
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Use the stiffness method to determine the rotations at all nodes and reactions at supports.
Assume support 1 and 3 are rollers and support 2 is pinned.
EI is constant.
w = 40 kNm
L1 = 5.5m
L2 = 11m
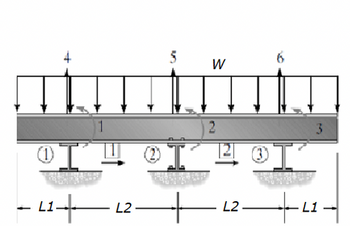
Transcribed Image Text:Io
— 21——————| L2
5 W
L2
3
-L1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: Given
VIEW Step 2: Kinematic indeterminacy
VIEW Step 3: Stiffness matrix (Part-1)
VIEW Step 4: Stiffness matrix (Part-2)
VIEW Step 5: Stiffness matrix (Part-3)
VIEW Step 6: Assemblage of stiffness matrix
VIEW Step 7: Joint displacement
VIEW Step 8: Support moments
VIEW Step 9: Support reactions
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 10 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A fixed-end beam AB carries point load P acting at point C. The beam has a rectangular cross section (b = 85 mm, h = 175 mm). P = 3.4 kN 3 m A C B L = 5 m Calculate the reactions of the beam. Assume that E = 190 GPa. (Solve by the method of superposition. The beam has constant flexural rigidity EI. Assume that the +x-axis is to the right and the +y-axis is up along the page, with the origin at A. Use the statics sign convention. Assume the positive direction for moments is counterclockwise. Enter your forces in kN and your moments in kN · m.) kN RB kN MA kN - m MB kN . m Calculate the displacement at point C. (Enter your answer in mm. Use the statics sign convention.) mmarrow_forwardTABLE 1.2 Minimum Densities for Design Loads from Materials Aluminum Concrete, cinder Concrete, stone Clay, dry Clay, damp Sand and gravel, dry loose Sand and gravel, wet Masonry, lightweight concrete Masonry, normal weight units Steel, cold-drawn Wood, Douglas Fir Wood, Southern Pine Wood, spruce AN/w 27 120 22.6 123 15.7 18.9 165 21.2 5.7 723 5.3 5.8 45 TABLE 1.3 Minimum Design Dead Loads From Paris and Walls Wood 1x plated Woodplatered Woodst 51x32mm, platered Cindere per Lightweight complaine Ceilings Aucuntic Shond Spendedahand Angle 5.54 9.57 2017 005 8:24 0.41 904 TABLE 1.4 Minimum Live Loade Oorspany or Use Amely Fixed seats and at Garage (can only) Officeday Lebbin Love Load 4.79 192 4.79 VEST S Occupancy or Use Dwelings (one-and two-mily) Hotels and many bo Private and don Campos Fint Coor comidon Comidon abfint floor Live Lead KN/² 190 4.39 3.33arrow_forwardThe rigid bar ABC pivots about support B. After application of load P, end C of the rigid bar moves upward by 0.07 in. If the length of bar (1) is L₁ = 41 in., determine the average normal strain in bar (1). Assume that a = 100 in., b = 25 in., and c = 0.05 in. 4₁ Answer: VA = (1) Determine the distance that end A of the rigid bar moves downward, if end C moves upward by 0.07 in. i a Rigid bar in.arrow_forward
- A frame and loading are shown. B 90 mm D 120 mm ' 120 mm' 120 mm Determine the force acting on member ABCat C. Take P= 420 N. The force acting on member ABC at Cis N.arrow_forwardCompound axial member ABC has a uniform diameter of d = 1.2 in. Segment (1) is an aluminum [E₁ = 10,000 ksi] alloy and segment (2) is a copper [E₂ = 17,000 ksi] alloy. The lengths of segments (1) and (2) are L₁ = 80 in. and L2 = 140 in., respectively. Determine the force P required to stretch compound member ABC by a total of 0.10 in. LI L2 A d Aluminum Copper Answer: P = i B kipsarrow_forwardShow full solutionarrow_forward
- Member AC of the following truss is subjected to a temperature change of +110 °C. Calculate the displacements of node A and the forces in each member using the stiffness method. Take: a= 2x 10-5; EA= 2x 104 kN; the cross section area of AC as A; the cross section area of AD as A√2; the cross section area of AB as 5.0A. 1.732 m 1 m Part 1. The displacements at joint A: a) A₂ = b) Ay = mm mm Part 2. The force in each member: a) NAB = b) NAC = c) NAD kN kN kN Aarrow_forwardSolve with Free body diagramarrow_forwardSolve correctlyarrow_forward
- For the indeterminate frames shown, determine the support reactions using force method. EI is constant.arrow_forwardSolve correctly please.arrow_forwardThe beam consists of three segments pin connected at B and E. Determine the shear force and bending moment in the beam. Use w = 14 kN/m, a= 9.5 m, b= 4.5 m, and c= 65 m. The shear force at the point B of the beam in kN is (round to the nearest integer): The bending moment at the point A of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): kN.m The bending moment at the point B of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | KN.m The bending moment at the point C of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | kN.m The bending moment at the point D of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | KN.m The bending moment at the point F of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | KN.m The maximum bending moment in the section AB of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | kN.m The maximum bending moment in the section CD of the beam in kN.m is (round to the nearest integer): | KN.m The maximum bending moment in the section DF of the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning