
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
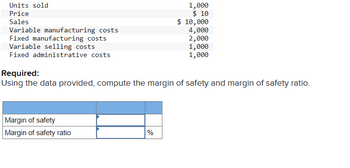
Transcribed Image Text:Units sold
Price
Sales
Variable manufacturing costs
Fixed manufacturing costs
Variable selling costs
Fixed administrative costs
Margin of safety
Margin of safety ratio
1,000
$ 10
$ 10,000
4,000
Required:
Using the data provided, compute the margin of safety and margin of safety ratio.
%
2,000
1,000
1,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following information: Costs Activity (hours) $ 51,000 40,000 $ 50,000 41,000 $ 58,000 42,000 $ 56,000 43,000 What cost and activity would be used as the high data point in high-low cost estimation? Multiple Choice None of these. $58,000 and 42,000 hours $58,000 and 43,000 hours $56,000 and 43,000 hours $56,000 and 42,000 hoursarrow_forwardCost Volume Profit (CVP) Relationships (Algo) You are provided with the following data. Unit sales Selling price per unit Variable expenses per unit Fixed expenses Target Profit 80,000 units $70 per unit $ 28 per unit $ 2,688,000 $ 1,610,000 Required: Compute the CM ratio and variable expense ratio. Compute the break-even. Compute the target profit. Compute the margin of safety with the original data. Compute the degree of operating leverage with the original data. Use the Degree of Operating Leverage to determine the new Net Operating Income if sales increase by: 16% 1. Use the Open Excel in New Tab button to launch this question. 2. When finished in Excel, use the Save and Return to Assignment button in the lower right to return to Connect.arrow_forwardSales revenue Less Variable costs Materials Direct labor Variable overhead Variable marketing and administrative Total variable costs Contribution margin Less Fixed costs Manufacturing overhead Marketing Administrative Total fixed costs Operating profits Required: Prepare a profit variance analysis for Fournier Fixtures actual orders for 414,400 units) $ 7,873,600 for 370,000 units) $ 7,400,000 2,646,400 238,000 1,218,400 876,000 $ 4,978,800 $ 2,894,800 1,632,000 556,600 372,000 $ 2,560,600 $ 334,200 2,350,000 218,000 1,082,000 786,000 $ 4,436,000 $ 2,964,000 1,660,000 540,000 405,000 $ 2,605,000 $ 359,000 Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, or "U" for unfavorable. If there is no effect, do not select either option. Sales revenue Variable costs: Materials Direct labor Variable overhead Variable marketing and administrative Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs: Manufacturing overhead Marketing…arrow_forward
- Determine the missing amounts. 1. 2. 3. $ Unit Selling Price $800 $350 (e) $ $ Unit Variable Costs $336 (c) (f) $ Unit Contribution Margin $147 $800 (a) Contribution Margin Ratio % (b) % (d) 40 %arrow_forwardHigh-low method Evander Inc. has decided to use the high-low method to estimate the total cost and the fixed and variable cost components of the total cost. The data for various levels of production are as follows: Units Produced 1,430 2,530 3,630 Total Costs $190,080 262,310 295,680 a. Determine the variable cost per unit and the total fixed cost. Variable cost $ Total fixed cost $ b. Based on part (a), estimate the total cost for 1,820 units of production. Total cost for 1,820 units $arrow_forwardPlease do not give solution in image format thankuarrow_forward
- h1arrow_forwardHigh-low method Evander Inc. has decided to use the high-low method to estimate the total cost and the fixed and variable cost components of the total cost. T Units Produced Total Costs 1,350 2,570 4,350 $183,600 225,220 285,600 a. Determine the variable cost per unit and the total fixed cost. Variable cost $ Total fixed cost $ b. Based on part (a), estimate the total cost for 2,050 units of production. Total cost for 2,050 units $arrow_forward27-By considering the following given information, find out the margin of safety. Fixed cost OMR 150000, Variable cost OMR 200,000 and total sales revenue OMR 400,000. O a. OMR 100000 O b. OMR 200000 O c. OMR 400000 O d. OMR 600000arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education