Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
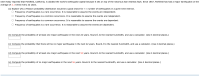
Transcribed Image Text:USA Today reported that Parkfield, California, is dubbed the world's earthquake capital because it sits on top of the notorious San Andreas fault. Since 1857, Parkfield has had a major earthquake on the
average of 2.1 times every 22 years.
(a) Explain why a Poisson probability distribution would be a good choice for r =
number of earthquakes in a given time interval.
Frequency of earthquakes is a rare occurrence. It is reasonable to assume the events are independent.
Frequency of earthquakes is a common occurrence. It is reasonable to assume the events are independent.
Frequency of earthquakes is a common occurrence. It is reasonable to assume the events are dependent.
O Frequency of earthquakes is a rare occurrence. It is reasonable to assume the events are dependent.
(b) Compute the probability of at least one major earthquake in the next 22 years. Round A to the nearest hundredth, and use a calculator. (Use 4 decimal places.)
(c) Compute the probability that there will be no major earthquake in the next 22 years. Round A to the nearest hundredth, and use a calculator. (Use 4 decimal places.)
(d) Compute the probability of at least one major earthquake in the next 56 years. Round A to the nearest hundredth, and use a calculator. (Use 4 decimal places.)
(e) Compute the probability of no major earthquakes in the next 56 years. Round A to the nearest hundredth, and use a calculator. (Use 4 decimal places.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.