
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337406659
Author: WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:University of Florida football programs are printed 1 week prior to each home game. Attendance averages 60,000 screaming and loyal Gators fans, of
whom two-thirds usually buy the program, following a normal distribution, for $5 each. Unsold programs are sent to a recycling center that pays only 10
cents per program. The standard deviation is 5,000 programs, and the cost to print each program is $2. Refer to the standard normal table for z-values.
a) What is the cost of underestimating demand for each program?
Cs = $
(round your response to two decimal places).
b) What is the overage cost per program?
Co = $
c) How many programs should be ordered per game?
programs should be ordered per game (round your response to the nearest whole number).
d) What is the stockout risk for this order size?
(round your response to two decimal places).
Stockout risk =
(round your response to four decimal places).
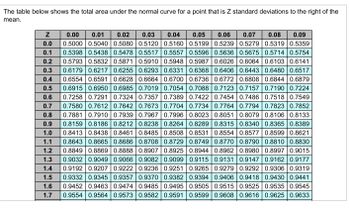
Transcribed Image Text:The table below shows the total area under the normal curve for a point that is Z standard deviations to the right of the
mean.
Z
0.0
0.1
0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09
0.5000 0.5040 0.5080 0.5120 0.5160 0.5199 0.5239 0.5279 0.5319 0.5359
0.5398 0.5438 | 0.5478 0.5517 0.5557 0.5596 0.5636 | 0.5675 0.5714 0.5754
0.5793 0.5832 0.5871 0.5910 0.5948 0.5987 0.6026 0.6064 0.6103 0.6141
0.6179 0.6217 0.6255 0.6293 0.6331 0.6368 0.6406 | 0.6443
0.6554 0.6591 0.6628 0.6664
0.2
0.3
0.6480 | 0.6517
0.4
0.6844 0.6879
0.5
0.7190 0.7224
0.7518 0.7549
0.9
1.0
0.6700 | 0.6736 0.6772 | 0.6808
0.6915 0.6950 0.6985 0.7019 0.7054 0.7088 | 0.7123 | 0.7157
0.6
0.7258 0.7291 0.7324 0.7357 0.7389 0.7422 0.7454 0.7486
0.7 0.7580 0.7612 | 0.7642 | 0.7673 | 0.7704 | 0.7734 | 0.7764 | 0.7794 0.7823 0.7852
0.8 0.7881 0.7910 | 0.7939 0.7967 0.7996 0.8023 0.8051 | 0.8079 0.8106 0.8133
0.8159 0.8186 0.8212 0.8238 0.8264 | 0.8289 0.8315 | 0.8340 | 0.8365 0.8389
0.8413 0.8438 | 0.8461 0.8485 0.8508 0.8531 0.8554 0.8577 | 0.8599 0.8621
0.8643 0.8665 | 0.8686 | 0.8708 | 0.8729 0.8749 0.8770 | 0.8790 | 0.8810 | 0.8830
0.8849 0.8869 0.8888 | 0.8907 | 0.8925 | 0.8944 0.8962 | 0.8980 | 0.8997 0.9015
0.9032 0.9049 0.9066 0.9082 0.9099 0.9115 0.9131 0.9147 0.9162 0.9177
0.9192 0.9207 0.9222 0.9236 0.9251 0.9265 0.9279 0.9292 0.9306 0.9319
1.5 0.9332 0.9345 0.9357 0.9370 0.9382 0.9394 0.9406 0.9418 0.9430 0.9441
1.6 0.9452 0.9463 0.9474 0.9485 0.9495 0.9505 0.9515 0.9525 0.9535 0.9545
1.7 0.9554 0.9564 0.9573 | 0.9582 | 0.9591 0.9599 0.9608 0.9616 0.9625 0.9633
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Dalia, the office manager of a desktop publishing outfit, stocks replacement toner cartridges for laser printers. Demand for cartridges is approximately 30 per year and is quite variable (Le., can be represented using the Poisson distribution). Cartridges cost $100 each and require three weeks to obtain from the vendor. Dalia uses a (Q, r) approach to control stock levels (a). If Dalia wants to restrict replenishment orders to twice per year on average, what batch size Q should she use? If she wants to ensure a service level (i.e., probability of having the cartridge in stock when 2 out of 2 needed) of at least 98 percent, what reorder point r should she use? (Hint: Use Table 2.6.(b). If Dalia is willing to increase the number of replenishment orders per year to six, how do Q and r change? Explain the difference in r.arrow_forwardA small grocery store sells fresh produce, which it obtains from a local farmer. During the strawberry season, demand for fresh strawberries can be reasonably approximated using a normal distribution with a mean of 36 quarts per day and a standard deviation of 7 quarts per day. Excess costs run .40 cents per quart. The grocer orders 42 quarts per day.Use Table. What is the implied cost of shortage per quart?arrow_forwardCaring Hospital's dispensary reorders doses of a drug when the supply on hand falls to 18 units. Lead time for resupply is three days. Given the typical usage over the last 10 days, what service level is achieved with the hospital's reorder policy? (Hint. Use the following formula.) (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your "z" value and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Use Table. ROP =dLT +2 (od) √LT Day Units 1 3 2 3 4 4 7 5 Service level Click here for the Excel Data File 5 5 % 6 6 7 4 8 3 9 4 10 5arrow_forward
