
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Two objects (m1=5.00kg and m2=3.00kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in Figure P5.71. The 5.00kg object is released from rest at a point h=4.00m above the table. (a)Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. (b)Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 5.00kg object hits the table.
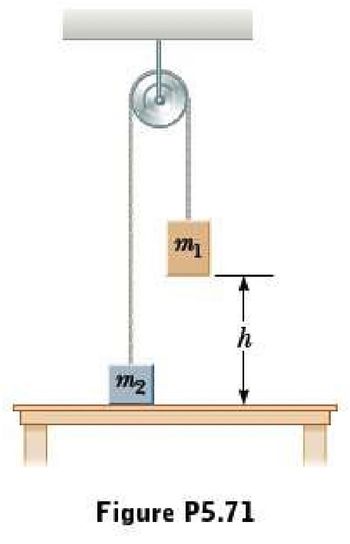
Transcribed Image Text:M₂
7741
h
Figure P5.71
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The drawing shows two boxes resting on frictionless ramps. One box is relatively light and sits on a steep ramp. The other box is heavier and rests on a ramp that is less steep. The boxes are released from rest at A and allowed to slide down the ramps. The two boxes have masses of 10 and 31 kg. If A and B are 3.0 and 1.5 m, respectively, above the ground, determine the speed of (a) the lighter box and (b) the heavier box when each reaches B. (c) What is the ratio of the kinetic energy of the heavier box to that of the lighter box at B? (a) VB= (b) VB= (c) KEheavier KElighter Number i Number i Number i VA= 0 m/s "A=0 m/s AT K HA B hg Units Units Units <arrow_forwardTwo objects (m1 = 4.70 kg and m2 = 2.85 kg) are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The 4.70-kg object is released from rest at a point h = 4.00 m above the table. answer all of the follwing parts (a) Determine the speed of each object when the two pass each other. m/s(b) Determine the speed of each object at the moment the 4.70-kg object hits the table. m/s(c) How much higher does the 2.85-kg object travel after the 4.70-kg object hits the table?arrow_forward. An electron in a television tube is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed of 8.4×107m/s over a distance of 2.5 cm. What is the power delivered to the electron at the instant that its displacement is 1.0 cm?arrow_forward
- A cylinder was dropped vertically from rest in a very high, evacuated tube near the surface of the earth. The mass of the cylinder is 6kg. What is its speed after the cylinder has fallen 4.0 m? 7 m/s В 11 m/s C) 2 m/s 9 m/sarrow_forwardA particular spring has a rest length of 5.0 cm when it is not compressed, and a length of 4.5 cm when a mass of 10kg is placed on top of it. How long is the spring with the 10kg mass on top when it is taken into an elevator accelerating upwards at 1.0 m/s2 ?arrow_forwardAssume that the force of a bow on an arrow behaves like the spring force. In aiming the arrow, an archer pulls the bow back 48 cm and holds it in position with a force of 163 N. If the mass of the arrow is 51 g and the "spring" is massless, what is the speed of the arrow immediately after it leaves the bow? v=v= m/s A boy throws a ball of mass 0.2 kg straight upward with an initial speed of 22 m/s When the ball returns to the boy, its speed is 17 m/s How much work does air resistance do on the ball during its flight? W=W= J (give the absolute value, rounded to one decimal place)arrow_forward
- The drawing shows two boxes resting on frictionless ramps. One box is relatively light and sits on a steep ramp. The other box is heavier and rests on a ramp that is less steep. The boxes are released from rest at A and allowed to slide down the ramps. The two boxes have masses of 8 and 33 kg. If A and B are 4.5 and 0.5 m, respectively, above the ground, determine the speed of (a) the lighter box and (b) the heavier box when each reaches B. (c) What is the ratio of the kinetic energy of the heavier box to that of the lighter box at B? (a) VB= (b) VB= (c) KEheavier KElighter Number i Number i = Number i VA= 0 m/s A HA B- hg VA= 0 m/s Units Units Unitsarrow_forwardAn object of mass m = 2.9 kg is free to move on a horizontal surface without any friction. It is initially at rest and starts moving under a net force of F = (3N)i + (4N)j. What is the object's speed in m/s after moving 1 meter?arrow_forwardFor how long should a force of 135 N be applied to an object of mass 50 kg to change its speed from 25 m/s to 45 m/s?arrow_forward
- The desperate contestants on a TV survival show are very hungry. The only food they can see is some fruit hanging on a branch high in a tree. Fortunately, they have a spring they can use to launch a rock. The spring constant is 1300 N/m, and they can compress the spring a maximum of 38 cm. All the rocks on the island seem to have a mass of 480 g. With what speed does the rock leave the spring?arrow_forwardWhen a m = 12 kg mass is on a frictionless incline of 30 degrees and takes 270 N to compress a spring 2.0 cm: The block briefly stops when the spring is compressed to 5.5 cm a) How far did it travel. I found the answer is 35 cm b) What is the speed of the 12 kg block as it touches the spring? How do I do part b? I got the spring constant k = 13500 and used 1/2 kx^2 to find how many joules it has at compressing the spring to 5.5 cm. When I set that equal to 1/2 mv^2 I did not get the right answer. How would I go about finding b?arrow_forwardA ball of mass m= 0.38 kg is tied to a massless string of length L=1.2m. The ball is released at rest from point A as shown in the figure. a) What is the speed of the ball as it passes through point B? b) What is the tension in the string at point B?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON