Question
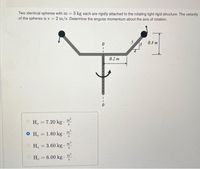
Transcribed Image Text:Two identical spheres with m 3 kg each are rigidly attached to the rotating light rigid structure. The velocity
of the spheres is v = 2 m/s. Determine the angular momentum about the axis of rotation.
5
13
0.3 m
0.2 m
m'
H, = 7.20 kg ·
O H, 1.80 kg·
m2
%3D
O H. 3.60 kg.
m'
H. = 6.00 kg .
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- QUESTION 6 A main sequence star of mass, M, and radius, R, collapses to a white dwarf star with a radius 1.0% as big as the original star. If w is the angular velocity of the original star, what is the angular velocity of the white dwarf star? Approximate the star to be a uniform solid sphere. а. 10,000w b. 1,000w С. 5,000w d. 20,000w е. 50,000warrow_forwardA star with a mass of 3.41 x 1030 kilograms and a radius of 8.20 x 108 meters rotates on its axis once every 33 days.a. What is the angular momentum of the star? Include units in your answer. More information. b. After running out of fusible matter, the star collapses under its own gravity to form a pulsar with a radius of 24.1 kilometers. What is the period of rotation of the pulsar? Include units in your answer. More information. PLEASE ANSWER IN HANDWRITINGarrow_forward8arrow_forward
- Q1. Determine the resultant moment +be fig show n below: 200N 70 SOONarrow_forwardA mass on the end of a 0.50 m long string is spun overhead with a velocity of 3.5 m/s. What is the angular velocity of the mass? 0.14 rad/sec 1.17 rad/sec 7.00 rad/sec 24.5 rad/sec t 9964arrow_forward6. Spinning Ice Skater: A 50 kg ice skater is spinning around at 2 revolutions per second with her arms tucked in. You may consider her to be a cylinder 1.5 meters high with a radius of 15 cm. She sticks her arms straight out to slow herself down. Each of her arms is 2 kg and 75 cm long. How fast does she rotate with her arms extended?arrow_forward
- #1. Due to the conservation of angular momentum, moving mechanical parts in a spacecraft can affect the orientation and rate of angular rotation of the craft. Let us, crudely speaking, model Voyager II as a uniform disk with a mass of 720 kg and an effective radius of 1.0 meters. What is the moment of inertia of Voyager II under these assumptions? A.720kgm^2 B.580kgm^2 C.360kgm^2 D.180kgm^2 #1-1. Suppose the spacecraft in #1 is initially not rotating as a whole, and none of its compo- nents are rotating. A data tape spool with a moment of inertia of 1.25 × 10^−4 kg m^2 begins to spin at a rate of 15.5 Rad/s. What is the angular momentum of the spacecraft as a whole? A. 3.88×10^−3 kg·m^2/s B. 1.94×10^−3 kg·m^2/s C. 9.69×10^−4 kg·m^2/s D. 0.0 kg·m^2/s # 1-3. As the result of the tape spool operation, what is the magnitude of the angular speed of the spacecraft in #1-1 as a whole? A. 0.0 Rad/s B. 5.38 × 10^−6 Rad/s C. 1.07 × 10^−5 Rad/s D. 2.14 × 10^−5 Rad/sarrow_forwardpls also draw a picture/representation of the scenario described, thank you!arrow_forwardTwo particles are moving uniformly in opposite directions along parallel trajectories. The distance between the trajectories is d, as shown. Find: a. The total linear momentum of the particles. b. The angular momentum of the particles with respect to point O. c. Repeat part b. for points O, and O2. d. Answer the questions a through c if p, = p.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios