
Chemistry: The Molecular Science
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781285199047
Author: John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Can I get the lewis structures for both molecules? With minimum formal charges
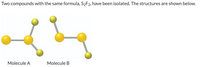
Transcribed Image Text:Two compounds with the same formula, S2F2, have been isolated. The structures are shown below.
Molecule A
Molecule B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 16. Which of the following structures is the CORRECT resonance structure of the following. molecule: (A) (B) (C) (D) CH3- CH₂ CH3 -H CH₂CH3 CH₂CH-CH₂ CH3 CH3arrow_forwardWhich among the following is not an isomer of CsH100? H.arrow_forwardWhat is the IHD of a chemical compound with a formula of C6H5NO2? a 4 b 5 c 6 d 7arrow_forward
- Unshared, or lone, electron pairs play an important role in determining the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Thus, it is important to know which atoms carry unshared pairs. Use the structural formulas below to determine the number of unshared pairs at each designated atom. (Be sure your answers are consistent with the formal charges on the formulas.) The number of unshared pairs at atom a is со b The number of unshared pairs at atom b is H3C CH3 The number of unshared pairs at atom c is The number of unshared pairs at atom a is b H3C- The number of unshared pairs at atom b is CCH2 The number of unshared pairs at atom c isarrow_forwardCalculate the Enthalpy Change (ΔH) from average bond energies, which have been listed below in KJ/mol, for the following reaction and identify the nature of the reaction: CH3COOH + CH3OH → CH3COOCH3 + H2O [C‒H: 413; C‒C: 347; C=O: 745; C=C: 614; Cl‒Cl: 239, C‒O: 358; O‒H: 467]arrow_forwardHow many different structural isomers are there for octahedral molecules with the general formula AX2Y3 if A is the inner atom and there are no X-Y, X-X and Y-Y bonds?arrow_forward
- Write the names of the molecules whose explicit structures are given below, according to the naming system. Write the open structures of the named compounds NH2 NO2 "Br O,N d) соон CH3 a) COOH b)arrow_forwardThe partial Lewis structure that follows is for a hydrocarbonmolecule. In the full Lewis structure, each carbon atomsatisfies the octet rule, and there are no unshared electronpairs in the molecule. The carbon—carbon bondsare labeled 1, 2, and 3. (a) How many hydrogen atomsare in the molecule? (b) Rank the carbon–carbonbonds in order of increasing bond length. (c) Whichcarbon—carbon bond is the strongest one?arrow_forwardEmpirical formulas for: C2H6 N2O4 C4H6O2 NH3arrow_forward
- What is the skeletal structure for the following molecule: (CH3)2C═CH(CH2)4CH3arrow_forwardUnshared, or lone, electron pairs play an important role in determining the chermical and physical properties of organic compounds. Thus, it is important to know which atoms carry unshared pairs. Use the structural formulas below to determine the number of unshared pairs at each designated atom. Be sure your answers are consistent with the formal charges on the formulas. The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is HyC CH The number of unshared pairs at atom e is The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is HC CH The number of unshared pairs at atom e isarrow_forward(a) Determine the formal charge of oxygen in the following structure. If the atom is formally neutral, indicate a charge of zero. (b) Draw an alternative Lewis (resonance) structure for the compound given in part (a). Show the unshared pairs and nonzero formal charges in your structure. Don't use radicals. Formal charge on O 0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax