
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:LEMMA 1.60
If a language is regular, then it is deseribed by a regular expression.
PROOF IDEA We need to show that if a language A is regular, a regular
expression describes it. Because A is regular, it is accepted by a DFA. We describe
a procedure for converting DFAS into equivalent regular expressions.
We break this procedure into two parts, using a new type of finite automaton
called a generalized nondeterministic finite automaton, GNFA. First we show
how to convert DFAS into GNFAS, and then GNFAS into regular expressions.
Generalized nondeterministic finite automata are simply nondeterministic fi-
nite automata wherein the transition arrows may have any regular expressions as
labels, instead of only members of the alphabet or e. The GNFA reads blocks of
symbols from the input, not necessarily just one symbol at a time as in an ordi-
nary NFA. The GNFA moves along a transition arrow connecting two states by
reading a block of symbols from the input, which themselves constitute a string
described by the regular expression on that arrow. A GNFA is nondeterministic
and so may have several different ways to process the same input string. It ac-
cepts its input if its processing can cause the GNFA to be in an accept state at the
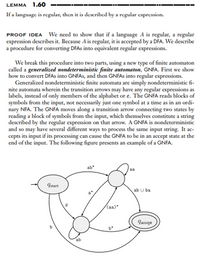
end of the input. The following figure presents an example of a GNFA.
Fstart
ab U ba
a)*
Taccept
ab
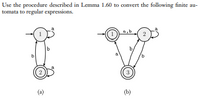
Transcribed Image Text:Use the procedure described in Lemma 1.60 to convert the following finite au-
tomata to regular expressions.
a,b
2
b
3
(a)
(b)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How to prove the Regular expression identities: (x + y)* = (a*y)*x*arrow_forwardUse the procedure described in slides chapter6-part1 (proof 2, pages 8-13) to convert the following finite automaton to a regular expression.arrow_forwardTo determine the global minimum of the error function, the backpropagation method is employed. T or Farrow_forward
- Please use matlabarrow_forwarda) Write an expression for the shown function x(t) x(t) 1 -1 1 2 -1arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure below is stretched from its equilibrium position at x = 0 to a positive coordinate xo. ko HINT x = 0 x = xo PE sn PE 50 The force on the spring is F and it stores elastic potential energy PESO. If the spring displacement is tripled to 3x, determine the ratio of the new force to the original force, and the ratio of the new to the original elastic potential energy, Fo Fo PESO (a) the ratio of the new force to the original force, PE ST PE SO (b) the ratio of the new to the original elastic potential energy,arrow_forward
- Determine whether the following argument is valid using truth tables. Please show workarrow_forwardForm boolean equations in POS and SOP forms from the truth table attached (PLEASE EXPLAIN ALL STEPS), then simplify (showing ALL steps) SOP using boolean identities (EXPLAIN USE OF IDENTITIES WITHIN STEPS).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education