
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
USE IMAGE BELOW
Question; Draw and fully label the Freebody diagram of the BEAM in the picture below.
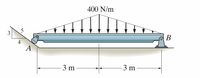
Transcribed Image Text:400 N/m
5
3
В
-3 m
3 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw (FBD) and calculate the support reactions in the simply support beam ABCD below 0.3m B 3kN 0.5m 1.2m 5kN Lo ** 60⁰ 0.4marrow_forwardsolve, show all steps and fbd. do not provide copied answer or I will report Do problem 12 -22 using double integration. Also find how much additional deflection is added (to the max) if we account for the beam self-weight. Find this additional deflection using the table in appendix C. mechanics of materials chapter 12 (integration of moment)= theta, and integration of theta = varrow_forwardThe beam is subjected to a point load and a distribution load as shown in Figure 3-1 below. (a) Find the reaction from supports B and E.(b) Draw a beam's Shear Force Diagram.(c) Draw the moment diagram of the beam.(d) If the cross-sectional area is shown in Figure 3-2, how many mm is the neural axis NA from the bottom? (e) Find the second moment of area, INA from the neural axis.(f) Find the maximum shear stress mmax from the beam.(g) Find the maximum tensile flexural stress mmax, T and maximum compressive flexural stress mmax, C on the beam, respectively.arrow_forward
- A uniform beam is fixed at end x=0 and simply supported at x = L. Find the shape of the center line of the beam, given the weight per unit Length is w. a. b. C. e. O y(x) = d. y(x) = a y(x) = y(x) = y(x) = W 24 El -[x4 - 4Lx³ +6L²x²] =[x4-2Lx³ + L²x²] -[x4-2Lx³ + L³x] -[2x4-5Lx³+3L²x²] [2x4-3L³x³ +3L²x²] W 24 El W 24 El W 24 El - W 24 EIarrow_forwardThe beam is subjected to a point load and a distribution load as shown in Figure 2-1 below.(a) Draw a Shear Force Diagram in the beam ABC interval.(b) Draw a Moment Diagram in the beam ABC interval.(c) If the cross-sectional area is shown in Figure 2-2, how many mm is the neural axis NA from the bottom?(d) Find the second moment of area, INA from the natural axis.(e) Find the maximum shear stress JJ on the stem side at the connection between flange and stem in the beam ABC interval. (f) Find the maximum shear stress mmax in the beam ABC interval.(g) Find the maximum tensile flexural stress mmax, T and maximum compressive flexural stress mmax, C in the beam ABC interval, respectively.arrow_forwardFor the composite beam section in Figure Q2b, calculate the second moment of area (Ixx) about its centroid x-axis.arrow_forward
- Pin-joint construction supports point loads as shown below: P Al ΕΙ C B 2/3 L 1/3 L a) Find the equation for the deflection of the bar at point B! b) Determine the equation for the moment that occurs at point A!arrow_forwardFor the structural beam loaded and supported as shown in Figure 2, (a) Draw a free body diagram and find the support reaction forces/moments.arrow_forward1. In figure (1), shows a uniform beam subjected to a linear increasing distributed load. The equation for the resulting elastic curve is: w y = 120EIL (-x5+2L?x3 - L*x) Using the numerical methods to determine the point of max. deflection (that is, the value of x where "Y 0. Then substitute dx this value in the given equation to find the value of maximum deflection. Using the following parameter values in your computations: L = 600cm; E50000 k N/cm2;1=30000cm* and w =2.5k N/cm. (a) r Ly 0) =0, v- 0) (b) Figure (1)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY