
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Do parts b,c,d and e
![Use the chi-square test to determine if the listed occupations and personality preferences are
independent at the 0.01 level of significance.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
Hi: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
profession are independent.
H: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are independent.
profession are not independent.
H₁: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are independent.
profession are independent.
Hi: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
Are all the expected frequencies greater than 5?
Yes No
What sampling distribution will you use?
uniform chi-square normal binomial Student's t
(b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least
three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.)
What are the degrees of freedom?
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
(c) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic.
p-value > 0.100 0.050 < p-value < 0.100
0.005< p-value < 0.010 p-value < 0.005
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
0.025 < p-value < 0.050 0.010 < p-value < 0.025
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis of
independence?
Since the P-value > x, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Since the P-value > x, we reject the null
]
hypothesis. Since the P-values x, we reject the null hypothesis. Since the P-values x, we fail
to reject the null hypothesis.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
At the 1% level of significance, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that Myers-Briggs preference
and the profession are not independent. At the 1% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to
conclude that Myers-Briggs preference and the profession are not independent.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ff072a7d-17de-4b51-9c55-f2704da35c92/89e422cf-660f-4c2d-a9ad-6eafe54bf781/ye5wdqc_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:Use the chi-square test to determine if the listed occupations and personality preferences are
independent at the 0.01 level of significance.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
Hi: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
profession are independent.
H: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are independent.
profession are not independent.
H₁: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are independent.
profession are independent.
Hi: Myers-Briggs preference and profession are not independent.
Are all the expected frequencies greater than 5?
Yes No
What sampling distribution will you use?
uniform chi-square normal binomial Student's t
(b) Find the value of the chi-square statistic for the sample. (Round the expected frequencies to at least
three decimal places. Round the test statistic to three decimal places.)
What are the degrees of freedom?
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
(c) Find or estimate the P-value of the sample test statistic.
p-value > 0.100 0.050 < p-value < 0.100
0.005< p-value < 0.010 p-value < 0.005
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
Ho: Myers-Briggs preference and
0.025 < p-value < 0.050 0.010 < p-value < 0.025
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis of
independence?
Since the P-value > x, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Since the P-value > x, we reject the null
]
hypothesis. Since the P-values x, we reject the null hypothesis. Since the P-values x, we fail
to reject the null hypothesis.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
At the 1% level of significance, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that Myers-Briggs preference
and the profession are not independent. At the 1% level of significance, there is sufficient evidence to
conclude that Myers-Briggs preference and the profession are not independent.
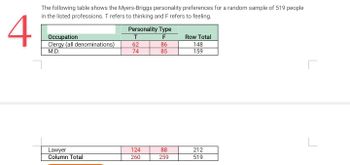
Transcribed Image Text:4
The following table shows the Myers-Briggs personality preferences for a random sample of 519 people
in the listed professions. T refers to thinking and F refers to feeling.
Occupation
Clergy (all denominations)
M.D.
Lawyer
Column Total
Personality Type
F
T
62
74
124
260
86
85
88
259
Row Total
148
159
212
519
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Determine the level of significance and State the hypotheses.
VIEW Step 2: Obtain the value of the test statistic.
VIEW Step 3: Determine whether the expected frequencies are greater than 5 or not and distrubution used
VIEW Step 4: Determine the degrees of freedom and estimate the P-value.
VIEW Step 5: Determine the decision and interpret the conclusion
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A car knocked over a stop again, but then sped off. The only information that an eyewitness remembers is that the car’s license plates contains two W’s and one D, but not necessarily in this order. How many license plates must check?arrow_forwardNeed help with #1 parts a, b, and carrow_forwardges. The results 89 take French. 92 take German. 44 take French and German. 47 take German and Russian. 19 take French as their only foreign language. 23 take French, Russian, and German.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman