
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
For the potential energy curve shown as shown, (a) determine whether the force Fx is positive, negative, or zero at the five points indicated. (b) Indicate points of stable, unstable, and neutral equilibrium. (c) Sketch the curve for Fx versus x from x = 0 to x = 9.5 m.
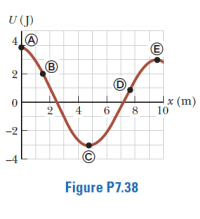
Transcribed Image Text:U (J)
B
x (m)
10
2
4
6
8
-2
-4
Figure P7.38
E,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A woman places a 2 kg block against a horizontal spring of force constant K = 300 N/m and compresses it 9 cm. a) Find the work done by the woman and the work done by the spring.b) The block is released and leaves the spring when the spring is at its original position. Find the speed of the block when it leaves the spring.arrow_forwardAs a segment of an workout regiment to toughen their pectoral muscles, a man stretches a spring which has a spring constant k=605N/m. a) If x=0 corresponds to when the springs are at their relaxed state, which image best represents the magnitude of the force applied to the springs as a function of the stretch distance (see image). b) Write an equation for the work necessary to stretch the spring from the relaxed state to a distance x1. c) Calculate the work, in joules, required to stretch the spring from its relaxed state to the position x1=59.7cm d) Write an equation for the work necessary to stretch the spring from the position x1 to position x2. e) Calculate the work, in joules, required to stretch the spring from x1=59.7cm to x2=96.8cm.arrow_forwardA 6 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a rough surface ( c) by a constant horizontal force of F = 12 N at an angle 0 = 30° as shown in the figure. The block is moved over a distance of 3 m and Its final speed is 2 m/s. F Find the following : 1. The normal force? 2. The work done by force F? 3. The total work done on the block? 4. The work done by frictional force? 5. The kinetic frictional force (f)? 6. The coefficient of kinetic friction (u,) between the block and the surface ? 7. The increase in the internal energy?arrow_forward
- I need help with part D!!arrow_forwardYou drop a 1.50 kg book to a friend who stands on the ground at distance D= 12.0 m below. If your friend's outstretched hands are at distance d = 1.30 mabove the ground (see the figure), (a) how much work W, does the gravitational force do on the book as it drops to her hands? (b) What is the change AU in the gravitational potential energy of the book-Earth system during the drop? If the gravitational potential energy Uof that system is taken to be zero at ground level, what is U (c) when the book is released and (d) when it reaches her hands? Now take U to be 100 J at ground level and again find (e) W, (f)AU. (g) U at the release point, and (h) U at her hands. (a) Number Units (b) Number Units (c) Number Units (d) Number Units (e) Number Units (f) Number Units (g) Number Units (h) Number Units >arrow_forwardA potential energy function for a system in which a two-dimensional force acts is of the form U = 3x5y − 2x. Find the force that acts at the point (x, y). (Use the following as necessary: x and y.) F =arrow_forward
- show workarrow_forwardA child of mass m = 16 kg slides down a slide of height h = 2.7 m without friction. Let gravitational potential energy be zero at ground level. a)Write an expression for the child's total mechanical energy, E, at the top of the slide, in terms of the variables in the problem and the acceleration due to gravity g. b)Calculate the change in the child's potential energy, ΔU in joules, from the top to the bottom of the slide at ground level (i.e. ΔU = Uground - Utop). c)What is the child's final speed, vf in m/s?arrow_forwardA person secures a 4.8-m-long rope of mass 0.46 kg at one end and pulls on the rope, exerting a 124-N force. The rope vibrates in three segments with nodes separating each segment. Correct Part D Determine the frequency of vibration. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 0 f = 0.23 Submit Hz wwwww. Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 4 attempts remainingarrow_forward
- The force required to compress a non-standard spring as a function of displacement is given by the equationF(x) = -Asin(bx) + kx,where A = 25 N, b = 11 rad/m, and k = 68 N/m. Enter a general equation in terms of the given variables for the work required to compress this spring from position x1 to x2. Calculate the work done in joules as the spring is compressed from x = 0 to x1 = 21 cm. Calculate the work done in joules as the spring is compressed from x1 = 21 cm to x2 = 66 cmarrow_forwardYou drop a 2.50 kg book to a friend who stands on the ground at distance D-13.0 m below. If your friend's outstretched hands are at distance d-1.60 m above the ground (see the figure), (a) how much work W, does the gravitational force do on the book as it drops to her hands? (b) What is the change AU in the gravitational potential energy of the book-Earth system during the drop? If the gravitational potential energy U of that system is taken to be zero at ground level, what is U (c) when the book is released and (d) when it reaches her hands? Now take U to be 100 J at ground level and again find (e) W. (f) AU, (g) U at the release point, and (h) U at her hands. 10000 Elarrow_forwardThe figure shows four situations where a force F is applied to the same block. In each case the force has the same magnitude, and the displacement of the block in each case is the same (marked as Delta(x)) - to the right with the same magnitude.Rank the four situations in order of the work done by the force F on the block, from most positive to most negative. A) c,a,d,b B) b,d,a,c C) The Force does the same work on the block in all four situations. D) C,b,a,darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON