
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Two kilograms of water undergo a process from an initial state where the water is saturated vapor at 120°C, the velocity is 30 m/s, and the elevation is 6 m to a final state where the water is saturated liquid at 10°C, the velocity is 25 m/s, and the elevation is 3 m. Determine in kJ:
a) the exergy at the inital state
b) the exergy at the final state,
c) the change in exergy
Let To = 25°C, Po =1 atm, and g = 9.8 m/s2
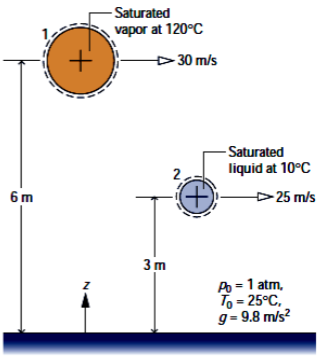
Transcribed Image Text:### Figure Description for Educational Website
**Title: Fluid Dynamics Analysis**
The provided illustration depicts an analysis of fluid dynamics involving both saturated vapor and liquid.
1. **Point 1: Saturated Vapor at 120°C**
- At the first marked point (Point 1), there is a flow of saturated vapor.
- The temperature of the vapor is 120°C.
- The velocity of the vapor flow at this point is 30 m/s.
- Point 1 is situated 6 meters above the reference level.
2. **Point 2: Saturated Liquid at 10°C**
- At the second marked point (Point 2), there is a flow of saturated liquid.
- The temperature of the liquid is 10°C.
- The velocity of the liquid flow at this point is 25 m/s.
- Point 2 is situated 3 meters above the reference level and 3 meters below Point 1.
**Reference Conditions:**
- Ambient pressure (\(p_b\)) is 1 atmosphere (atm).
- Reference temperature (\(T_0\)) is 25°C.
- Gravitational acceleration (\(g\)) is 9.8 meters per second squared (m/s²).
**Diagram Details:**
- The figure highlights the vertical placement of the two points: Point 1 is higher than Point 2.
- Both points have annotations indicating the flow direction and velocity with arrows.
- The reference level is marked at the bottom with axis notation, showing a vertical direction labeled as \(z\).
This setup is typical in studying the behavior and properties of different phases of a substance in fluid mechanics and thermodynamics, where understanding velocity, temperature, and position are crucial for applications such as heat exchangers, distillation columns, and refrigeration cycles.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 8arrow_forward(5)An insulated piston-cylinder device contains 15 L of saturated liquid water at a constant pressure of 950 kPa. Water is stirred by a paddle wheel while a current of 15 A flows for 28 min through a resistor placed in the water. If 64% of the liquid is evaporated during this constant pressure process and the paddle-wheel work amounts to 600 kJ, determine the voltage of the source. Also, show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines. H,0 P= constant W. W.arrow_forward8. 1.8-m³ rigid tank contains steam at 220 °C. One-third of the volume is in the liquid phase and the rest is in the vapor form. Determine (a) the pressure of the steam, (b) the quality of the saturated mixture, and (c) the density of the mixture.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The