- All EXCEPT which of the following statements about ABC analysis are TRUE? O In ABC analysis, inventory may be categorized by measures other than dollar volume. O ABC analysis suggests that all items require the same high degree of control. O ABC analysis categorizes on-hand inventory into three groups based on annual dollar volume. O ABC analysis is an application of the Pareto principle.arrow_forwardPlease answer for carrow_forwardSouthern Markets, Inc. is considering the use of ABCanalysis to focus on the most critical SKUs in its inventory.Currently, there are approximately 20,000 different SKUswith a total dollar usage of $10,000,000 per year.a. What would you expect to be the number of SKUs and thetotal annual dollar usage for A items, B items, and C itemsat Southern Markets, Inc.? b. The following table provides a random sample of the unitvalues and annual demands of eight SKUs. Categorizethese SKUs as A, B, and C items.arrow_forward
- 13 Pam’s demand for hats is normally distributed with mean 500 and standard deviation 100. She sells her hats for $50 each and buys hats for $10 each, and anything she can't sell by the end of the year, the wholesaler will buy for $5 each. How many hats should she order for next year to maximize profit?arrow_forwardBarbara Flynn is in charge of maintaining hospital supplies at General Hospital. During the past year, the mean lead time demand for bandage BX-5 was 70 (and was normally distributed). Furthermore, the standard deviation for BX-5 was 7. Ms. Flynn would like to maintain a 90% service level. Refer to the standard normal table for z-values. a) What safety stock level do you recommend for BX-5? Safety stock = units (round your response to the nearest whole number).arrow_forwardIn a Q system, the demand rate for strawberry ice cream is normally distributed, with an average of 295 pints per week. The lead time is 6 weeks. The standard deviation of weekly demand is 16 pints. Refer to the standard normal table for z-values. a. The standard deviation of demand during the 6-week lead time is 39 pints. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.) b. The average demand during the 6-week lead time is 1770 pints. (Enter your response as an integer.) c. The reorder point that results in a cycle-service level of 96 percent is pints. (Enter your response rounded to the nearest whole number.)arrow_forward
- X1=210 X2=3 I need a clear step by step answer please :)arrow_forwardBased on the information, which of the following themes are related to: PRODUCT ☐ ORDER PRODUCT-ORDERED NONE OF THE ABOVE ☐ CUSTOMERarrow_forwardIn an ABC system based on revenue, C items individually make the lowest annual revenue contribution. TRUE FALSEarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781259667473Author:William J StevensonPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781259666100Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B ChasePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.
Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...Operations ManagementISBN:9781478623069Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon OlsenPublisher:Waveland Press, Inc.

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:Cengage,

Operations Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259667473
Author:William J Stevenson
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Operations and Supply Chain Management (Mcgraw-hi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781259666100
Author:F. Robert Jacobs, Richard B Chase
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Purchasing and Supply Chain Management
Operations Management
ISBN:9781285869681
Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. Patterson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Production and Operations Analysis, Seventh Editi...
Operations Management
ISBN:9781478623069
Author:Steven Nahmias, Tava Lennon Olsen
Publisher:Waveland Press, Inc.