
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
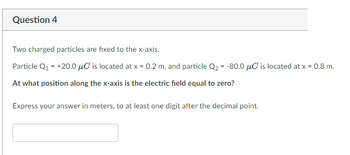
Transcribed Image Text:Question 4
Two charged particles are fixed to the x-axis.
Particle Q₁ = +20.0 μC is located at x = 0.2 m, and particle Q₂ = -80.0 μC is located at x = 0.8 m.
At what position along the x-axis is the electric field equal to zero?
Express your answer in meters, to at least one digit after the decimal point.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A closed surface is constructed in the space between two large parallel metal plates, where there is a constant electric field E. The magnitude of the field is El=1170 N/C. The numbers (1), (2), and (3) in the simulation label small increments of area of 1.5 cm² on the surface. The direction of each increment is defined to be the direction of a vector out of the surface and perpendicular to the increment's surface area. With that definition assume the direction of the first increment AA, is 65° from the direction of E, that the second increment AÃ, is oriented 90° from the direction of E, and that the third increment AA is oriented 135 from the direction of E. Find the flux through each of the three increments of area. For area AA, Nm²/C For area A For area A Pemb 9- Nm²/C Nm²/Carrow_forwardParticle 1 has mass 6.09 kg and charge 8.05 C. Particle 2 has mass 2.26 kg and charge -4.19 C. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point P in the figure if a = 6.65 m and b = 5.41 m. Answer in units of N/C.arrow_forwardConsider two oppositely charged, parallel metal plates. The plates are square with sides of 58 cm and carry charges 74 μC and -74 μC. What is the magnitude of the electric field (in N/C) in the region between the plates?arrow_forward
- Four concentric very long cylindrical shells (made of thin plastic) of radii a, b, c and d have charges +Q, -Q, +Q and -Q per one meter of length of cylinders, respectively. The cross-section of the cylindrical shells is shown in the figure below. Assume that charges are uniformly distributed. Determine the magnitude of the electric field at points A, B, C and D, which are at radial distances Ra, Rg, Rc and Rp, from the center of the smallest cylindrical shell. Express the answers in terms of Q, RA, R3, Rc, Rp and constants. A·B •C •D darrow_forwardA thin rod carries linear charge density according to the distribution X(z) = Aox/L, where Xo = 29.7 nC/cm and L is the length of the rod. The rod extends from x = 0 cm tc I=28 cm. What is the magnitude of the electric field at a location = 6.0 cm? (please provide your answer in kN/C to 1 decimal place) Type your answer.....arrow_forwardmh.2arrow_forward
- Find the x and y components of the electric field produced by q1 and q2 in the figure shown below at point A and point B. (Take q1 = 1.98 µC and q2 = −1.04 µC.) Point A Ex = Ey = Point B Ex = Ey =arrow_forwardFigure 4 shows a section of a long, thin-walled solid infinitely long metal tube of radius R = 5.00 cm , with a charge per unit length of λ = 2.00 ×10−8C/m . What is the magnitude of the electric field at radial distancearrow_forwardFind the electric field at P in the figure shown below. (Take r = 1.2 m and 0 = 38°. Measure the angle counterclockwise from the positive x-axis.) magnitude direction q = 90x 10-9Carrow_forward
- At a particular moment, one negative and two positive charges are located as shown in the figure. Let Q1 = 2 µC, Q2 = 9 µC, and Q3 = -7 µC. What is the electric field at location A, due to all three charges in vector form?arrow_forwardWhat is the electric charge of 0.44 of a mole (NA = 6.023 × 1023) of alpha particles (ionized helium ions, He²+)? Express your answer in kilocoulombs, rounded to one decimal place.arrow_forwardIn a physics experiment, we place three charges at the corners of an equilateral triangle, where q1 = 2.75 μC, q2= - 3.45 μC, and q3 = 3.25 μC. If I were to measure the electric field right between charges q1 and q2, what would I find?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON