
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
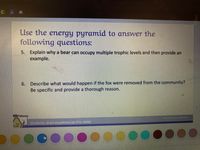
Transcribed Image Text:C 14
Use the energy pyramid to answer the
following questions:
5. Explain why a bear can occupy multiple trophic levels and then provide an
example.
6. Describe what would happen if the fox were removed from the community?
Be specific and provide a thorough reason.
Students, draw anywhere on this slide!
D0000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forwardState the second law of thermodynamics and apply it to the energy transfer from a trophic level to the next higher trophic level in a food chain.arrow_forwardQuestion 3. Which of the following dictates the number of trophic levels or feeding levels? a. Energy absorbed from the sun b. Energy stored by an organism c. Energy available in the ecosystem d. Energy lost as it flows through the ecosystemarrow_forward
- Food webs are helpful diagrams to understand the relationships of organisms within a biological community. Answer the following questions using the food web below. Baleen whale Smaller toothed Sperm whale whales Penguins Elephant seal Leopard seal Other birds Fish Other seals Squid Krill Other herbivorous zooplankton Carnivorous zooplankton Phytoplankton Which of the following can be a secondary consumer? squid other seals krill herbivorous zooplankton fish other birds elephant sealarrow_forwardAnswer clearlyarrow_forwardBackground A trophic level, or feeding level, is made up of all the organisms whose energy source is the same number of consumption steps from the sun in a given ecosystem. The trophic level of plants or producers is 1, while that of herbivores is 2 and that of animals that eat herbivores 3. Higher trophic levels can exist for animals even higher on the food chain. In this exercise, you will compute numerical values for human energy needs based on diets at different trophic levels. In this case study the owner of a farm raises soybeans and chickens. Grasshoppers feed on the farmers soybeans, and are in turn eaten by the chickens. Humans can, though rarely do, eat grasshoppers for sustenance. Humans can also eat soybeans. For the purpose of this exercise, make the following assumptions: A human requires 1 chicken/day There are 365 days/year 1 chicken eats 25 grasshoppers/day 1 grasshopper requires about 30 g of soybeans/year 1,000 grasshoppers have a mass of 1 kg 1 human requires…arrow_forward
- In a grassland ecosystem, a rabbit consumes 1000 kJ of plant material. Of this, 300 kJ is excreted as waste. How much energy is egested by the rabbit? Group of answer choices 1000 700 1300 300arrow_forwardWhat is the outcome for both species involved in a trophic interaction? +,arrow_forwardCreate a 4 species food chain using arrows to show the direction of energy flow.arrow_forward
- From your reading of the short article "Why Fish Need Trees and Trees Need Fish" by Anne Post, what is the amount of nutrients and energy that one adult chum salmon delivers to Alaskan streams? 20 grams of nitrogen 130 grams of phosphorus Over 20,000 kilojoules of energy 130 grams of nitrogen 20 grams of phosphorus Over 20,000 kilojoules of energy day 20 grams of nitrogen 80 grams of phosphorus Over 2,000 kilojoules of energy 80 grams of nitrogen 11 grams of phosphorus Over 20,000 kilojoules of energyarrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates a typical marine food web. Mercury, a toxic heavy metal, can accumulate in the fatty tissue of organisms. Which organism would you predict to have the highest level of mercury? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardSequence energy flow through ecosystemarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education