
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
![Use the information in the \( pK_a \) table to rank the molecules in order of increasing basicity. For example, select "1" in the second column for the weakest base and "2" for the next weakest base and so on.
**Table: Molecules**
- Cl\(^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- CH\(_3\)NH\(^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- NH\(_3\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- HSO\(_4^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
**\( pK_a \) table:**
- CH\(_4\): 48
- NH\(_3\): 38
- H\(_2\): 36
- CH\(_3\)NH\(_2\): 33
- H\(_2\)O: 15.7
- CH\(_3\)OH: 15.5
- CH\(_3\)NH\(_3^+\): 10.6
- CH\(_3\)SH: 10.4
- HCN: 9.4
- NH\(_4^+\): 9.2
- H\(_2\)S: 7.00
- CH\(_3\)CO\(_2\)H: 4.76
- HF: 3.17
- H\(_3\)O\(^+\): -1.7
- CH\(_3\)OH\(_2^+\): -2.2
- H\(_2\)SO\(_4\): -3.0
- HCl: -7
- HBr: -9](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/70c6702f-1254-4f2b-ba5a-ac93276291c3/d30cdccd-0ce4-48fc-9599-8655c98824df/x0hh9w5_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Use the information in the \( pK_a \) table to rank the molecules in order of increasing basicity. For example, select "1" in the second column for the weakest base and "2" for the next weakest base and so on.
**Table: Molecules**
- Cl\(^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- CH\(_3\)NH\(^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- NH\(_3\) [(Choose one) ▼]
- HSO\(_4^-\) [(Choose one) ▼]
**\( pK_a \) table:**
- CH\(_4\): 48
- NH\(_3\): 38
- H\(_2\): 36
- CH\(_3\)NH\(_2\): 33
- H\(_2\)O: 15.7
- CH\(_3\)OH: 15.5
- CH\(_3\)NH\(_3^+\): 10.6
- CH\(_3\)SH: 10.4
- HCN: 9.4
- NH\(_4^+\): 9.2
- H\(_2\)S: 7.00
- CH\(_3\)CO\(_2\)H: 4.76
- HF: 3.17
- H\(_3\)O\(^+\): -1.7
- CH\(_3\)OH\(_2^+\): -2.2
- H\(_2\)SO\(_4\): -3.0
- HCl: -7
- HBr: -9
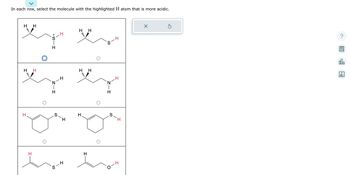
Transcribed Image Text:**Title: Determining Acidity of Highlighted Hydrogen Atoms in Organic Molecules**
---
**Instructions:**
In each row, select the molecule with the highlighted hydrogen (H) atom that is more acidic.
---
### Row 1:
- **Molecule 1:** Features a sulfur atom attached to a carbon-hydrogen chain. The highlighted hydrogen is bonded directly to a sulfur (SH).
- **Molecule 2:** Shows a similar carbon-hydrogen chain with sulfur, but the highlighted hydrogen is not directly bonded to sulfur.
**Selection:**
- The first molecule has the more acidic hydrogen atom, indicated by a checkmark circle.
### Row 2:
- **Molecule 1:** Contains a nitrogen atom bonded within the carbon chain. The highlighted hydrogen is on a nitrogen (NH).
- **Molecule 2:** Shows the highlighted hydrogen bonded to a nitrogen within a similar carbon structure.
**Selection:**
- No selection is indicated for either molecule.
### Row 3:
- **Molecule 1:** A cyclic structure with a sulfur atom. The highlighted hydrogen is bonded to a carbon in the ring.
- **Molecule 2:** A similar cyclic structure with sulfur, but the highlighted hydrogen is directly bonded to sulfur (SH).
**Selection:**
- No selection is indicated for either molecule.
### Row 4:
- **Molecule 1:** Linear carbon-hydrogen chain with the highlighted hydrogen on an end carbon.
- **Molecule 2:** Similar linear chain, but with the highlighted hydrogen closer to an oxygen atom (OH).
**Selection:**
- No selection is indicated for either molecule.
---
**Conclusion:**
The acidity of hydrogen atoms in organic molecules can vary significantly depending on the surrounding atoms and the functional group to which they are attached. Typically, hydrogen atoms bonded to electronegative elements or groups capable of stabilizing the negative charge are more acidic.
This exercise aims to enhance the understanding of how molecular structure impacts acidity, crucial for predicting reactivity and behavior in chemical reactions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the strongest base? NH₂ NH₂ 6 ONHarrow_forwardDraw the conjugate acid for the following base (lone pairs do not have to be drawn and do not show sodium): NaNH2arrow_forwardBr 2) Number these compounds in order of increasing acidity (most acidic = 1). COOH O₂N COOH COOH H₂C COOH COOHarrow_forward
- Use the information in the pK table to rank the molecules in order of decreasing basicity. For example, select "1" in the second column for the strongest base a and "2" for the next strongest base and so on. CH3 HS F CH,CO, Molecules (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) (Choose one) X Ś CHA 4 NH₂ H₂ CH3NH₂ 2 48 38 36 33 pk table pKa CH,NH, CH₂SH 10.4 H₂O* HCN + 10.6 9.4 NH H₂O 15.7 H₂S CH₂OH 15.5 CH,CO,H 4.76 9.2 7.00 HF CH₂OH₂ H₂SO4 HC1 HBr 3.17 -1.7 -2.2 -3.0 -7 -9arrow_forward16) Assign each of these formulas either strong acid, strong base, weak acid, weak base HCl KOH NH3 H2SO4 HC2H3O2arrow_forwardWhich of the following bases are the STRONGEST? pyridine, C5H5N urea, NH2CONH2 ammonia, NH3 butylamine, C4H9NH2arrow_forward
- For the following molecule, draw the major species at each pH. The carboxylic acid is drawn as a conjugate acid and the amine are drawn as the conjugate base. 1. pH of 2 2. pH of 4 3. pH of 7arrow_forwardBromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Select the modification that will make Bromfenac a weaker base. Bromfenac NH2 OH Br NH OH Br oror NH2 OH Br NH2 OH Brarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY