Question
Hello I need help with finding the solutions for these parts with explanations. Please and thank you.
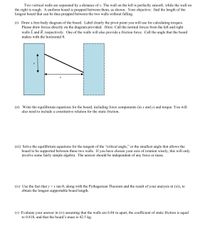
Transcribed Image Text:Two vertical walls are separated by a distance of x. The wall on the left is perfectly smooth, while the wall on
the right is rough. A uniform board is propped between them, as shown. Your objective: find the length of the
longest board that can be thus propped between the two walls without falling.
(i) Draw a free-body diagram of the board. Label clearly the pivot point you will use for calculating torques.
Please draw forces directly on the diagram provided. Hints: Call the normal forces from the left and right
walls L and R, respectively. One of the walls will also provide a friction force. Call the angle that the board
makes with the horizontal 0.
(ii) Write the equilibrium equations for the board, including force components (in x and y) and torque. You will
also need to include a constitutive relation for the static friction.
(iii) Solve the equilibrium equations for the tangent of the "critical angle," or the smallest angle that allows the
board to be supported between these two walls. If you have chosen your axis of rotation wisely, this will only
involve some fairly
mple
bra. The answer should be ind
ndent of any force or mass.
(iv) Use the fact that y =x tan 0, along with the Pythagorean Theorem and the result of your analysis in (iii), to
obtain the longest supportable board length.
(v) Evaluate your answer in (iv) assuming that the walls are 6.84 m apart, the coefficient of static friction is equal
to 0.818, and that the board's mass is 42.5 kg.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Thank you for the first part. Can I get help with the remaining sub-part?arrow_forwardPlease follow the instructions carefully and provide detailed answers. Answer only if you really know how to compute it and answer all of it :( Thank you so much!arrow_forwardsolve it clearly and correctly. i will ratearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios