
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
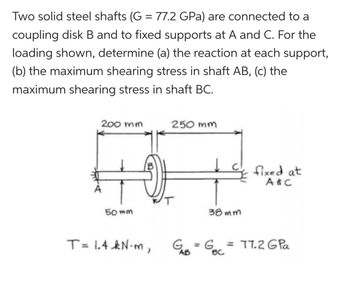
Transcribed Image Text:Two solid steel shafts (G = 77.2 GPa) are connected to a
coupling disk B and to fixed supports at A and C. For the
loading shown, determine (a) the reaction at each support,
(b) the maximum shearing stress in shaft AB, (c) the
maximum shearing stress in shaft BC.
200 mm
250 mm
82-
50mm
38mm
T= 1.4 kN·m, G₁B = GBC
fixed at
A&C
G = G = 77.2 GPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The springs BA and BC each have a stiffness of 500 N/m and an unstretched length of 3 m. Determine the horizontal force F applied to the cord which is attached to the small ring B so that the displacement of AB from thewall is d = 1.5 m.arrow_forwardIn the following structure, consider the following data: The connection at D is double and has a diameter of 50 mm. The beam BCDE has a thickness of 37.50 mm. The bar AB has a thickness of 37.50 mm and a width of 100. The connection at A is single and has a diameter of 67.50 mm. a. The normal stress in bar AB. Answ. 3.53 MPa b. The shear stress in the bolt at D. Answ. 6.25 MPa c. The shear stress in the bolt at A. Answ. 6.25 MPa d. The support stress between the beam and bolt D. Answ. 13.08 MPaarrow_forwardaShubber H.W.2: The load P produces an axial strain of -1,800 ue in post (2). Determine the axial strain in rod (1). 1,200 mm- (1) rigid plate 480 mm 1.5 mm D 300 mm 300 mm 600 mm (2) Earrow_forward
- 2.51 A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of steel (E, = 200 GPa, a, = 11.7 x 10-6/°C) and portion BC is made of brass (E = 105 GPa, a = 20.9 x 10-6/°C). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine the compressive force induced in ABC when there is a temperature rise of 50°C. 250 mm 300 mm Fig. P2.51 A B C 30-mm diameter 50-mm diameterarrow_forwardHW. 9-3. The state of stress at a point in a member is shown on the element. Determine the stress components acting on the inclined plane AB. Solve the problem using the method of equilibrium described in Sec. 9.1. 60 400 psi *650 pகம்arrow_forwardA steel pipe (1) is attached to an aluminum pipe (2) at flange B. Both steel pipe (1) and aluminum pipe (2) are attached to rigid supports at A and C, respectively. Member (1) has a cross-sectional area of A1 = 3,600 mm2 , an elastic modulus of E1 = 200 GPa, and an allowable normal stress of 160 MPa. Member (2) has a cross-sectional area of A2 = 2,000 mm2 , an elastic modulus of E2 =70 GPa, and an allowable normal stress of 120 MPa. Determine the maximum load P that can be applied to flange B without exceeding either allowable stress.arrow_forward
- Torialai Stan Problem 1-- Short link BD consists of a single steel bar 40 mm wide and 12 mm thick. Knowing that = Call 100 Mpa, determine: a) The maximum value of the normal stress in the link BD b) The required pin diameter at support D. 20kN 100 150 mm 300 mm D 30arrow_forwardThe compound shaft is attached to a rigid wall at each end. a = 2 m and b = 1.5 m. For the bronze segment AB, the diameter is 82 mm and G = 35 GPa. For the steel segment BC, the diameter is 62 mm and G = 83 GPa. The maximum shear stress is limited to 50 MPa in the bronze and 60 MPa in the steel. 75 mm 50 mm Bronze Steel a 1. Compute the largest torque kN-m that can be applied considering the maximum shear stress of the bronze segment. a. 8.07 kN-m b. 11.01 kN-m c. 7.26 kN-m d. 8.60 kN-m 1. Compute the largest torque kN-m that can be applied considering the maximum shear stress of the steel segment. e. 5.11 kN-m f. 5.52 kN-m g. 4.67 kN-m h. 4.08 kN-m 1. Compute the largest torque in kN-m that can be applied to the compound shaft. choose from the choices given above.arrow_forwardTwo horizontal 22 kN forces are applied to pin B of the assembly shown. Knowing that a pin of 20 mm diameter is used at each connection, determine the maximum value of the average normal stress (a) in link AB, (b) in link BC. 12 mm 45 mm 22 kN 22 kN (Note that maximum normal stress in link AB and BC are required.) 12 mm 60 45 mm 45 Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning