the least-squares linear regression line to predict a subject's range of ankle motion while wearing medical shoes, ?̂ , based on their range of ankle motion while barefoot, ? . Round your coefficients to two decimal places of precision. ?̂ = A physical therapist determines that her patient Jan has a range of ankle motion of 7.26°7.26° while barefoot. Predict Jan's range of ankle motion while wearing medical shoes, ?̂ . Round your answer to two decimal places. ?̂ = Suppose Jan's…arrow_forwardData was collected for a regression analysis comparing car weight and fuel consumption. b0 was found to be 32.7, b1 was found to be -7.6, and R2 was found to be 0.86. Interpret the y-intercept of the line. On average, each one unit increase in the weight of a car decreases its ful consumption by 7.6 units. On average, when x=0, a car gets -7.6 miles per gallon. On average, when x=0, a car gets 32.7 miles per gallon. On average, each one unit increase in the weight of a car increases its fuel comsumption by 32.7 units. We should not interpret the y-intercept in this problem.arrow_forwardA particular article used a multiple regression model to relate y = yield of hops to x₁ = mean temperature (°C) between date of coming into hop and date of picking and x₂ = mean percentage of sunshine during the same period. The model equation proposed is the following. y = 415.116.6x₁4.50x2+e (a) Suppose that this equation does indeed describe the true relationship. What mean yield corresponds to a temperature of 20 and a sunshine percentage of 39? (b) What is the mean yield when the mean temperature and percentage of sunshine are 19.1 and 42, respectively? You may need to use the appropriate table in Appendix A to answer this question.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman