
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
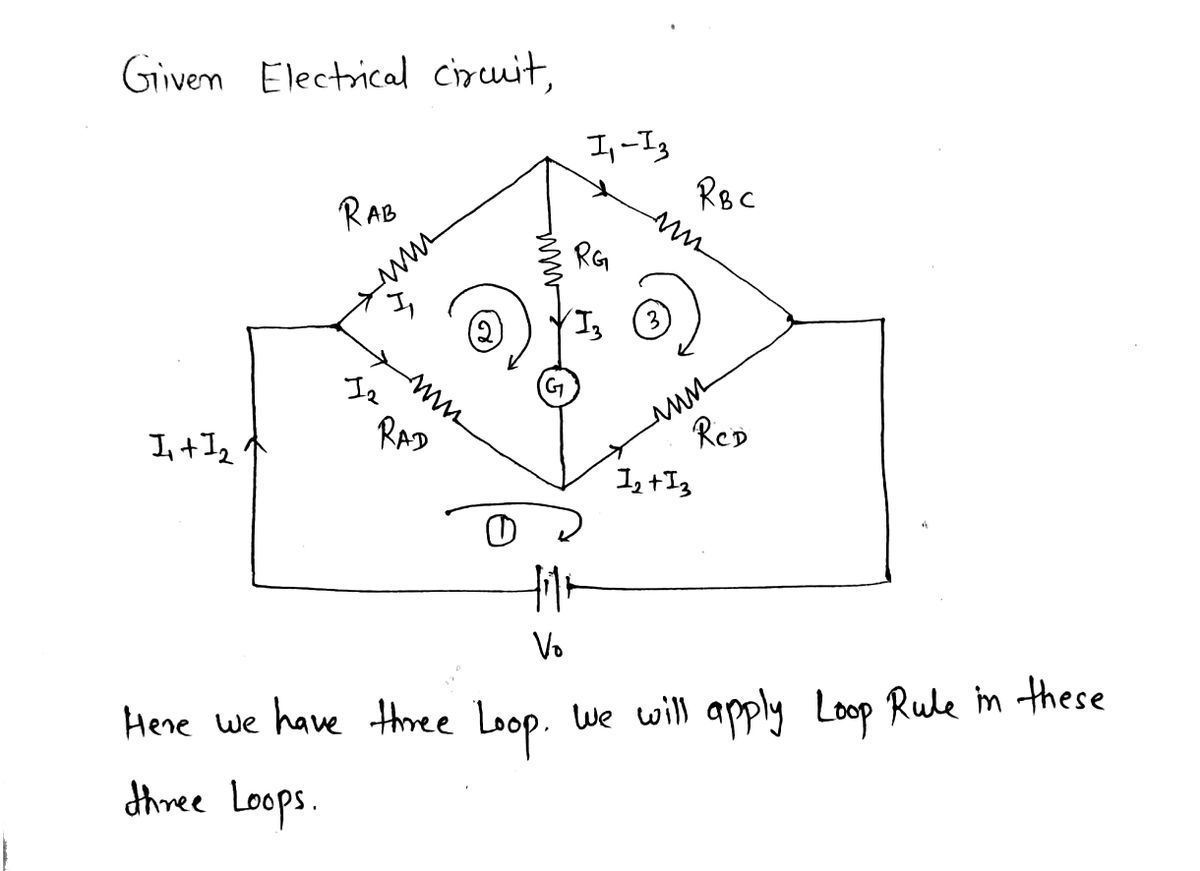
Apply the Loop Rule to ABHDA.

Transcribed Image Text:Use Kirchhoff’s junction rule and voltage/loop rule to find the current through each resistor in the following circuit: \(R_{AB} = 10 \, \Omega\), \(R_{BC} = 15 \, \Omega\), \(R_{AD} = 6 \, \Omega\), \(R_{CD} = 12 \, \Omega\), \(R_{G} = 4 \, \Omega\), and \(V_o = 10 \, \text{V}\).
![The image depicts a Wheatstone bridge circuit, which is used to measure unknown electrical resistances. It consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape and a galvanometer.
### Explanation of the Diagram:
- **Points and Resistors:**
- **A, B, C, D:** These are the junction points of the circuit.
- **\(R_{AB}\), \(R_{BC}\), \(R_{CD}\), \(R_{AD}\):** These are the resistors in the circuit.
- **\(R_G\):** The resistor on the bridge between points B and D, connected through the galvanometer \(G\).
- **Current Flow:**
- **\(I_1\):** The current flowing from point A to point B.
- **\(I_2\):** The current flowing from point A to point D.
- **\(I_3\):** The current flowing through the galvanometer \(G\) from B to D.
- Arrows indicate the direction of the current.
- **Galvanometer (G):**
- Located between points B and D, it measures the current flowing through \(R_G\).
- **Voltage Source:**
- \(V_0\) represents the potential difference across the circuit, with positive and negative terminals located at points F and K, respectively.
### Usage of Wheatstone Bridge:
The Wheatstone bridge is balanced when \(I_3 = 0\), meaning no current flows through the galvanometer. This condition allows determination of the unknown resistor value by using the known values of the other resistors and the equation:
\[ \frac{R_{AB}}{R_{BC}} = \frac{R_{AD}}{R_{CD}} \]
This principle makes Wheatstone bridges essential tools in laboratories for precise resistance measurements.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/1d93de19-418c-4f30-8c4a-2a6a3330d625/5f42508f-c7c8-4ff3-a20b-6fb4e3d7149b/gh3zad8_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a Wheatstone bridge circuit, which is used to measure unknown electrical resistances. It consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape and a galvanometer.
### Explanation of the Diagram:
- **Points and Resistors:**
- **A, B, C, D:** These are the junction points of the circuit.
- **\(R_{AB}\), \(R_{BC}\), \(R_{CD}\), \(R_{AD}\):** These are the resistors in the circuit.
- **\(R_G\):** The resistor on the bridge between points B and D, connected through the galvanometer \(G\).
- **Current Flow:**
- **\(I_1\):** The current flowing from point A to point B.
- **\(I_2\):** The current flowing from point A to point D.
- **\(I_3\):** The current flowing through the galvanometer \(G\) from B to D.
- Arrows indicate the direction of the current.
- **Galvanometer (G):**
- Located between points B and D, it measures the current flowing through \(R_G\).
- **Voltage Source:**
- \(V_0\) represents the potential difference across the circuit, with positive and negative terminals located at points F and K, respectively.
### Usage of Wheatstone Bridge:
The Wheatstone bridge is balanced when \(I_3 = 0\), meaning no current flows through the galvanometer. This condition allows determination of the unknown resistor value by using the known values of the other resistors and the equation:
\[ \frac{R_{AB}}{R_{BC}} = \frac{R_{AD}}{R_{CD}} \]
This principle makes Wheatstone bridges essential tools in laboratories for precise resistance measurements.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON