Question
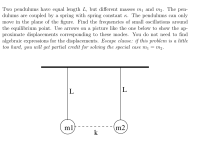
Transcribed Image Text:Two pendulums have equal length L, but different masses mị and m2. The pen-
dulums are coupled by a spring with spring constant K. The pendulums can only
move in the plane of the figure. Find the frequencies of small oscillations around
the equilibrium point. Use arrows on a picture like the one below to show the ap-
proximate displacements corresponding to these modes. You do not need to find
algebraic expressions for the displacements. Escape clause: if this problem is a little
too hard, you will get partial credit for solving the special case mı = m2.
L
|L
ml
m2
k
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please solve the problem below. Thank you so much!!arrow_forwardItem 1 Learning Goal: To understand the application of the general harmonic equation to the kinematics of a spring oscillator. One end of a spring with spring constant k is attached to the wall. The other end is attached to a block of mass m. The block rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. The equilibrium position of the left side of the block is defined to be x = 0. The length of the relaxed spring is L. (Figure 1) The block is slowly pulled from its equilibrium position to some position init> 0 along the x axis. At time t = 0, the block is released with zero initial velocity. The goal is to determine the position of the block (t) as a function of time in terms of w and init It is known that a general solution for the displacement from equilibrium of a harmonic oscillator is x(t) = C cos (wt) + S sin (wt), where C, S, and w are constants. (Figure 2) Your task, therefore, is to determine the values of C and S in terms of w and init Figure 1 of 3 L Xinit win x = 0 Part A Using the…arrow_forwardDevelop a Lagrangian for the double pendulum. You may need to make some assumptions to simplify the problem. You may also need to introduce some new variables to make the problem work. Make sure that is explained.arrow_forward