
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Use a table of Standard Reduction Potentials to predict if a reaction will occur between Fe metal and F2(g), when the two are brought in contact via standard half-cells in a voltaic cell. If a reaction will occur, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction, assuming that the product ions are in aqueous solution. If no reaction will occur, leave all boxes blank.
Fill 4 blanks ____
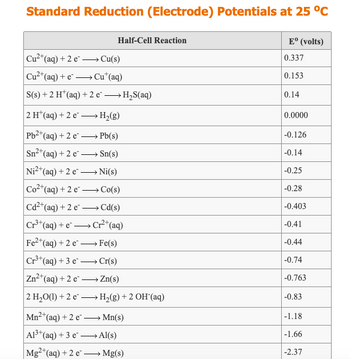
Transcribed Image Text:Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25 °C
Cu2+(a
*(aq) + 2 e →→→→Cu(s)
Cu²+ (aq) + e →→→→Cu* (aq)
S(s) + 2 H+ (aq) + 2 e² →→→→ H₂S(aq)
2 H(aq) + 2 e →→→ H₂(g)
(aq) + 2 e Pb(s)
→
Sn²+ (aq) + 2 e→→→→→→Sn(s)
Ni2+ (aq) + 2 e² →→→→→→Ni(s)
Co2+ (aq) + 2 e. Co(s)
→
Cd2+ (aq) + 2 e-
Cd(s)
Cr³+ (aq) + e-
Cr²+ (aq)
e2+ (aq) + 2 e
Fe(s)
Cr³+ (aq) + 3 e →→→ Cr(s)
Zn²+ (aq) + 2 e- Zn(s)
→
2 H₂O(l) +2e →→→→ H₂(g) + 2 OH(aq)
Pb2+(
Fe2+
Half-Cell Reaction
→
Mn²+ (aq) +2 e- →→→→Mn(s)
A1³+ (aq) + 3 e²Al(s)
Mg2+ (aq) + 2 e→→→→→→ Mg(s)
Eº (volts)
0.337
0.153
0.14
0.0000
-0.126
-0.14
-0.25
-0.28
-0.403
-0.41
-0.44
-0.74
-0.763
-0.83
-1.18
-1.66
-2.37
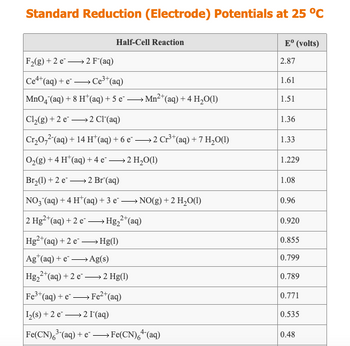
Transcribed Image Text:Standard Reduction (Electrode) Potentials at 25 °C
Half-Cell Reaction
F₂(g) +2 e 2 F"(aq)
Ce4+ (aq) + eCe³+ (aq)
MnO4 (aq) + 8 H(aq) + 5 e- —Mn2+(aq)+4 H,O(1)
Cl₂(g) +2 e
2 Cl(aq)
Cr₂O2(aq) + 14 H(aq) + 6 e² →→→ 2 Cr³+ (aq) + 7 H₂O(1)
O₂(g) + 4 H*(aq) + 4e → 2 H₂O(1)
Br₂(1) +2 e2 Br(aq)
NO3(aq) + 4 H¹ (aq) + 3 e¯ →→→ NO(g) + 2 H₂O(1)
2 Hg2+ (aq) + 2 e →→→→→Hg₂²+ (aq)
Hg2+ (aq) + 2 e →→→→Hg(1)
Ag (aq) + e- →→→→→Ag(s)
Hg₂
₂2+ (aq) + 2 e-
→ 2 Hg(1)
Fe³+ (aq) + e Fe²+ (aq)
→
1₂(s) +2 e 2 I¯ (aq)
→
Fe(CN)6³(aq) + e→→→→→→Fe(CN)6+ (aq)
Eº (volts)
2.87
1.61
1.51
1.36
1.33
1.229
1.08
0.96
0.920
0.855
0.799
0.789
0.771
0.535
0.48
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 27.Use the standard half-cell potentials listed below to calculate the standard cell potential for the following reaction (as written) occurring in an electrochemical cell at 25°C. (The equation is balanced.) Pb(s) + Br2(l) → Pb2+(aq) + 2Br⁻(aq) Pb2+(aq) + 2 e⁻ → Pb(s) E° = -0.13 V Br2(l) + 2 e⁻ → 2Br⁻(aq) E° = +1.07 V Group of answer choices +1.20 V +0.94 V -0.94 V -1.20 V -0.60 Varrow_forwardConsider the pictured voltaic cell. ZnSO4 is dissolved in the left solution and CuSO4 is dissolved in the right solution. The salt bridge is comprised of KNO3. Match each cell compound or component with its correct identity or function. Anode Cathode The salt bridge ion that travels into the anode solution The salt bridge ion that travels into the cathode solution The correct cell notation The correct overall redox reaction equation [answer choices] It is not possible to write the correct chemical equation from the information given Cu|Cu2+||Zn2+|Zn Cu + Zn2+ --> Zn + Cu2+ where Cu is oxidized to Cu2+ nitrate (NO3 -) K+ where Cu2+ is reduced to Cu Zn|Cu||Zn2+|Cu2+ Cu2+|Zn2+||Cu|Zn Zn|Zn2+||Cu2+|Cu Zn2+ Zn + Cu --> Cu2+ + Zn2+ Cu2+ Zn + Cu2+ --> Cu + Zn2+ where Zn is…arrow_forwardRegarding the following reaction: F2 (g) + 2 I^- (aq) → 2 F^- (aq) + I2 (s) a. List the species being oxidizedb. List the species being reducedc. Calculate Eo for this cell. d. Which species receives electrons from the anode? e. Which species donates electrons to the cathode?arrow_forward
- 5. A voltaic cell is constructed using the reaction of chromium metal and iron (II) ions. 2 Cr(s) + 3 Fe*(aq) → 2 Cr*(aq) + 3 Fe(s) Complete the following sentences: Electrons in the external circuit flow from the . .electrode to the Negative ions move in the salt bridge from the. .electrode. half-cell to the half-cell. The half-reaction at the anode is , ..and that at the cathode isarrow_forwardChemistry Write the reduction half-reaction for the corrosion of iron. Express your answer as a half-reaction including phases. ΑΣφ ? O A chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Maka a sketch of an electrolysis cell that could be used to electroplate nickel onto other metal surtaces. Label the anode and the cathode and show the reactions that occur at each. Drag the labels to the appropriate targets Reset Help power supply Cathode Anode Part B Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases your answer. ΑΣφ anode reaction: OA chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Submit Request Answer Part C Express your answer as a chemical equation. Identify all of the phases in your answer. cathode reaction: OA chemical reaction does not occur for this question. Submit Denunet Anenarrow_forwardUse the standard reduction potentials given below to predict if a reaction will occur between Hg(s) and Br₂ (1), when the two are brought in contact via standard half-cells in a voltaic cell. red Br₂ (1) + 2e¯¯ → 2Br¯(aq) Eº Hg²+ (aq) + 2e¯¯ → Hg(1) E red = 1.080 V 0.855 V - If a reaction will occur, write a balanced net ionic equation for the reaction, assuming that the product ions are in aqueous solution. If no reaction will occur, leave all boxes blank. + (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s). If a box is not needed, leave it blank.) +arrow_forward
- 2.Write half-reaction for the cell's anode. Include the phases of all species in the chemical equation.arrow_forwardIn a galvanic cell, a zinc electrode in a zinc(II) sulfate solution is one half-cell, and a copper electrode in a copper(1I) sulfate solution is the other. The two half-cells must be connected by a _to complete the circuit. beaker battery O salt bridge O fusearrow_forward2. The net equation for a given voltaic cell is: Sn (s) + 2 Agt → Sn²+ + 2 Ag (s) a. b. Write the two half-reactions involved, and identify each in terms of (1) site of oxidation or reduction and (2) anode or cathode. Calculate the net potential of the cell (the voltage), assuming standard conditions. c. Draw a fully labeled diagram of the galvanic cell. Be sure to indicate the flow of electrons in the external circuit (through the wire) and the flow of ions in the solution.arrow_forward
- Please Help me answer this, thank u rarrow_forwardO ELECTROCHEMISTRY Designing a galvanic cell from a single-displacement redox reac... Suppose the galvanic cell sketched below is powered by the following reaction: Mn(s)+ZnSO,(aq) → MNSO,(aq)+Zn(s) 4 E1 E2 S1 S2 Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the cathode of this cell. ロ→ロ Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the anode of this cell. Of what substance is E1 made? Of what substance is E2 made? What are the chemical species in solution S1? What are the chemical species in solution S2?arrow_forwardA chemist designs.a galvanic cell that uses these two half-reactions: O₂(g)+4H(aq)+4e Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the cathode. 3+ 2+ Fe (aq)+e → Fe (aq) Write a balanced equation for the half-reaction that happens at the anode, half-reaction Answer the following questions about this cell. Write a balanced equation for the overall reaction that powers the cell. Be sure the reaction is', spontaneous as written. Do you have enough information to calculate the cell voltage under standard conditions? If you said it was possible to calculate the cell voltage, do so and enter your answer here. Round your answer to 2. significant digits. 0 Yes 1 O No 2 H₂O(1) Ov standard reduction potential -0 E red = +1.23 V Ered=+0.771 V 0-0 P₁ X A10 5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY