
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
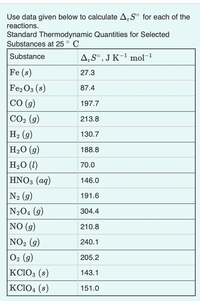
Transcribed Image Text:Use data given below to calculate A,S° for each of the
reactions.
Standard Thermodynamic Quantities for Selected
Substances at 25 ° C
Substance
A‚S°,J K-1 mol-1
Fe (s)
27.3
Fe2 O3 (s)
CO (g)
87.4
197.7
CO2 (g)
213.8
На (9)
130.7
H2O (g)
H2O (1)
188.8
70.0
HNO3 (aq)
146.0
N2 (g)
191.6
N204 (9)
304.4
NO (g)
210.8
NO2 (g)
240.1
O2 (g)
KC103 (s)
KC104 (8)
205.2
143.1
151.0

Transcribed Image Text:KC1O; (s) + 02 (9) → KC1O4 (8)
Express your answer using one decimal place.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction CS2 (9) + 4H2 (9) = CH4 (9) + 2H2S(g) a. Calculate AH°, AS“ , and AG° at 25°C for this reaction. AĦ¡ (kJ/mol) S° (J/mol-K) CS2 (9) H2 (9) CH4 (9) H2S(9) 116.9 237.9 130.6 -74.87 186.1 -20.50 205.6 ΔΗ : kJ %3! AS J/K AG° kJ b. Assume AH° and AS° are constant with respect to a change of temperature. Now calculate AG° at 250°C. AG = kJ c. Compare the two values of AG". What can you say about the spontaneity of the reaction at 25°C and at 250°C? The reaction will be spontaneous at 25°C, and it will be nonspontaneous at 250°C. The reaction will be nonspontaneous at 25°C, and it will be spontaneous at 250°C. The reaction will be spontaneous at both 25°C and 250°C. The reaction will be nonspontaneous at both 25°C and 250°C.arrow_forwardSolve the following problems. Write your solution and box your final answer.arrow_forwardThe below reaction was found to have AH :-491 kJ mol-1 and AS = -543 J mol-1 K-1. What is AG for this reaction at 117.9 °C? 2Fe(s) + 3CO(g) → Fe2O3(s) + 3C(s) a. -427 kJ mol-1 b. -703 kJ mol-1 c. 211849 kJ mol-1 d. 52 kJ mol-1 e. -279 kJ mol-1arrow_forward
- A student determines the value of the equilibrium constant to be 6.04x10-37 for the following reaction. 2N2(g) + O2(g) 2N20(g) ht Based on this value of Keg: than zero. AG° for this reaction is expected to be (greater, less) Calculate the free energy change for the reaction of 2.09 moles of N2(g) at standard conditions at 298K. AG°rxn kJarrow_forwardNeed help solving this equation, please explain all the steps.arrow_forwardcalculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of each gas is 15.93 mm Hg.arrow_forward
- Use the data given here to calculate the values of AGn at 25 °C for the Compound AG; (kJ/mol) reaction described by the equation A +387.7 A + B 2C B - 596.8 C +402.0 543.1 AGixn kJ Incorrect If AHxn and ASxn are both negative values, what drives the spontaneous reaction and in what direction at standard conditions? The spontaneous reaction is enthalpy-driven to the left. entropy-driven to the right. entropy-driven to the left. O enthalpy-driven to the right. Incorrect O O O Oarrow_forward[Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A student determines the value of the equilibrium constant to be 1.21x1012 for the following reaction. CO(g) + Cl2(g)- COC12(g) Based on this value of Keg AG° for this reaction is expected to be (greater,less) than zero. Calculate the free energy change for the reaction of 1.65 moles of CO(g) at standard conditions at 298K. AG rxn kJarrow_forwardTrue or false? Why?arrow_forward
- Use standard thermodynamic data (in the Chemistry References) to calculate AG at 298.15 K for the following reaction, assuming that all gases have a pressure of 19.35 mm Hg. 2NO(g) + 02(g)→2NO2(g) AG = kJ/molarrow_forwardTrue or false and how?arrow_forwardConsider the reaction 12(g) + Cl₂(g) 2ICI(g) Use the standard thermodynamic data in the tables linked above. Calculate AG for this reaction at 298.15K if the pressure of ICI(g) is reduced to 16.66 mm Hg, while the pressures of l2(g) and Cl₂(g) remain at 1 atm. kJ/mol ANSWER: (Please type answer).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY