
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Dynamics Lesson:I want detailed and manual solution.
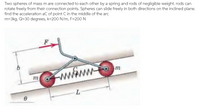
Transcribed Image Text:Two spheres of mass m are connected to each other by a spring and rods of negligible weight. rods can
rotate freely from their connection points. Spheres can slide freely in both directions on the inclined plane.
find the acceleration aC of point Cin the middle of the arc
m=3kg, Q=30 degrees, k=200 N/m, F=200 N
m
wwww
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given: A uniform slender rod is at rest upon a frictionless horizontal surface when a force (F) is applied in the direction shown. Assume that the rod has mass m and length L. A L Horizontal Plane Given that F = 74lb, L = 7.1 ft, mg = 4.6lb, and 0 = 73deg What is the component of acceleration of the mass at point G in the i direction? Answer: Check What is the component of acceleration of the mass at point G in the j direction? Answer: Check What is the component of angular acceleration of the mass in the k direction? (remember your signs) Answer: Checkarrow_forwardA solid bar of mass m and length L stands vertically on a frictionless table and is then released to fall down. The moment of inertia about the center of mass is Ic = mL²/12. At the moment when the top end B just reaches the ground (0-0), (a) what are the angular velocity and angular acceleration? (b) what is the center-of-mass acceleration? (c) what is the normal force of the ground to end D? Hint: It may be helpful to find out the instant rotation axis. В m. L Darrow_forwardA hanging mass, M1 = 0.5 kg, is attached by a light string that runs over a frictionless pulley to a mass M2 = 1.5 kg that is initially at rest on a frictionless ramp. The ramp is at an angle of θ = 30.0° above the horizontal and the pulley is at the top of the ramp. Find the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of M1. a. 4.905 m/s2 , upward c. 4.905 m/s2 , upward b. 4.805 m/s2 , downward d. 4.805 m/s2 , downwardarrow_forward
- Do all 3 parts ASAParrow_forwardweighs 60 N on Earth. (3). A system consists of a pulley (vertical wheel) that is only allowed to rotate (spin). A cord is passed over the pulley and at each end there is a mass attached to the end of the cord. The mass attached on the left is m, =0.6 kg and at the right the mass is m2 = 0.8 kg. a) Calculate both the Tension in the cord and the acceleration of the system. b) What are the accelerations of both masses, if you were to cut the cord? Neglect the friction between cord and wheel,arrow_forwardConsider a square plate at rest in the horizontal plane with mass m, sides of length 2L, and center of mass at point G (located at the center of the square). Two forces are applied to the plate: FA is applied at corner A with some angle o relative to the edge of the plate, and FB is applied at point B parallel with the edge of the plate, as shown. The resulting motion is a pure acceleration (translation) to the right of magnitude a. The plate does not rotate. Determine the magnitude of the force applied at B, ||FB||. (Hint: Use Euler's 2nd Law about an arbitrary point (in this case about point A). FAS 2L 2L F B B aarrow_forward
- A uniform rod of mass M = 2.3 kg and length L = 0.2 m, lying on a frictionless horizontal plane, is free to pivot about a vertical axis through one end, as shown. The moment of inertia of the rod about this axis is given by 1/3 ML2. If a force F = 7 N, q = 47° acts as shown, what is the resulting angular acceleration (in rad/s2) about the pivot point?arrow_forwardA gear of mass m = 10 kg and radius R=0.25 m may rotate about its center of mass C, which is fixed. A rack of mass m = 10 kg is subjected to a constant force Fo = 20 N, as shown. The rack and gear are geared together (gear teeth not shown), so that the force Fo drives the rack to the right and rotates the gear. Find the angular ácceleration a of the gear and find the force f exerted by the rack on the gear. The gear is to be modeled as a uniform circular disc. Fixed Fo3 20 N Rackarrow_forwardDerive the equations of motion using Lagrange's equations. (I, =mr? ) THE MOTION IS ON THE HORIZONTAL PLANE (NO GRAVITY) Trailer, mass M Cylinder, k1 mass m k2arrow_forward
- LG 1.5m has cordy W₂ = 2₁2 rad/s 5 x = 604 rad/5²15) (constant) A disk is to a fixed axis of rotation through its center as. and a cord wraps around it, and attaches to a block. Assuming that the disk's initial angular velocity is w₂ = 2.2 rad/s CCW, and that its angulars acceleration is x = 6₁4 rad /s² cew (and that a is constant),"" find (a) the acceleration of the block (mag and direc) (b), the velocity of the block after 2.8s (mag and direc) (c) the distance traveled by the block during that time. • shown,arrow_forwardA weight with mass mw=150 g is tied to a piece of thread wrapped around a spool, which is suspended in such a way that it can rotate freely. When the weight is released, it accelerates toward the floor as the thread unwinds. Assume that the spool can be treated as a uniform solid cylinder of radius R=4.00 cm and mass Ms=200 g. Find the magnitude ?a of the acceleration of the weight as it descends. Assume the thread has negligible mass and does not slip or stretch as it unwinds. Use ?=9.81 m/s2. Find the tension T in the thread.arrow_forwardRod OA rotates counterclockwise at a constant angular rate 0-4 rad/s. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other collar slides over the circular rod described by the equation r= (1.6 cos 6) m. Both collars have a mass of 0.65 kg. Motion is in the vertical plane. (Figure 1) Figure r=1.6 cos 9. 0-4 rad/s 0.8 m 1 of 1 Part A Determine the magnitude of the force which the circular rod exerts on one of the collars at the instant 0=45 Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) F= Value Submit μÁ Part B Previous Answers Units X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining Determine the magnitude of the force that OA exerts on the other colar at the instant @-45. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY