
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
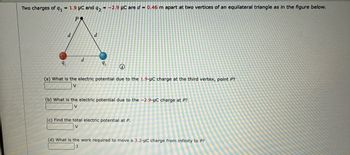
Transcribed Image Text:Two charges of q₁1.9 μC and 92 = -2.9 μC are d = 0.46 m apart at two vertices of an equilateral triangle as in the figure below.
PR
9₁
d
d
d
9₂
(a) What is the electric potential due to the 1.9-μC charge at the third vertex, point P?
(b) What is the electric potential due to the -2.9-µC charge at P?
V
(c) Find the total electric potential at P.
(d) What is the work required to move a 3.2-μC charge from infinity to P?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Three charged balls, with charges of +q, -3q, and +2q, are placed at the corners of a square that measures L = 80.0 cm on each side, as shown in the figure. The value of q is 2.90 × 10-6 C. Assume that the potential an infinite distance from the charges is zero. +q -39 +2q Enter a number. L (a) What is the electric potential at the lower left corner of the square, due to the three charges? V ..(b)..What is the electric potential at the center of the square, due to the three charges? X Varrow_forwardA charge Q=-67 nC is placed at the origin. What is the electric potential at point A=(7.1, -2.4) cm? Provide your answer in volts to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardAt a distance of 0.40 m from a proton, calculate its electric field strength. At this distance, what is the electric potential?arrow_forward
- What will be the electric potential at a distance of 2.5 m from a point charge of 7.5 uC? Group of answer choices 2.7 x 10^4 V 7.9 x 10^4 V 3.8 x 10^4 V 5.2 x 10^4 Varrow_forwardConsider a point charge q = 1.3 µC, point A at distance d₁ = 2.0 m from q, and point B at distance d₂ = 1.3 m. (a) If A and B are diametrically opposite each other, as in Figure (a), what is the electric potential difference VA - VB? (b) What is that electric potential difference if A and B are located as in Figure (b)? B di B A (a) (b)arrow_forwardA non-conducting rod (see diagram below) has a uniform charge density magnitude A = 3.00 x 106 C/m. The left half of the rod is negatively charged, and the right half of the rod is positively charged. The rod is 1.00 m long. P 0.5m +++++++++++ m. Taking the electric potential, V, to be 0 at infinity, what is the electric potential at point P at a distance of 0.50 m above the middle of the rod along the rod's perpendicular bisector? Express your answer to the nearest volt.arrow_forward
- Consider the figure shown below. Q1=2.15×10−9 C and Q2=−7.35×10−9 C. Calculate the electric potential at the location marked '3'. Charges Q1, Q2, and point '3' are all located at integer coordinates that you can read off of the graph. Assume the electric potential at infinity is zero.arrow_forwardThe three charges in the figure below are at the vertices of an isosceles triangle. Let q = 6.50 nC and calculate the electric potential at the midpoint of the base. (Let d, = 1.50 cm and d, = 7.00 cm.) d2 d1 -20436.21 Your response differs significantly from the correct answer. Rework your solution from the beginning and check each step carefully. kVarrow_forwardA point charge of q₁ = 4.13 μC is located at x₁ = 0.000 m and a second charge of q2 = -1.26 μC is located at %2" 0.256 m. What is the electric potential energy of this system of charges? Your Answer: Answer In a certain region of space, the electric potential is given by V=2y2²+5xy-3xyzarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON