
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
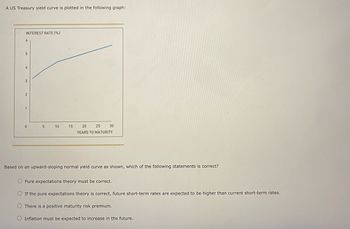
Transcribed Image Text:A US Treasury yield curve is plotted in the following graph:
**Graph Description:**
- The graph displays the relationship between interest rates and years to maturity for US Treasury bonds.
- The x-axis is labeled "YEARS TO MATURITY" and ranges from 0 to 30 years.
- The y-axis is labeled "INTEREST RATE (%)" and ranges from 0% to 6%.
- The curve depicted is upward-sloping, starting around 2% and approaching 6% as maturity increases to 30 years.
**Question:**
Based on an upward-sloping normal yield curve as shown, which of the following statements is correct?
1. Pure expectations theory must be correct.
2. If the pure expectations theory is correct, future short-term rates are expected to be higher than current short-term rates.
3. There is a positive maturity risk premium.
4. Inflation must be expected to increase in the future.
![**Factors Affecting the Treasury Yield Curve**
There are three factors that can affect the shape of the Treasury yield curve: the real risk-free rate (\(r^*\)), the expected inflation rate (\(IP_t\)), and the maturity risk premium (\(MRP_t\)). Additionally, five factors can influence the shape of the corporate yield curve: \(r^*_t\), \(IP_t\), \(MRP_t\), the default risk premium (\(DRP_t\)), and the liquidity premium (\(LP_t\)). The yield curve reflects the aggregation of impacts from these factors.
**Current Conditions and Yield Curve Shapes**
Suppose the real risk-free rate and inflation rate are expected to remain at their current levels throughout the foreseeable future. Consider all factors that affect the yield curve. Then identify which of the following shapes the US Treasury yield curve can take.
Check all that apply:
- [ ] Inverted yield curve
- [ ] Downward-sloping yield curve
- [ ] Upward-sloping yield curve
**Evaluate the Truthfulness of the Following Statements**
Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false.
1. If inflation is expected to decrease in the future and the real rate is expected to remain steady, then the Treasury yield curve is downward sloping. (Assume MRP = 0.)
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
2. All else equal, the yield on new bonds issued by a leveraged firm will be less than the yield on the new bonds issued by an unleveraged firm.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
3. The yield curve for a BBB-rated corporate bond is expected to be above the US Treasury bond yield curve.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
4. Yield curves of highly liquid assets will be lower than yield curves of relatively illiquid assets.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/37e2f913-30b2-4c8c-98d5-339163057ff1/a72d6d4b-b950-425c-a71e-2575a3709cb6/6u0xdod_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:**Factors Affecting the Treasury Yield Curve**
There are three factors that can affect the shape of the Treasury yield curve: the real risk-free rate (\(r^*\)), the expected inflation rate (\(IP_t\)), and the maturity risk premium (\(MRP_t\)). Additionally, five factors can influence the shape of the corporate yield curve: \(r^*_t\), \(IP_t\), \(MRP_t\), the default risk premium (\(DRP_t\)), and the liquidity premium (\(LP_t\)). The yield curve reflects the aggregation of impacts from these factors.
**Current Conditions and Yield Curve Shapes**
Suppose the real risk-free rate and inflation rate are expected to remain at their current levels throughout the foreseeable future. Consider all factors that affect the yield curve. Then identify which of the following shapes the US Treasury yield curve can take.
Check all that apply:
- [ ] Inverted yield curve
- [ ] Downward-sloping yield curve
- [ ] Upward-sloping yield curve
**Evaluate the Truthfulness of the Following Statements**
Identify whether each of the following statements is true or false.
1. If inflation is expected to decrease in the future and the real rate is expected to remain steady, then the Treasury yield curve is downward sloping. (Assume MRP = 0.)
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
2. All else equal, the yield on new bonds issued by a leveraged firm will be less than the yield on the new bonds issued by an unleveraged firm.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
3. The yield curve for a BBB-rated corporate bond is expected to be above the US Treasury bond yield curve.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
4. Yield curves of highly liquid assets will be lower than yield curves of relatively illiquid assets.
- [ ] True
- [ ] False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use the table of data to answer the following question: Table 17.3 Nominal interest rate 7% Inflation rate 1.5% Risk premium 1% Suppose you have the option to purchase for $955 a two-year old bond with a $1,000 face value and one year left that has a coupon rate of 8-percent, or, purchase a new one-year bond for $1,000. What should you do? O a. Purchase used bond because the real interest rate is higher than the new bond's real interest rate. O b. Purchase new bond because the real interest rate is higher than the used bond's real interest rate. OC There is not enough information to determine the best investment option. O d. Purchase either bond because the real interest rate is the same for both options.arrow_forward12. Inflation-induced tax distortions Loc receives a portion of his income from his holdings of interest-bearing U.S. government bonds. The bonds offer a real interest rate of 4.5% per year. The nominal interest rate on the bonds adjusts automatically to account for the inflation rate. The government taxes nominal interest income at a rate of 10%. The following table shows two scenarios: a low-inflation scenario and a high- inflation scenario. Given the real interest rate of 4.5% per year, find the nominal interest rate on Loc's bonds, the after-tax nominal interest rate, and the after-tax real interest rate under each inflation scenario. Inflation Rate Real Interest Rate Nominal Interest Rate After-Tax Nominal Interest Rate After-Tax Real Interest Rate (Percent) (Percent) (Percent) (Percent) (Percent) 3.5 4.5 8.5 4.5 Compared with lower inflation rates, a higher inflation rate will nominal interest income. This tends to the economy's long-run growth rate. saving, thereby the after-tax…arrow_forward2. The inflation-unemployment relationship The following graph shows the combinations of unemployment and inflation that existed in the United States for selected years between 1961 and 1969. Click on any blue point (circle symbol) on the graph to get its exact coordinates. You can also use the black point (cross symbol) to find the coordinates of other points along the curve. (Note: You will not be graded for any adjustments made to the graph.) INFLATION RATE (Percent) 1969 5.2 4.5 1988 85 1967 20 1.5 10 0.5 1960 1984 1963 1981 0 2.0 3.5 40 4.5 5.0 5.5 GO 4.5 7.0 UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)arrow_forward
- For this question, assume that the expected rate of inflation is a function of past year's inflation. Also assume that the unemployment rate has been greater than the natural rate of unemployment for a number of years. Given this information, we know that the inflation rate will be approximately equal to the natural rate of unemployment. А. the rate of inflation will approximately be equal to zero. В. C. the rate of inflation should steadily decrease. Op the rate of inflation should steadily increase over time. the rate of inflation should neither increase nor decrease. Е.arrow_forwardestion 5 2 Which statement is CORRECT? By keeping actual output approximately equal to potential output, a nation's macro-policy makers risk producing employment problems. By keeping actual output approximately equal to potential output, a nation's macro-policy makers risk producing inflation problems. By keeping actual output above potential output, a nation's macro-policy makers can achieve the goal of high output. By keeping actual output approximately equal to potential output, a nation's macro-policy makers can achieve the goal of high output. O By keeping actual growth rate of output at its maximum pace, a nation's macro-policy makers can achieve the goal of high output. A Moving to the next question prevents changes to this answer. 4 % 5 JUL 20 tv 6 MacBook Pro & 7 *00 8 Nc 9arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education