
Trigonometry (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134217437
Author: Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
![Use the following matrices to determine the dimensions of CD.
A = [2 -1 4]
A. 1 x 2
B. 2x1
C. Cannot be determined
OA
U
3
B = 5
0
0 = [25¹]
C-
D= [32]](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/2d99e172-0a0b-4972-acfe-82dc96a1ae81/eca021e8-930f-40cd-b984-06e31299e1d7/c2num1_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Use the following matrices to determine the dimensions of CD.
A = [2 -1 4]
A. 1 x 2
B. 2x1
C. Cannot be determined
OA
U
3
B = 5
0
0 = [25¹]
C-
D= [32]
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
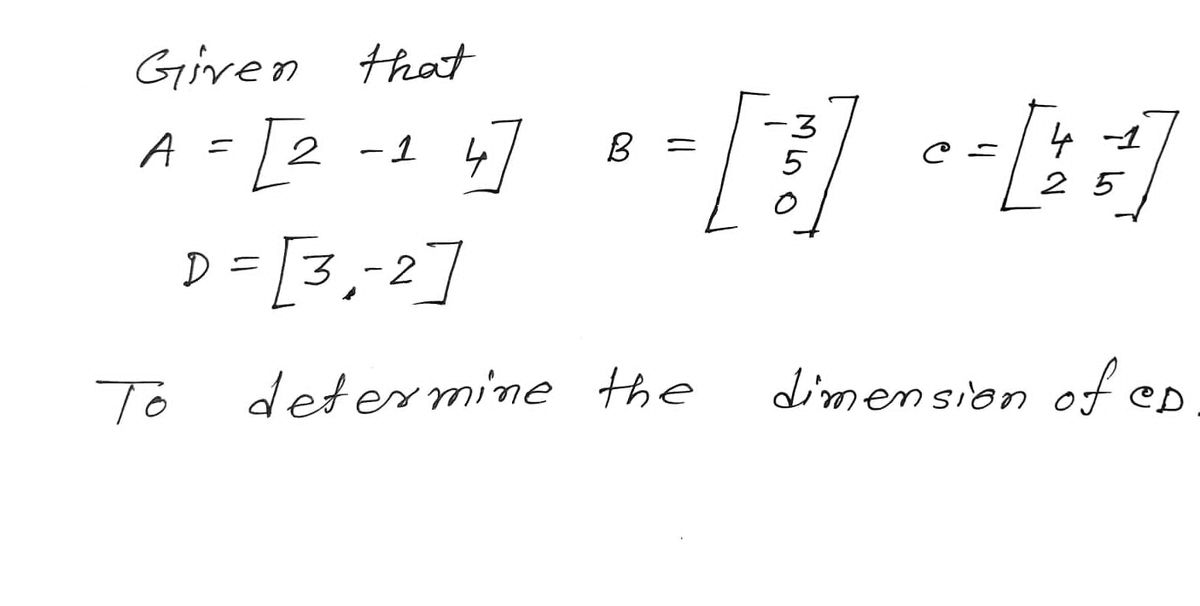
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- If A, B, and C are 5 x 5, 5 x 3, and 3 x 9 matrices respectively, determine which of the following products are defined. For those defined, enter the dimension of the resulting matrix (e.g. "3x4", with no spaces between numbers and "x"). For those undefined, enter "undefined". AC: AB: BC: A². UUarrow_forwardI believe A is correct, but I am not sure about w. It needs to be written as a fraction. Thanks!arrow_forwardQ.5 Write each product as a single matrix: 1 02 1 1 [3 -2 2] 2 i. ii. iii. iv. 3 1 -1 2 -1 -2 57 -2 -1 -1 3 2 -2 -1 1 0 -1-1 -2 4 -2 52 -2 L 1 -1 -1 -1 3 1 1 -2 -1 -2 4 1 0 -1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON
Trigonometry (11th Edition)TrigonometryISBN:9780134217437Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie DanielsPublisher:PEARSON Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (11th Edition)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9780134217437
Author:Margaret L. Lial, John Hornsby, David I. Schneider, Callie Daniels
Publisher:PEARSON

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning