Question
a) Calculate the distance between the final image and 22-cmcm-focal-length lens.
b) Calculate the image height.
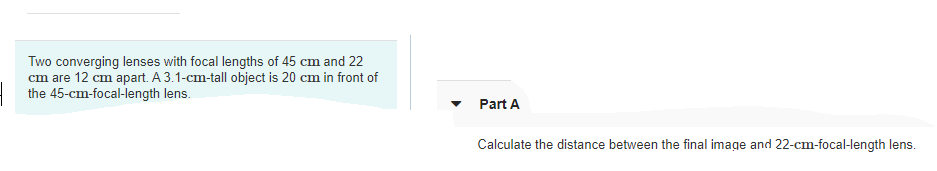
Transcribed Image Text:Two converging lenses with focal lengths of 45 cm and 22
cm are 12 cm apart. A 3.1-cm-tall object is 20 cm in front of
the 45-cm-focal-length lens.
Part A
Calculate the distance between the final image and 22-cm-focal-length lens.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 6. A thin positive lens is used to enlarge the image of a slide on a wall 10 m from the lens. If the slide is 20 x 30 mm², and the image occurs 2 x 3 m², what is the focal length from the lens and the distance from the slide to the lensarrow_forwardAn object is placed at a distance of 1.33 metres from a convex lens that has a focal length of 40 millimetres.a) Where would you look (distance and apparent location from the lens) for a focused image to appear?b) What orientation would the image appear: right-side-up or upside-down?c) Determine the magnification of the image. Does your value confirm the answer in part b)?10d) If the object’s distance from the lens was shortened to 1.33 centimetres, how would the focused image change, including the magnification?arrow_forwardAn image of the moon produced by a converging lens is focused onto a screen; the focal length is f. (Stump) The diameter of the moon is d, and its mean distance from the earth is D. What is the diameter of the moon's image? 3 parameters: 33.7 cm, 3.48 Mm, 385 Mm.arrow_forward
- 2. A Nikon 50mm camera lens is approximated as a cylinder with a diameter of 72mm and a length of 52.5mm. Determine the volume of the lens in cubic inches. Use correct significant figures in your answer. Assume 1cm = 10mm, 2.54cm = 1 in. Veylinder = ar2harrow_forward4. A convex (converging) lens produces a real, inverted image of an object that is magnified 2.20 times when the object is 37.0 cm from the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? cmarrow_forwardA small insect is placed 5.40 cm from a 6.00-cm-focal-length lens. a) Calculate the position of the image. Follow the sign conventions. Express your answer using two significant figures and include the appropriate units. b) Calculate the angular magnification. Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forward
- A concave lens has a focal length of -45 cm. a) Find the image distance that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens. b) Find the magnification that results when an object is placed 32 cm in front of the lens.arrow_forwardA student performs the lab as described. Leaving the object and 10 cm lens in place, a student places the 5 cm lens 35 cm away from the 10 cm lens. a) Calculate the object distance for the 5 cm lens. b) Calculate the image distance from the 5 cm lens. c) Calculate the magnification of the 5 cm lens. d) Calculate the total magnification from both lenses. e) Calculate the expected final image height (from both lenses). f) Is the final image upright or inverted?arrow_forwardLight comes from an object and passes through a thin lens of unknown shape, creating an image shown in (Figure 1). a) If height h=3.00 mm and D=15.8cm what is the focal length of the lense in cm? b)what type of lens is it? c)what is the height of the image in mm? is the image real or virtual?arrow_forward
- An image is located 346 mm behind a 204 mm focal length lens. A) Find the object distance. B) Find the magnification of the image. C) Is the image upright or inverted? factor of 4 or when you place it 8.0 cm behind a lens thearrow_forward2. An object is placed 50.cm in front of a converging lens and then 15.5cm in front of a diverging lens. Both lenses have a focal length of 12.0cm. For both cases, find the image distance.arrow_forwardProblem 96. Indicate the single lens type (converging or diverging) and object position that will lead to the following kind of images. If no single lens system can produce the particular image indicate that this is so. A) real, upright, enlarged image. B) huge image at "infinity". C) real, enlarged, inverted image. D) tiny inverted image very near the focal point. E) real, reduced in size, inverted image. F) virtual, reduced in size, upright image. G) virtual, enlarged, upright image. H) real, inverted image that is the same size as the object. I) virtual, enlarged, inverted image. Problem 97. You are handed a converging lens and you have a ruler. Describe two different simple ways to determine the focal length of this lens. Each way should involve making only one measurement.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios