
Concept explainers
Two simulations that were used are below:
This activity is structured as a game, wherein your challenge is to create correct ionic compound formulas by combining individual ions based on their charges. Once you correctly connect the atoms in the interactive website, a common use for that compound will be revealed. In this worksheet, you must record both the correct formula for each of the seven ionic compounds and their common uses as revealed by the interactive program.
Throughout the activity, you will have the option of skipping each compound – if you choose to do this, its common use will not be revealed. You must correctly write the formulas and match the common uses.
Website for first simulation: https://www.learner.org/wp-content/interactive/periodic/bonding
- Click “Begin” on the first page you see.
- For each compound name listed at the top of the interactive, choose the correct cation and anion which you think belong to the formula for that compound.
For example: Sodium Chloride, click “Na+” and “Cl-“.
3. Drag one ion on top of the other until the two ions you want to connect are highlighted yellow. We recorded this info in a table.
The second/last simulation:
Open the following website: https://javalab.org/en/ion_model_en/
Use the puzzle pieces to form the ionic compounds listed in data table 2, and then fill in data table 2 with that information. Write the formula for that compound and draw or copy and paste your completed puzzle for each ionic compound into the table.
Explain the virtual labs used and what they helped show us. An example of how to answer this is below. The charts created from the simulations are below as well.

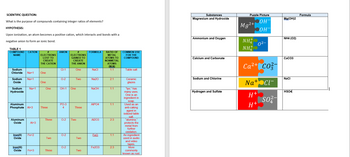
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- using the attached image, Decide whether each pair of elements in the table below will form an ionic compound. If they will, write the empirical formula and name of the compound formed in the spaces provided.arrow_forward1) Chemical formulas can be written as empirical formulas, molecular formulas, or structural formulas. Explain why these different forms of molecular expression are necessary. Chemical formula of a compound can be explained by the following forms - An Empirical formula gives the simplest, whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. A Molecular formula uses chemical symbols and subscripts to indicate the exact numbers of different atoms in a molecule or compound. A Structural formula indicates the bonding arrangement of the atoms in the molecule. 1) Chemical formulas can be written as empirical formulas, molecular formulas, or structural formulas. Explain why these different forms of molecular expression are necessary. Chemical formula of a compound can be explained by the following forms - An Empirical formula gives the simplest, whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound. A Molecular formula uses chemical symbols and subscripts to indicate the exact numbers of different atoms in a…arrow_forward1. Compare cations, anions, and polyatomic ions. What do they all have in common? How are they different? 2. How can the periodic table help to remember the charges on the simple ions of the representative elements? 3. Is there more than one chemical name that can be used for baking soda?arrow_forward
- 1.Write the formula for each of the following compounds (do not use subscripts, but remember parentheses, where they are needed) 2.If possible, include the other systematic names (classic or Stock system names or alternative names for anions). If only one name is possible (not including trivial names), write "not applicable" in the "Name" 1. Ammonium acetate 2. Potassium phosphite 3. Sodium hydroxidearrow_forwardPlease answer all questions.arrow_forwardRead: An Ion is a charged atom, # protons ≠ # electrons. On page three, paragraph one states, “The prefix poly- means many and atomic refers to atoms, so a polyatomic ion is an ion that contains more than one atom. This differentiates polyatomic ions from monatomic ions, which contain only one atom.” Ions that contain only one atom are called monoatomic ions. Ions that contain more than one atom are called polyatomic ions. A monatomic ion is a single charged atom, with the number of protons not equal to the number of electrons. A polyatomic ion is a group of covalently-bonded atoms, with the total number of protons not equal to the total number of electrons. Using the image attached how could you further elaborate this answer? Cite evidence from the image.arrow_forward
- Please provide the chemical formula that would form between the provided ions. Do not worry about using super- or subscript for your answer. Just insert any numbers that are necessary as normal-sized font. Combining Cu+ and O2- would form the chemical compound:arrow_forwardDecide whether each pair of elements in the table below will form an ionic compound. If they will, write the empirical formula and name of the compound formed in the spaces provided. empirical formula of ionic name of ionic compound compound Forms ionic element #1 element #2 compound? cesium bromine O yes O no sodium sulfur O yes O no strontium potassium O yes O no chlorine magnesium O yes O noarrow_forwardGive detailed Solution with explanation needed..don't give Handwritten answer .don't use Ai for answering thisarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





