
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Use the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use α = 0.05.)
X
y
10
9.14
8
8.15
13
8.75
9
8.76
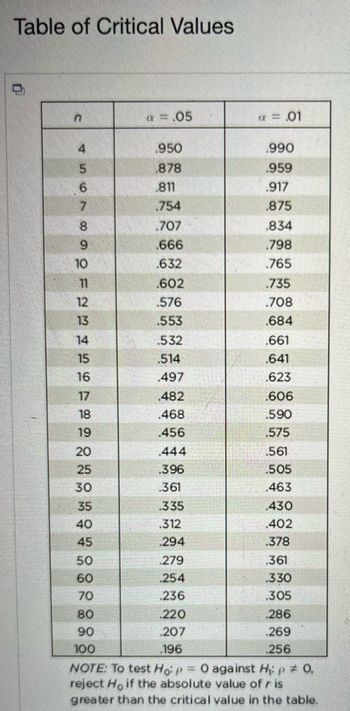
Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient.
4
8 12 16
4
8 12 16
11
9.27
14
8.11
6
6.13
4
3.09
12
9.13
7
7.27
5
4.74
4
8 12 16
04 8
12 16
b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables.
The linear correlation coefficient is r = 0.816.
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the
correct answer below.
OA. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables.
B. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables.
OC. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables.
OD. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables.
c. Identify the feature of the data that would be missed if part (b) was completed without constructing the scatterplot. Choose the correct answer below.
OA. The scatterplot reveals a distinct pattern that is not a straight-line pattern.
OB. The scatterplot does not reveal a distinct pattern.
OC. The scatterplot reveals a distinct pattern that is a straight-line pattern with negative slope.
OD. The scatterplot reveals a distinct pattern that is a straight-line pattern with positive slope.
Transcribed Image Text:Table of Critical Values
n
a = .05
a = .01
4
.950
.990
5
.878
.959
6
.811
.917
7
.754
.875
8
.707
.834
9
.666
.798
10
.632
.765
11
.602
.735
12
.576
.708
13
.553
.684
14
.532
.661
15
.514
.641
16
.497
.623
17
.482
.606
18
.468
.590
19
.456
.575
20
.444
.561
25
.396
.505
30
.361
.463
35
.335
.430
40
.312
.402
45
.294
.378
50
.279
.361
60
.254
.330
70
236
.305
80
220
286
90
.207
.269
100
196
256
NOTE: To test Hop = 0 against H: p = 0,
reject Ho if the absolute value of r is
greater than the critical value in the table.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a = 0.05.) 10 8 13 11 14 4 12 7 y 7.46 6.76 12.73 7.11 7.82 8.85 6.07 5.39 8.15 6.43 5.73 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. a. Construct a scatterplot. Choose the correct graph below. OA. В. Oc. OD. Ay 16- AY 16- Ay 16- Ay 16- 12- 12- 12- 12- 8- 8- 8- 8- 000.. 4. .... 4- 4- 4- 0- 0- 0- 0- 8 12 16 12 8 12 16 4 12 16 b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the correct answer below.arrow_forwardThe data below are the final exam scores of 10 randomly selected statistics students and the number of hours they studied for the exam. Calculate the correlation coefficient r. Hours, x 8 10 7 13 7 9. 9 10 11 8 Scores, y 61 76 56 84 62 74 81 86 86 67 Α. 0.761 В. 0.847 C. 0.991 D. 0.654arrow_forwardUse the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a=0.05.) 12 7 9 11 14 6. 7.26 4.74 10 8 13 6.12 9.13 8.74 8.76 9.26 8.11 3.11 y 9.13 8.15 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. .... a. Construct a scatterplot. Choose the correct graph below. B. Oc. OD. A. AY 10- Ay 10- Ay 10- Ay 10- 8- 8- 8- 8- 6- 6 6- 6- 4- 4- 4- 4- 2- 2- 2- 2- 0- 4 8 4 8 12 16 12 16 0- 04 8. 12 16 4 12 16 b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r=. (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Use the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a=0.05.) 10 13 11 14 8.84 12 y 7.45 6.77 12.73 7.11 7.81 6.08 5.39 8.16 6.41 5.72 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. * KIR MM IVY E Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the correct answer below. O A. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables. O B. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables. O C. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. D. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. c. Identify the feature of the data that would be missed if part (b) was completed without…arrow_forwardUse the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a = 0.05.) 10 8 13 9. 11 14 4 12 7 y 7.45 6.77 12.73 7.11 7.81 8.84 6.08 5.39 8.16 6.41 5.72 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the correct answer below. O A. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables. O B. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables. O C. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. O D. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. c. Identify the feature of the data that would be missed if part (b) was completed without constructing…arrow_forward(Use alpha equals0.05.) a. Construct a scatterplot. b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Use the given data set to complete parts (a). (Use α=0.05.) a. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use α=0.05.) x 10 8 13 9 11 14 6 4 12 7 5 y 9.14 8.14 8.74 8.78 9.26 8.11 6.12 3.11 9.12 7.26 4.73 LOADING... Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. a. Construct a scatterplot. Choose the correct graph below. A. 04812160246810xy A scatterplot has a horizontal x-scale from 0 to 16 in increments of 2 and a vertical y-scale from 0 to 10 in increments of 1. Eleven points strictly follow the pattern of a line passing through the points (4, 6) and (14, 1). All coordinates are approximate. B. 04812160246810xy A scatterplot has a horizontal x-scale from 0 to 16 in increments of 2 and a vertical y-scale from 0 to 10 in increments of 1. Eleven points strictly follow the pattern of a curve that rises from left to right passing through the…arrow_forwardAnnual high temperatures in a certain location have been tracked for several years. Let XX represent the year and YY the high temperature. Based on the data shown below, calculate the correlation coefficient (to three decimal places) between XX and YY. Use your calculator! x y 3 14.3 4 13.89 5 15.58 6 14.87 7 12.66 8 10.15 9 9.54 10 8.13 11 11.42 12 9.81 13 6.6 r=arrow_forward
- Use the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a = 0.05.) 10 8 13 11 14 6 4 12 7 5 y 7.46 6.77 12.74 7.11 7.81 8.84 6.09 5.39 8.14 6.43 5.72 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. A. В. O C. D. Ay 16- Ay 16- Q Ay 16- Ay 16- Q 12- 12- 12- 12- 8- 8- 8- 8- .. 4- 4- 4- 4- 0- 4 0- 0- 0+ 4 12 16 4 12 16 16 4 12 16 b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= 0.816. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the correct answer below. A. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a nonlinear correlation between the two variables. B. There is sufficient evidence to…arrow_forwardUse the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a = 0.05.) х 10 8 13 11 14 4 12 У 9.14 8.14 8.74 8.77 9.25 8.09 6.14 3.11 9.13 7.26 4.74 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. a. Construct a scatterplot. Choose the correct graph below. ici O A. B. OC. OD. Ay 10- Ay 10- Ay 10- Ay 10- 8- 8- 8- 8- 6- 6- 6- 6- 4- 4- 4- 4- 2- 2- 2- 2- 0- 0+ 0+ 4 0+ 4 12 16 8 12 16 12 16 4 12 16 b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Using the linear correlation coefficient found in the previous step, determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. Choose the correct answer below. A. There is insufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between…arrow_forwardUse the given data set to complete parts (a) through (c) below. (Use a =0.05.) 10 8 13 9. 11 14 4 12 7 y 9.15 8.14 8.74 8.77 9.25 8.11 6.12 3.09 9.14 7.26 4.74 Click here to view a table of critical values for the correlation coefficient. Ay 10- Ay 10- 本Y 10- y 10- 8- 8- 6- 8- 8- 6- 6- 6- 4- 4- 4 4. 2- 2- 2- 2- 0- 4 8 12 16 4 8 12 16 4 18 12 16 4 8. 12 16 b. Find the linear correlation coefficient, r, then determine whether there is sufficient evidence to support the claim of a linear correlation between the two variables. The linear correlation coefficient is r= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman