
Physical Chemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781133958437
Author: Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher: Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:8:21 >4OB 00 •
83% i
00
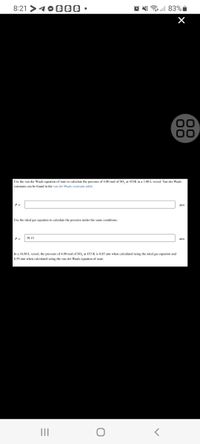
Use the van der Waals equation of state to calculate the pressure of 4.00 mol of SO, at 453K in a 3.80 L vessel. Van der Waals
constants can be found in the van der Waals constants table.
Use the ideal gas equation to cakulate the pressure under the same conditions.
P =
39.15
atm
In a 16.80 L vessel, the pressure of 4.00 mol of SO, at 453 K is 8.85 atm when calculated using the ideal gas equation and
8.59 atm when calculated using the van der Waals equation of state.
II

Transcribed Image Text:8:22 >10 000 •
83% i
00
In a 16.80 L vessel, the pressure of 4.00 mol of SO, at 453 K is 8.85 atm when calkulated using the ideal gas equation and
8.59 atm when calculated using the van der Waals equation of state.
Why is the percent difference in the pressures calculated using the two different equations greater when the gas is in the
3.80 L vessel compared to the 16.80L vessel?
O The attractive forces between molecules become less ofa factor at the hisher pressure in the 3,80L vessel.
O The molecular volume is a smaller part of the total volume of the 3.8OL vessel.
O The molecular volume is a larger part of the total volume of the 3.80L vessel.
O The attractive forces between molecules become a greater factor at the higher pressure in the 3.80 L vessel.
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Under what conditions does the behavior of a real gas begin to differ significantly from the ideal gas law?arrow_forwardA 1.000-g sample of an unknown gas at 0C gives the following data: P(atm) V (L) 0.2500 3.1908 0.5000 1.5928 0.7500 1.0601 1.0000 0.7930 Use these data to calculate the value of the molar mass at each of the given pressures from the ideal gas law (we will call this the apparent molar mass at this pressure). Plot the apparent molar masses against pressure and extrapolate to find the molar mass at zero pressure. Because the ideal gas law is most accurate at low pressures, this extrapolation will give an accurate value for the molar mass. What is the accurate molar mass?arrow_forwardConsider a 5.00-L tank containing 375 g of Ar at a temperature of 25 C. (a) Calculate the pressure in the tank using both the ideal gas law and the van der Waals equation. (b) Which correction term, a(n/V)2 or bn, has the greatest influence on the pressure of this system?arrow_forward
- A 275-mL sample of CO gas is collected over water at 31C and 755 mmHg. If the temperature of the gas collection apparatus rises to 39C, what is the new volume of the sample? Assume that the barometric pressure does not change.arrow_forward93 The complete combustion of octane can be used as a model for the burning of gasoline: 2C8H18+25O216CO2+18H2O Assuming that this equation provides a reasonable model of the actual combustion process, what volume of air at 1.0 atm and 25°C must be taken into an engine to burn 1 gallon of gasoline? (The partial pressure of oxygen in air is 0.21 atm and the density of liquid octane is 0.70 g/mL.)arrow_forwardThe chlorofluorocarbon CCl2F2 can be recycled into a different compound by reaction with hydrogen to produce CCl2F2(g), a compound useful in chemical manufacturing: CCl2F2(g)+4H2(g)CH2F2(g)+2HCl(g) (a) Outline the steps necessary to answer the following question: What volume of hydrogen at 225 atm and 35.5 C would be required to react with 1 ton (1.000103kg) of CCl2F2? (b) Answer the question.arrow_forward
- The density of air 20 km above Earths surface is 92 g/m3. The pressure of the atmosphere is 42 mm Hg, and the temperature is 63 C. (a) What is the average molar mass of the atmosphere at this altitude? (b) If the atmosphere at this altitude consists of only O2 and N2, what is the mole fraction of each gas?arrow_forwardYou have an equimolar mixture of the gases SO2 and O2, along with some He, in a container fitted with a piston. The density of this mixture at STP is 1.924 g/L. Assume ideal behavior and constant temperature and pressure. a. What is the mole fraction of He in the original mixture? b. The SO2 and O2 react to completion to form SO3. What is the density of the gas mixture after the reaction is complete?arrow_forwardDescribe the factors responsible for the deviation of the behavior of real gases from that of an ideal gas.arrow_forward
- A gas effuses through an opening one-fifth as fast as helium gas effuses through the same opening. (a) Is the gas heavier than helium? (b) What is the molar mass of the gas?arrow_forwardHelium gas, He, at 22C and 1.00 atm occupied a vessel whose volume was 2.54 L. What volume would this gas occupy if it were cooled to liquid-nitrogen temperature (197C)?arrow_forwardMost mixtures of hydrogen gas with oxygen gas are explosive. However, a mixture that contains less than 3.0 % O2 is not. If enough O2 is added to a cylinder of H2 at 33.2 atm to bring the total pressure to 3-13 atm, is the mixture explosive?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,
Physical ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781133958437Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, TomasPublisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133958437
Author:Ball, David W. (david Warren), BAER, Tomas
Publisher:Wadsworth Cengage Learning,

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580343
Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning