
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
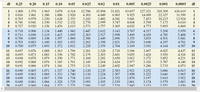
Chapter 10 number 15
use the table provided in attachments.
to test H0: u=100 versus h1 u not equal to 100, a simple random
if xbar =104.2 and 8.5, compute the test statistic.
T= 2.154
B. if the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the a=.01 level of significance, determine the critical values
C. Construct a 99% confidence interval to test the hypothesis.
Transcribed Image Text:df
0.25
0.20
0.15
0.10
0.05
0.025
0,02
0,01
0.005
0.0025
0.001
0.0005
df
1
1.000
1.376
1.963
3.078
6.314
12.706
15.894
31.821
63.657
127.321
318.309
636.619
1
1.386
1.250
1.190
6.965
4.541
3.747
2
0.816
1.061
1.886
2.920
4.303
4.849
9.925
14.089
22.327
31.599
2
3
4
0.765
0.741
0.978
0.941
3.182
2.776
3.482
2.999
7.453
5.598
1.638
2.353
2.132
5.841
4.604
10.215
12.924
8.610
3
1.533
7.173
5.893
0.727
0.920
1.156
1.476
2.015
2.571
2.757
3.365
4.032
4.773
6.869
5
1.943
5.208
4.785
4.501
6
0.718
0.906
1.134
1.440
2.447
2.612
3.143
3.707
4.317
5.959
6.
7
0.711
0.706
0.896
0.889
1.119
1.108
1.415
1.895
1.860
2.365
2.306
2.517
2.449
2.998
2.896
3.499
3.355
4.029
3.833
5.408
5.041
7
1.397
0.703
0.883
1.100
1.383
1.833
2.262
2.398
2.821
3.250
3.690
4.297
4.781
10
0.700
0.879
1.093
1.372
1.812
2.228
2.359
2.764
3.169
3.581
4.144
4.587
10
0.697
0.695
0.694
11
0.876
1.088
1.363
1.356
1.350
1.796
2.201
2.328
2.718
3.106
3.497
4.025
4.437
11
2.179
2.160
2,303
2.282
3.428
3.372
3.326
3.286
12
13
0.873
0.870
1.083
1.079
1.782
2.681
2.650
3.055
3.012
3.930
3.852
3.787
3.733
4.318
4.221
12
13
1.771
14
0.692
0.691
0.868
1.076
1.345
1.761
2.145
2.264
2.624
2.977
4.140
14
15
0.866
1.074
1.341
1.753
2.131
2.249
2.602
2.947
4.073
15
16
17
0.690
0.689
0.865
0.863
1.071
1.069
1.337
1.333
1.746
1.740
2.120
2.110
2.235
2.224
2.921
2.898
2,583
2.567
2.552
2.539
3.252
3.686
3.646
4.015
3.965
16
17
3.222
3.197
0.862
1.067
2.101
2.093
2 086
18
0.688
1.330
1.734
2.214
2.878
3.610
3.922
18
1.729
1 725
19
0.688
0.861
1.066
1.328
2.205
2.861
3.174
3.579
3.883
19
20
0 687
O 860
1064
1 325
2197
2528
2 845
3153
3552
3850
20

Transcribed Image Text:20
0.687
0.860
1.064
1.325
1.725
2.086
2.197
2.528
2.845
3.153
3.552
3.850
20
21
22
0.686
0.686
0.859
0.858
1.063
1.061
2.518
2.508
3.135
3.119
3.104
1.323
1.721
1.717
2.080
2.074
2.189
2.831
2.819
3.527
3.505
3.819
3.792
21
22
1.321
2.183
2.177
23
0.685
0.858
1.060
1.319
1.714
2.069
2.500
2.807
3.485
3.768
23
0.685
0.684
1.059
1.058
0.857
1.711
1.708
2.064
2.172
3.745
3.725
24
1.318
2.492
2.797
3.091
3.467
24
25
0.856
1.316
2.060
2.167
2.485
2.787
3.078
3.450
25
2.056
2.052
2.479
3.067
3.057
3.047
3.038
3.030
26
0.684
0.856
1.058
1.315
1.706
2.162
2.779
3.435
3.707
26
1.314
1.313
27
0.684
0.855
1.057
1.703
2.158
2.473
2.771
3.421
3.690
27
0.55
3.674
3.659
3.646
28
0.683
1.056
1.701
2.048
2.154
2.467
2.763
3.408
28
29
30
1.055
1.055
0.683
0.854
1.311
1.310
1.699
1.697
2.045
2.042
2.150
2.147
2.462
2.756
2.750
3.396
3.385
29
0.683
0.854
2.457
30
1.054
1.054
1.053
31
0.682
0.853
1.309
1.696
2.040
2.144
2.453
2.744
3.022
3.015
3.375
3.633
31
32
1.694
2.141
2.138
3.622
3.611
3.601
0.682
0.853
1.309
2.037
2.449
2.738
3.365
32
33
33
0.682
0.853
1.308
1.692
2.035
2.445
2.733
3.008
34
35
0.682
0.682
0.852
0.852
1.052
1.052
1.307
1.306
2.032
2.030
3.356
3.348
3.340
34
35
1.691
2.136
2.441
2.438
2.728
2.724
3.002
2.996
1.690
2.133
3.591
36
0.681
0.852
1.052
1.306
1.688
2.028
2.131
2.434
2.719
2.990
3.333
3.582
36
37
0.681
0.851
1.051
1.305
1.687
2.026
2.129
2.431
2.715
2.985
3.326
3.574
37
38
39
0.681
0.681
2.127
2.125
0.851
1.051
1.050
1.304
1.304
1.686
2.024
2.023
2.429
2.426
2.712
2.708
2.980
2.976
3.319
3.566
3.558
38
39
3.313
0.851
0.851
1.685
1.684
40
0.681
1.050
1.303
2.021
2.123
2.423
2.704
2.971
3.307
3.551
40
0670
1047
1200
1676
2 100
2 402
2679
2 027
2 361
2 406
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a hypothesis test about a population mean with a known population standard deviation, of H0 : µ = 100 against Hα : µ ≠ 100, the sample data yield the test statistic z = 2.17. The p-value for this test is?arrow_forwardUse the t-distribution and the sample results to complete the test of the hypotheses. Use a 5% significance level. Assume the results come from a random sample, and if the sample size is small, assume the underlying distribution is relatively normal.Test H0 : μ=15 vs Ha : μ>15 using the sample results x¯=17.2, s=6.4, with n=40. Give the test statistic and the p-value. What is the conclusion?arrow_forwardHeart rates are determined before and 30 minutes after a Kettleball workout. It can be assumed that heart rates (bpm) are normally distributed. Use the data provided below to test to determine if average heart rates prior to the workout are significantly lower than 30 minutes after a Kettleball workout at the 0.02 level of significance. Let μ₁ = mean before workout. Select the correct Hypotheses: Ho:με 2 με Η: μι = με Η: μη μ₂ O O O Conclusion: before 69 69 65 62 63 61 after 73 75 72 70 68 59 O Fail to Reject Ho ● Reject Ho Test Statistic = p-value = Ho:μd = 0 H₁: Hd ‡0 O [three decimal accuracy] [three decimal accuracy] Ho:μα 20 Ha:Pa 0 O Interpret the conclusion in context: ● There is enough evidence to suggest the mean bpm before a Kettleball workout is lower than 30 minutes after the workout. O There is not enough evidence to suggest the mean bpm before a Kettleball workout is lower than 30 minutes after the workout.arrow_forward
- 1. Find the critical values. 2. Find the standardized test statistic.arrow_forwardTest the claim about the difference between two population means µ1 and µ2 at the level of significance a. Assume the samples are random and independent, and the populations are normally distributed. Claim: 41 = H2; a = 0.05. Assume o? =o; Sample statistics: x, = 31.8, s, = 3.4, n, = 12 and X2 = 34.7, s2 = 2.3, n2 = 1 Identify the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below. O A. Ho: H12H2 Ha: H1 H2 OF. Ho: H1> H2 Ha: H1 SH2 Find the standardized test statistic t. t=| (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis and interpret the decision in the context of the original claim. Ho. There enough evidence at the 5% level of significance to reject the claim.arrow_forwardIn a random sample of 320 cars driven at low altitude, 40 of them exceeded the standard 10 grams of particulate pollution per gallon of fuel consumed. In another independent random sample of 80 cars driven at high altitude, 20 of them exceeded the standard. Let P 1be the true proportion of cars that exceed the standard in low altitudes and P 2be the true proportion of cars that exceed the standard in high altitudes. What is the test statistic for testing this hypothesis.arrow_forward
- According to the Official Stage Magician Handbook, magic rabbit weight (Ibs.) is normally distributed with u = 6.2 and o = 1.5. %3D Consider obtaining a random sample of 3 magic rabbits. Would it be unusual for the sample mean to be at least 6.5? Why or why not? Yes because the z-score corresponding to a sample mean of 6.5 would be z = 0.34. No because the z-score corresponding to a sample mean of 6.5 would be z = 0.34. O Yes because the z-score corresponding to a sample mean of 6.5 would be z = 0.20. O No because the z-score corresponding to a sample mean of 6.5 would be z = 0.20.arrow_forwardThe dataset below that contains information on fuel efficiency (in miles/gallon) from random samples of cars with manual and automatic transmissions as well as cars with other transmissions. Do these data provide strong evidence of a difference between the average fuel efficiency of cars with manual and automatic transmissions in terms of their average citymileage? 1. Set up the null and alternative hypotheses.2. Compute the test statistic.3. State the p-value for the test. State the decision and conclusion of the test in context. Feel free to use excel, Rstudio, or any other methods to answer the Question! Thanks Auto Manual 77 22 126 30 52 28 62 26 62 29 106 20 27 27 28 22 24 26 26 26 30 26 21 23 21 28 23 29 25 25 20 25 20 22 18 17 17 27 14 25 15 19 18 27 17 30 14 23 18 24 17 23 14 22 15 23 18 24 17 27 14 23 19 22 17 25 17 19 14 26 16 21 16 23 14 18 17 18 17 18 14 18 16 19 16 19 14 21 18 18…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman