
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
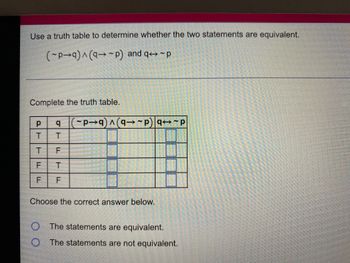
Transcribed Image Text:### Logical Equivalence and Truth Tables
**Instruction:**
Use a truth table to determine whether the two statements are equivalent: \((\neg p \rightarrow q) \land (q \rightarrow \neg p)\) and \(q \leftrightarrow \neg p\).
**Truth Table:**
| \(p\) | \(q\) | \(\neg p\) | \(\neg p \rightarrow q\) | \(q \rightarrow \neg p\) | \((\neg p \rightarrow q) \land (q \rightarrow \neg p)\) | \(q \leftrightarrow \neg p\) |
|:----:|:----:|:---------:|:-----------------------:|:-----------------------:|:-----------------------------------------------------:|:-------------------------:|
| T | T | F | T | F | F | F |
| T | F | F | T | T | T | T |
| F | T | T | T | T | T | T |
| F | F | T | F | T | F | F |
### Analysis:
- **Column \( \neg p \)**: Represents the negation of \( p \).
- **Columns \( \neg p \rightarrow q \) and \( q \rightarrow \neg p \)**: Represents conditional statements.
- **Column \((\neg p \rightarrow q) \land (q \rightarrow \neg p)\)**: Represents the conjunction of the two conditional statements.
- **Column \( q \leftrightarrow \neg p \)**: Represents the biconditional statement.
### Conclusion:
The truth values in columns \((\neg p \rightarrow q) \land (q \rightarrow \neg p)\) and \( q \leftrightarrow \neg p \) are identical for all possible truth values of \( p \) and \( q \). Hence, the statements are equivalent.
**Choose the correct answer below:**
- \( \textcircled{O} \) The statements are equivalent.
- \( \) The statements are not equivalent.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

